Question Number 170141 by sciencestudent last updated on 17/May/22
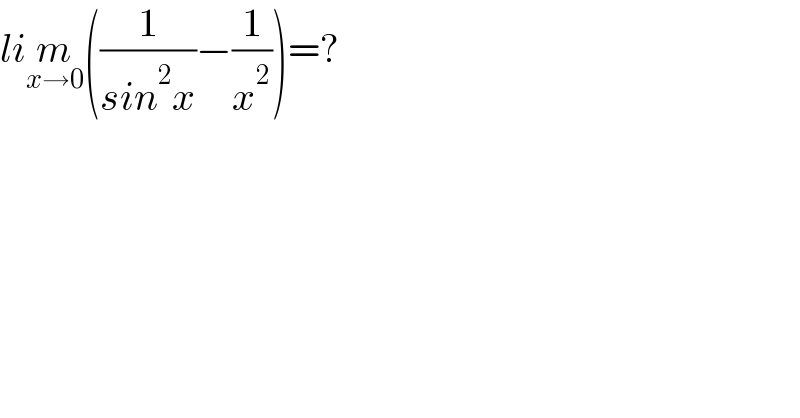
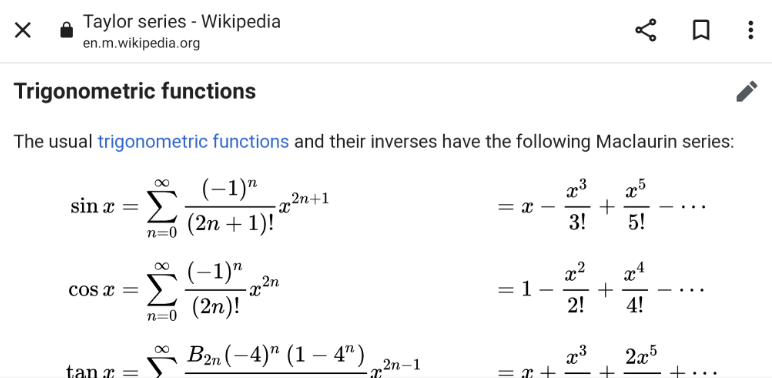
$${li}\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {{m}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} {x}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right)=? \\ $$
Commented by mr W last updated on 17/May/22
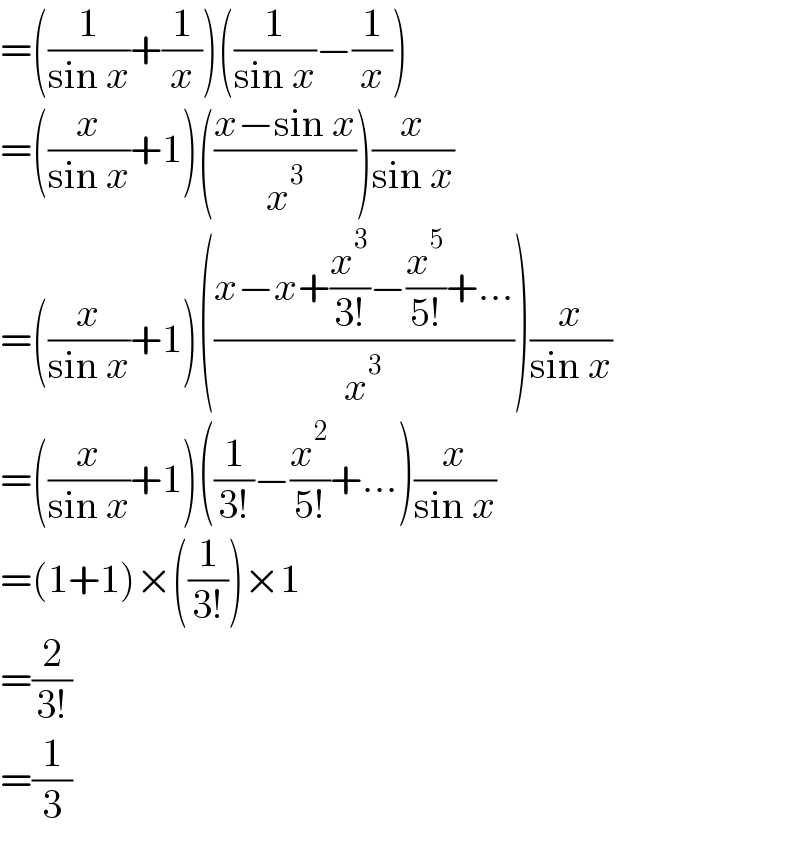
$$=\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{sin}\:{x}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}\right)\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{sin}\:{x}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}\right) \\ $$$$=\left(\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{sin}\:{x}}+\mathrm{1}\right)\left(\frac{{x}−\mathrm{sin}\:{x}}{{x}^{\mathrm{3}} }\right)\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{sin}\:{x}} \\ $$$$=\left(\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{sin}\:{x}}+\mathrm{1}\right)\left(\frac{{x}−{x}+\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{3}!}−\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{5}} }{\mathrm{5}!}+…}{{x}^{\mathrm{3}} }\right)\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{sin}\:{x}} \\ $$$$=\left(\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{sin}\:{x}}+\mathrm{1}\right)\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}!}−\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{5}!}+…\right)\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{sin}\:{x}} \\ $$$$=\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{1}\right)×\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}!}\right)×\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}!} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$
Commented by sciencestudent last updated on 17/May/22
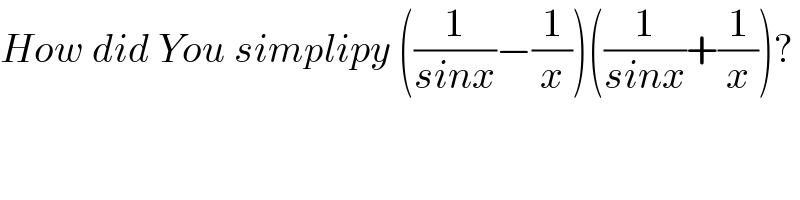
$${How}\:{did}\:{You}\:{simplipy}\:\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{sinx}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}\right)\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{sinx}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}\right)? \\ $$
Commented by mr W last updated on 17/May/22
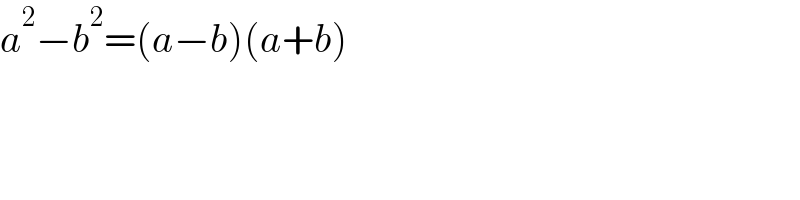
