Question Number 83361 by john santu last updated on 01/Mar/20
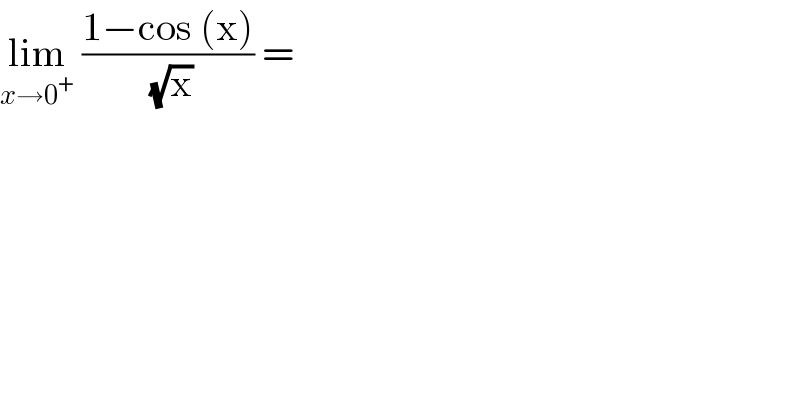
$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}^{+} } {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{cos}\:\left(\mathrm{x}\right)}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{x}}}\:=\: \\ $$
Commented by john santu last updated on 01/Mar/20
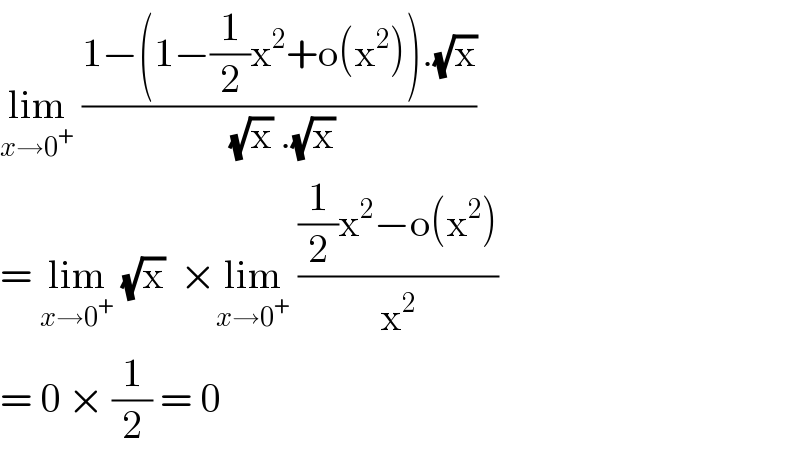
$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}^{+} } {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{\mathrm{1}−\left(\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{o}\left(\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\right).\sqrt{\mathrm{x}}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{x}}\:.\sqrt{\mathrm{x}}} \\ $$$$=\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}^{+} } {\mathrm{lim}}\:\sqrt{\mathrm{x}}\:\:×\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}^{+} } {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{o}\left(\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)}{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$=\:\mathrm{0}\:×\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:=\:\mathrm{0}\: \\ $$
Answered by mr W last updated on 01/Mar/20
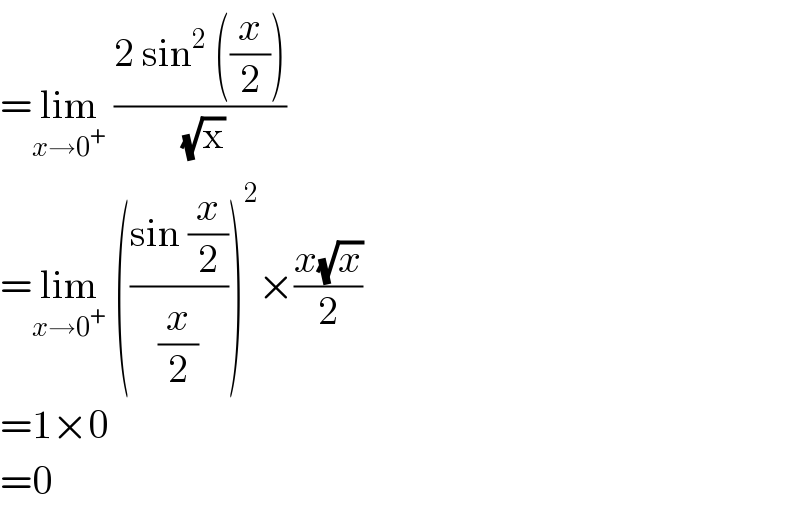
$$=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}^{+} } {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{\mathrm{2}\:\mathrm{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\left(\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{x}}}\: \\ $$$$=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}^{+} } {\mathrm{lim}}\:\left(\frac{\mathrm{sin}\:\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}}{\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} ×\frac{{x}\sqrt{{x}}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{1}×\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{0} \\ $$
