Question Number 186267 by TUN last updated on 02/Feb/23
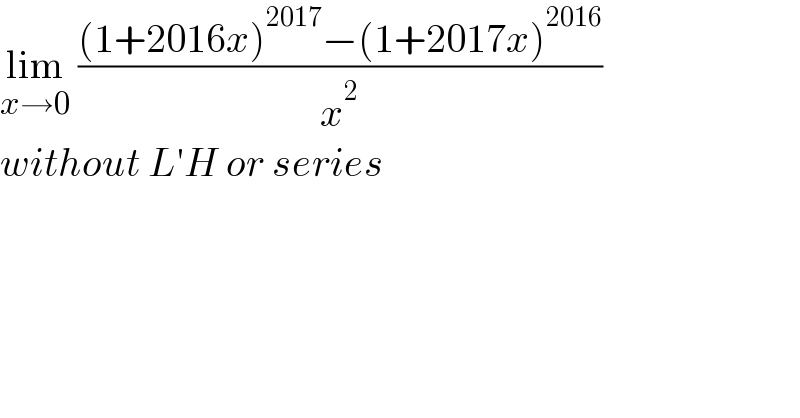
$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{2016}{x}\right)^{\mathrm{2017}} −\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{2017}{x}\right)^{\mathrm{2016}} }{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$${without}\:{L}'{H}\:{or}\:{series} \\ $$
Commented by JDamian last updated on 02/Feb/23
use binomial expansion
Answered by mahdipoor last updated on 02/Feb/23
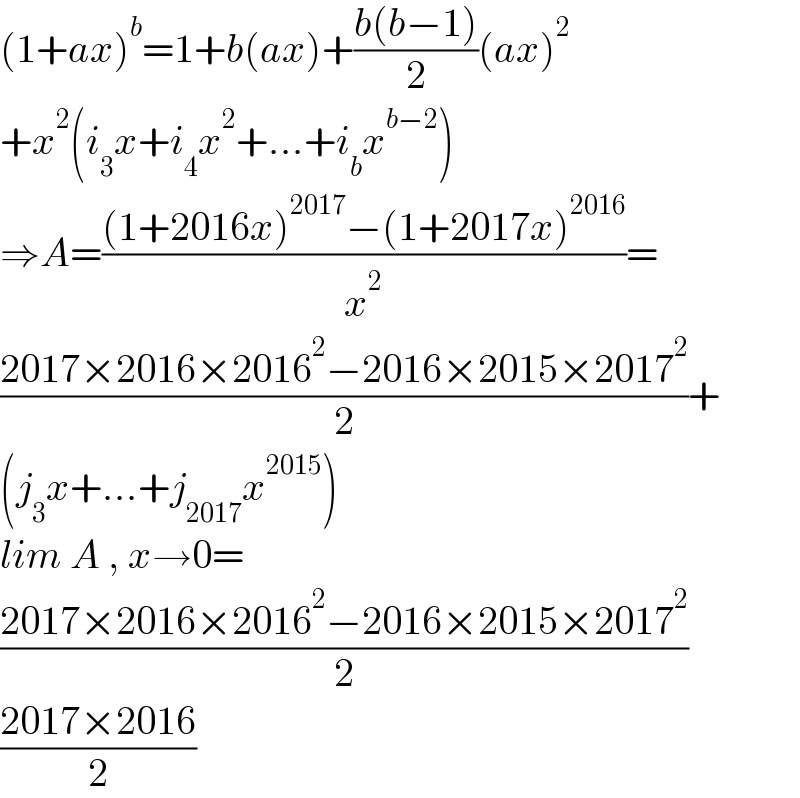
$$\left(\mathrm{1}+{ax}\right)^{{b}} =\mathrm{1}+{b}\left({ax}\right)+\frac{{b}\left({b}−\mathrm{1}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}\left({ax}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \left({i}_{\mathrm{3}} {x}+{i}_{\mathrm{4}} {x}^{\mathrm{2}} +…+{i}_{{b}} {x}^{{b}−\mathrm{2}} \right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{A}=\frac{\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{2016}{x}\right)^{\mathrm{2017}} −\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{2017}{x}\right)^{\mathrm{2016}} }{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }= \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{2017}×\mathrm{2016}×\mathrm{2016}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2016}×\mathrm{2015}×\mathrm{2017}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}+ \\ $$$$\left({j}_{\mathrm{3}} {x}+…+{j}_{\mathrm{2017}} {x}^{\mathrm{2015}} \right) \\ $$$${lim}\:{A}\:,\:{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}= \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{2017}×\mathrm{2016}×\mathrm{2016}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2016}×\mathrm{2015}×\mathrm{2017}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{2017}×\mathrm{2016}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
