Question Number 174152 by cortano1 last updated on 26/Jul/22
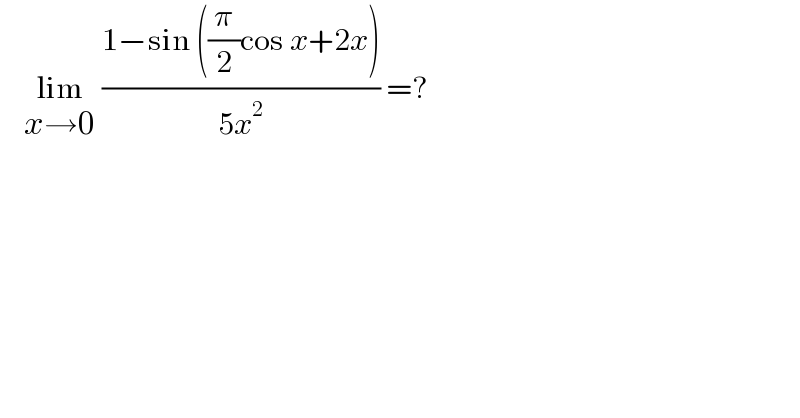
$$\:\:\:\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{sin}\:\left(\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{cos}\:{x}+\mathrm{2}{x}\right)}{\mathrm{5}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:=? \\ $$
Answered by CElcedricjunior last updated on 26/Jul/22
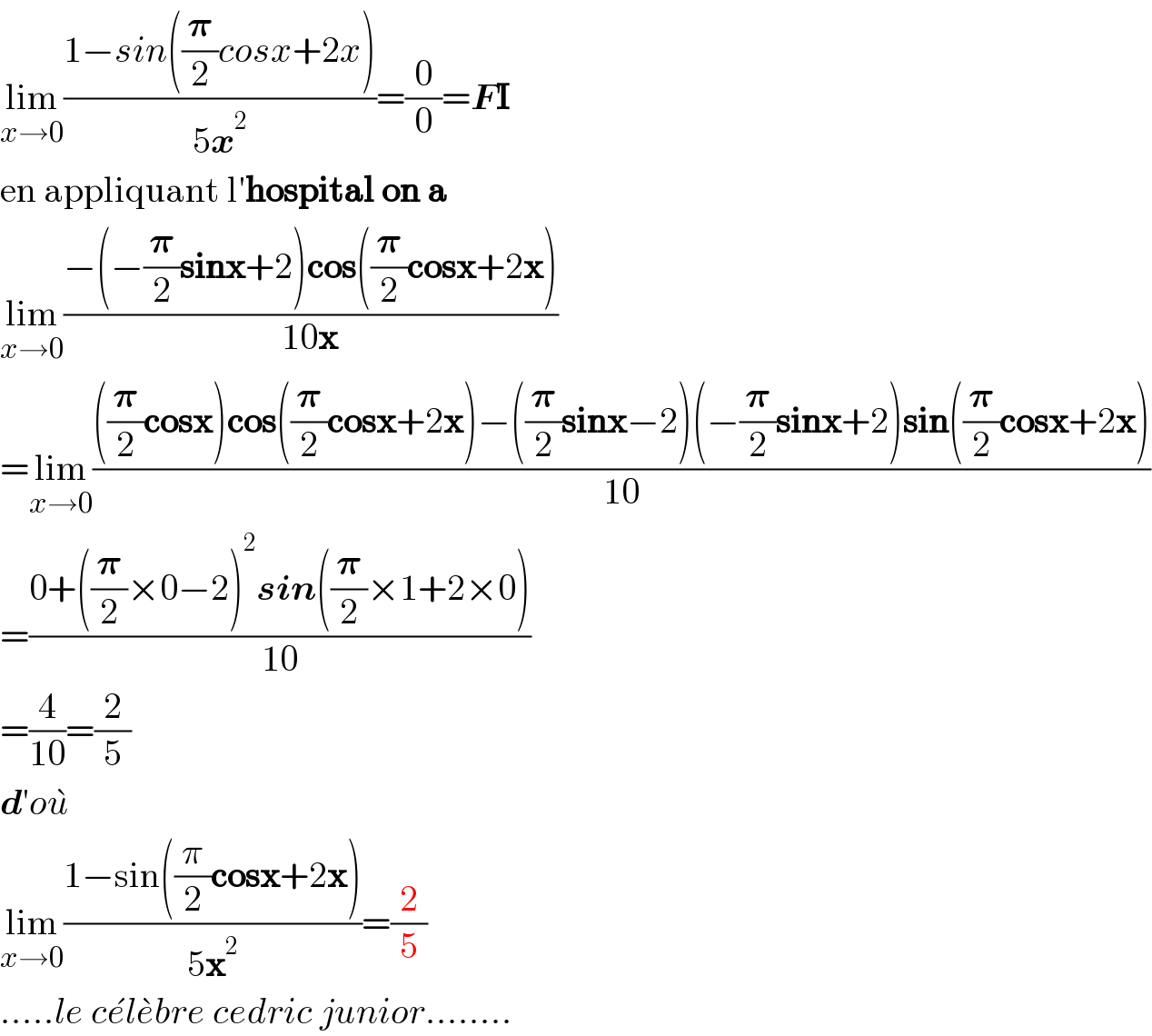
$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\mathrm{1}−{sin}\left(\frac{\boldsymbol{\pi}}{\mathrm{2}}{cosx}+\mathrm{2}{x}\right)}{\mathrm{5}\boldsymbol{{x}}^{\mathrm{2}} }=\frac{\mathrm{0}}{\mathrm{0}}=\boldsymbol{{F}\mathrm{I}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{en}\:\mathrm{appliquant}\:\mathrm{l}'\boldsymbol{\mathrm{hospital}}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{on}}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{a}} \\ $$$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{−\left(−\frac{\boldsymbol{\pi}}{\mathrm{2}}\boldsymbol{\mathrm{sinx}}+\mathrm{2}\right)\boldsymbol{\mathrm{cos}}\left(\frac{\boldsymbol{\pi}}{\mathrm{2}}\boldsymbol{\mathrm{cosx}}+\mathrm{2}\boldsymbol{\mathrm{x}}\right)}{\mathrm{10}\boldsymbol{\mathrm{x}}} \\ $$$$=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\left(\frac{\boldsymbol{\pi}}{\mathrm{2}}\boldsymbol{\mathrm{cosx}}\right)\boldsymbol{\mathrm{cos}}\left(\frac{\boldsymbol{\pi}}{\mathrm{2}}\boldsymbol{\mathrm{cosx}}+\mathrm{2}\boldsymbol{\mathrm{x}}\right)−\left(\frac{\boldsymbol{\pi}}{\mathrm{2}}\boldsymbol{\mathrm{sinx}}−\mathrm{2}\right)\left(−\frac{\boldsymbol{\pi}}{\mathrm{2}}\boldsymbol{\mathrm{sinx}}+\mathrm{2}\right)\boldsymbol{\mathrm{sin}}\left(\frac{\boldsymbol{\pi}}{\mathrm{2}}\boldsymbol{\mathrm{cosx}}+\mathrm{2}\boldsymbol{\mathrm{x}}\right)}{\mathrm{10}} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{0}+\left(\frac{\boldsymbol{\pi}}{\mathrm{2}}×\mathrm{0}−\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \boldsymbol{{sin}}\left(\frac{\boldsymbol{\pi}}{\mathrm{2}}×\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{2}×\mathrm{0}\right)}{\mathrm{10}} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{10}}=\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{5}} \\ $$$$\boldsymbol{{d}}'{o}\grave {{u}} \\ $$$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{sin}\left(\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\boldsymbol{\mathrm{cosx}}+\mathrm{2}\boldsymbol{\mathrm{x}}\right)}{\mathrm{5}\boldsymbol{\mathrm{x}}^{\mathrm{2}} }=\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{5}} \\ $$$$…..{le}\:{c}\acute {{e}l}\grave {{e}bre}\:{cedric}\:{junior}…….. \\ $$