$${a}^{\mathrm{2}} −{b}^{\mathrm{2}} =\left({a}−{b}\right)\left({a}+{b}\right) \\ $$
Answered by ajfour last updated on 17/May/22
![l=lim_(x→0) ((2/(1−cos 2x))−(1/x^2 )) =lim_(x→0) ((2/(1−[1−((4x^2 )/(2!))+((16x^4 )/(4!))−..]))−(1/x^2 )) =lim_(x→0) (1/x^2 )((/(1−((1x^2 )/3)+sx^4 −..))−1) =lim_(x→0) ((((1/3)−sx^2 +...)/(1−(x^2 /3)+sx^4 −...)))=(1/3)](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q170145.png)
$${l}=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{2}{x}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right) \\ $$$$\:\:=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{1}−\left[\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{4}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}!}+\frac{\mathrm{16}{x}^{\mathrm{4}} }{\mathrm{4}!}−..\right]}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right) \\ $$$$\:\:=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\left(\frac{}{\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{1}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{3}}+{sx}^{\mathrm{4}} −..}−\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$$\:\:=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\left(\frac{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}−{sx}^{\mathrm{2}} +…}{\mathrm{1}−\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{3}}+{sx}^{\mathrm{4}} −…}\right)=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$
Commented by sciencestudent last updated on 17/May/22
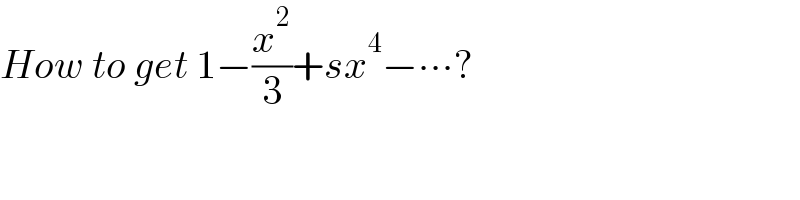
$${How}\:{to}\:{get}\:\mathrm{1}−\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{3}}+{sx}^{\mathrm{4}} −\centerdot\centerdot\centerdot? \\ $$
Commented by mr W last updated on 17/May/22
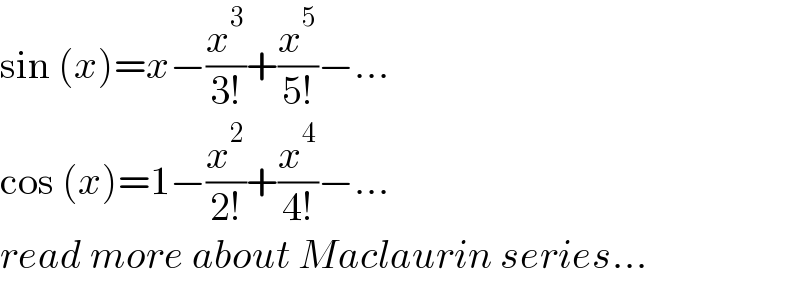
$$\mathrm{sin}\:\left({x}\right)={x}−\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{3}!}+\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{5}} }{\mathrm{5}!}−… \\ $$$$\mathrm{cos}\:\left({x}\right)=\mathrm{1}−\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}!}+\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{4}} }{\mathrm{4}!}−… \\ $$$${read}\:{more}\:{about}\:{Maclaurin}\:{series}… \\ $$
Commented by mr W last updated on 17/May/22