Question Number 50293 by pooja24 last updated on 15/Dec/18
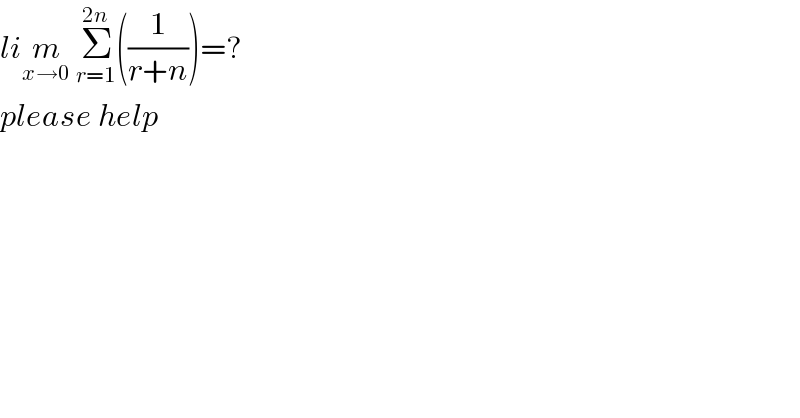
$${li}\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {{m}}\:\underset{{r}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\mathrm{2}{n}} {\sum}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{r}+{n}}\right)=? \\ $$$${please}\:{help} \\ $$
Commented by maxmathsup by imad last updated on 15/Dec/18
![let S_n =Σ_(k=1) ^(2n) (1/(k+n)) ⇒S_n =Σ_(k=1) ^n (1/(k+n)) +Σ_(k=n+1) ^(2n) (1/(k+n)) =A_n +B_n we have A_n =(1/n) Σ_(k=1) ^n (1/(1+(k/n))) →_(n→+∞) ∫_0 ^1 (dx/(1+x)) =ln∣1+x∣]_0 ^1 =ln(2) changement k−n =p give B_n =Σ_(p=1) ^n (1/(n+p+n)) =Σ_(p=1) ^n (1/(p+2n)) =(1/n) Σ_(p=1) ^n (1/(2+(p/n))) →_(n→+∞) ∫_0 ^1 (dx/(2+x)) =[ln∣2+x∣]_0 ^1 =ln(x)−ln(2) ⇒ lim_(n→+∞) S_n =lim_(n→+∞ ) (A_n +B_n )=ln(2)+ln(3)−ln(2) =ln(3)](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q50303.png)
$${let}\:{S}_{{n}} =\sum_{{k}=\mathrm{1}} ^{\mathrm{2}{n}} \:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{k}+{n}}\:\Rightarrow{S}_{{n}} =\sum_{{k}=\mathrm{1}} ^{{n}} \:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{k}+{n}}\:+\sum_{{k}={n}+\mathrm{1}} ^{\mathrm{2}{n}} \:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{k}+{n}}\:={A}_{{n}} \:+{B}_{{n}} \\ $$$$\left.{we}\:{have}\:{A}_{{n}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}\:\sum_{{k}=\mathrm{1}} ^{{n}} \:\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+\frac{{k}}{{n}}}\:\rightarrow_{{n}\rightarrow+\infty} \:\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\:\frac{{dx}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}}\:={ln}\mid\mathrm{1}+{x}\mid\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} ={ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right) \\ $$$${changement}\:{k}−{n}\:={p}\:\:{give}\:{B}_{{n}} =\sum_{{p}=\mathrm{1}} ^{{n}} \:\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}+{p}+{n}}\:=\sum_{{p}=\mathrm{1}} ^{{n}} \:\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{p}+\mathrm{2}{n}} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}\:\sum_{{p}=\mathrm{1}} ^{{n}} \:\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}+\frac{{p}}{{n}}}\:\rightarrow_{{n}\rightarrow+\infty} \:\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\:\:\frac{{dx}}{\mathrm{2}+{x}}\:=\left[{ln}\mid\mathrm{2}+{x}\mid\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:={ln}\left({x}\right)−{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${lim}_{{n}\rightarrow+\infty} \:{S}_{{n}} \:={lim}_{{n}\rightarrow+\infty\:} \left({A}_{{n}} +{B}_{{n}} \right)={ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)+{ln}\left(\mathrm{3}\right)−{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\:={ln}\left(\mathrm{3}\right) \\ $$
Commented by maxmathsup by imad last updated on 15/Dec/18
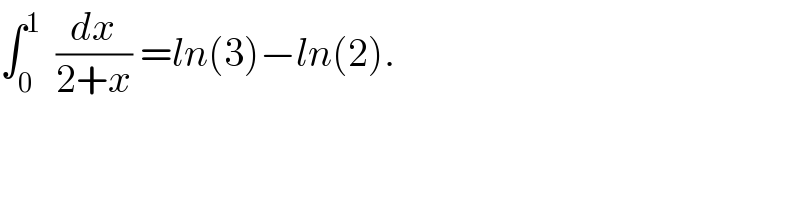
$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\:\frac{{dx}}{\mathrm{2}+{x}}\:={ln}\left(\mathrm{3}\right)−{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right). \\ $$
Commented by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 15/Dec/18
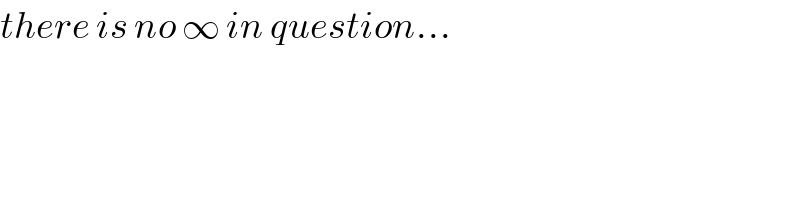
$${there}\:{is}\:{no}\:\infty\:{in}\:{question}… \\ $$
Commented by maxmathsup by imad last updated on 15/Dec/18
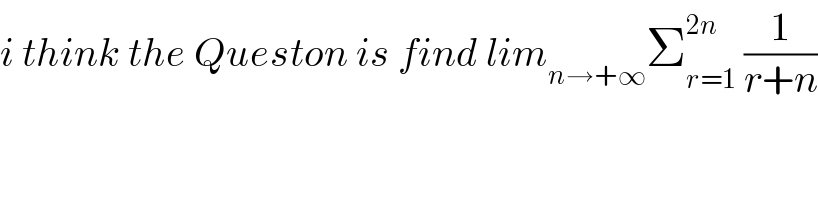
$${i}\:{think}\:{the}\:{Queston}\:{is}\:{find}\:{lim}_{{n}\rightarrow+\infty} \sum_{{r}=\mathrm{1}} ^{\mathrm{2}{n}} \:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{r}+{n}} \\ $$
Answered by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 15/Dec/18
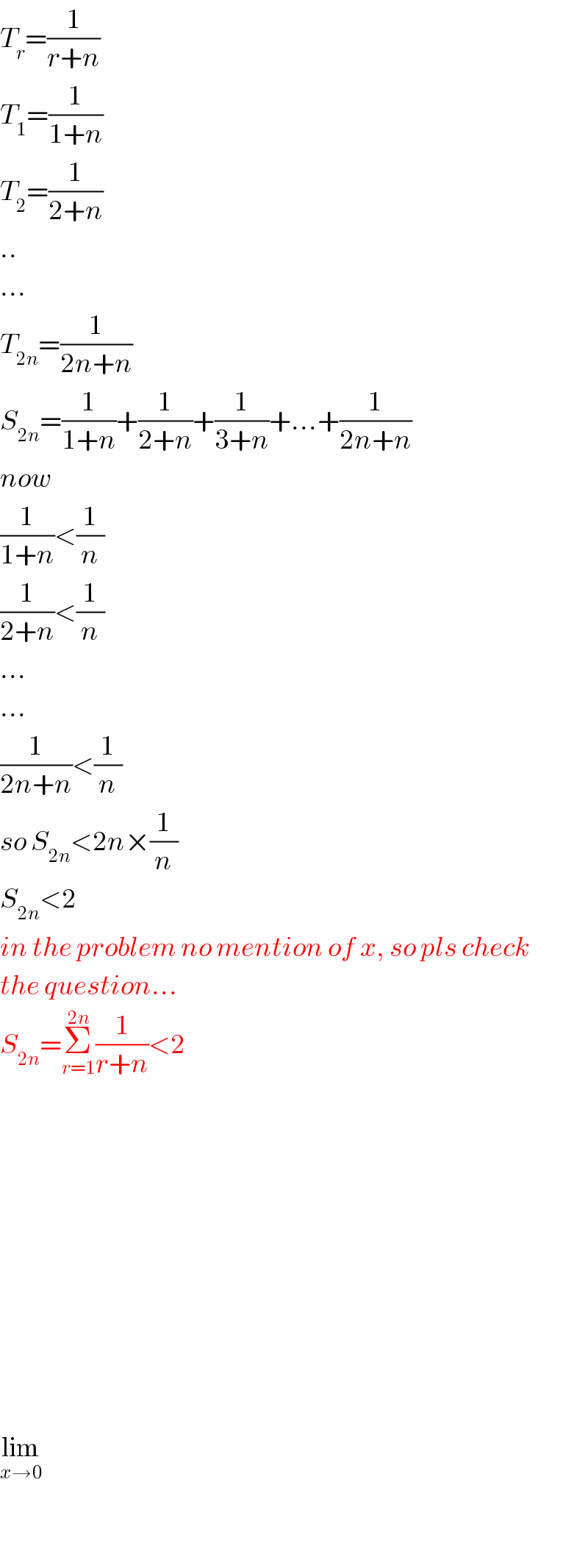
