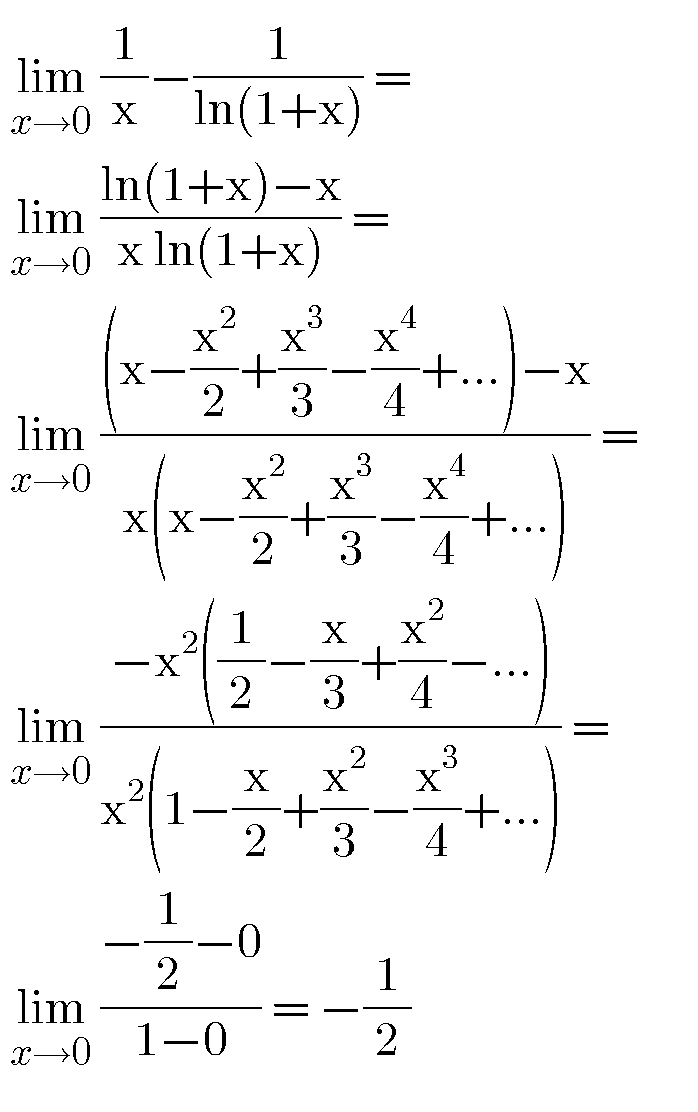Question Number 92256 by jagoll last updated on 05/May/20
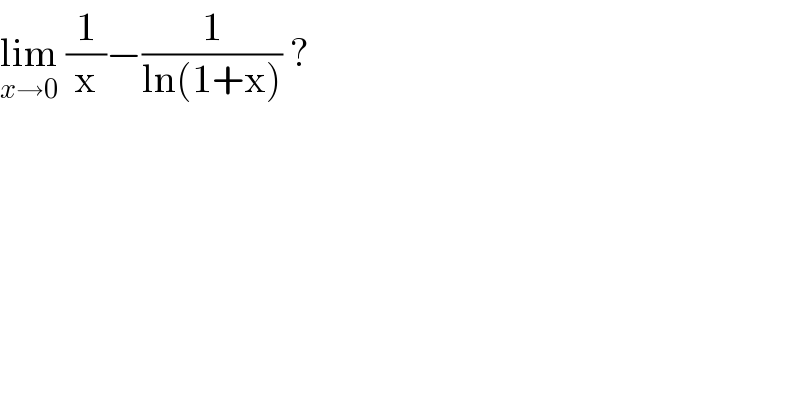
$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{x}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{x}\right)}\:? \\ $$
Commented by $@ty@m123 last updated on 05/May/20

$${See}\:{Q}.\:{No}.\:\mathrm{87105} \\ $$
Commented by john santu last updated on 05/May/20

$$\mathrm{different}\:\mathrm{sir}\:\mathrm{with}\:\mathrm{the}\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{problem}\:\mathrm{you}\:\mathrm{mean}\: \\ $$
Commented by john santu last updated on 05/May/20
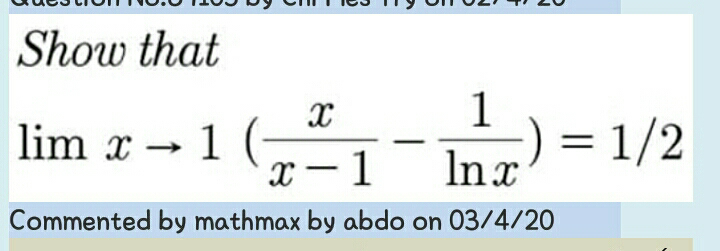
Commented by $@ty@m123 last updated on 05/May/20
Of course different.
But the procedure would be similar.
The main idea behind such questions is to use logarithmic expansion.
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 05/May/20
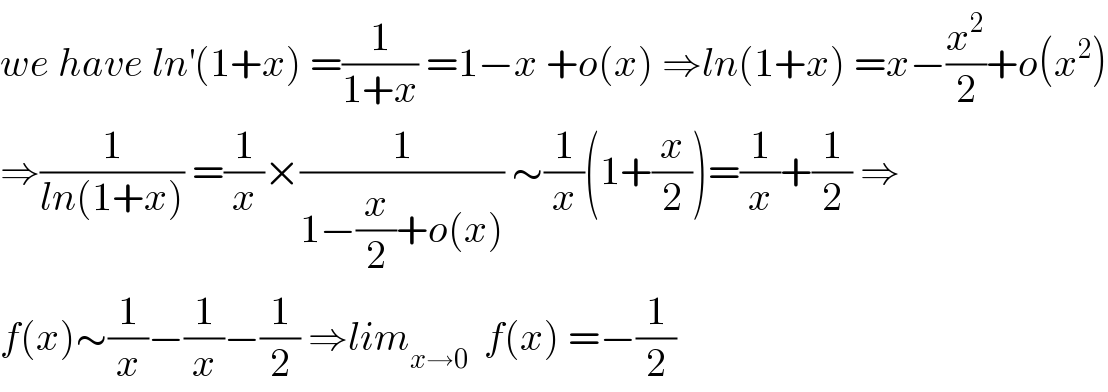
$${we}\:{have}\:{ln}^{'} \left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right)\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}}\:=\mathrm{1}−{x}\:+{o}\left({x}\right)\:\Rightarrow{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right)\:={x}−\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}+{o}\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right)}\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}×\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}−\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}+{o}\left({x}\right)}\:\sim\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}\left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${f}\left({x}\right)\sim\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\Rightarrow{lim}_{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} \:\:{f}\left({x}\right)\:=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
Answered by john santu last updated on 05/May/20