Answered by a.lgnaoui last updated on 26/Jul/22
![sin ((π/2)cos x+2x)=sin ((π/2)cos x)cos 2x+cos ((π/2)cos x)sin 2x L=lim_(x→0) ((1−[sin ((π/2)cos x)cos 2x+cos ((π/2)cos x)sin 2x])/(5x^2 )) =lim_(x→0) [(1/(5x^2 ))−((((π/2)+2cos (π/2)sin x)/(5x^2 )))] lim_(x→0) [(1/(5x^2 ))−((π/2)/(5x^2 ))] ; lim_(x→0) ((sin x)/x)=1 L=lim_(x→0) (((2−π)/(10x^2 )))=−∞](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q174176.png)
$$\mathrm{sin}\:\left(\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2x}\right)=\mathrm{sin}\:\left(\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{2x}+\mathrm{cos}\:\left(\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{2x} \\ $$$$\mathrm{L}=\mathrm{lim}_{\mathrm{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} \frac{\mathrm{1}−\left[\mathrm{sin}\:\left(\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{2x}+\mathrm{cos}\:\left(\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{2x}\right]}{\mathrm{5x}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$=\mathrm{lim}_{\mathrm{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} \left[\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5x}^{\mathrm{2}} }−\left(\frac{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}+\mathrm{2cos}\:\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{5x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right)\right] \\ $$$$\mathrm{lim}_{\mathrm{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} \left[\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5x}^{\mathrm{2}} }−\frac{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}}{\mathrm{5x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right]\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:;\:{l}\mathrm{im}_{\mathrm{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} \frac{\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{x}}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\mathrm{L}=\mathrm{lim}_{\mathrm{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} \left(\frac{\mathrm{2}−\pi}{\mathrm{10x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right)=−\infty \\ $$