$${T}_{{r}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{r}+{n}} \\ $$$${T}_{\mathrm{1}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+{n}} \\ $$$${T}_{\mathrm{2}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}+{n}} \\ $$$$.. \\ $$$$… \\ $$$${T}_{\mathrm{2}{n}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{n}+{n}} \\ $$$${S}_{\mathrm{2}{n}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+{n}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}+{n}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}+{n}}+…+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{n}+{n}} \\ $$$${now}\: \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+{n}}<\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}+{n}}<\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}} \\ $$$$… \\ $$$$… \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{n}+{n}}<\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}} \\ $$$${so}\:{S}_{\mathrm{2}{n}} <\mathrm{2}{n}×\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}} \\ $$$${S}_{\mathrm{2}{n}} <\mathrm{2} \\ $$$${in}\:{the}\:{problem}\:{no}\:{mention}\:{of}\:{x},\:{so}\:{pls}\:{check} \\ $$$${the}\:{question}… \\ $$$${S}_{\mathrm{2}{n}} =\underset{{r}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\mathrm{2}{n}} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{r}+{n}}<\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Answered by ajfour last updated on 15/Dec/18
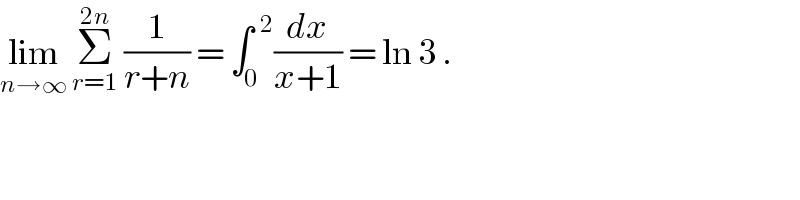
$$\underset{{n}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\underset{{r}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\mathrm{2}{n}} {\sum}}\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{r}+{n}}\:=\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\:\:\mathrm{2}} \frac{{dx}}{{x}+\mathrm{1}}\:=\:\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{3}\:. \\ $$
Commented by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 15/Dec/18
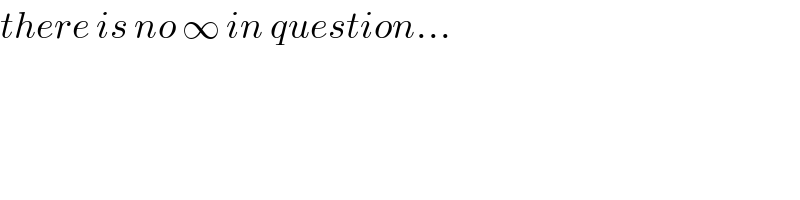
$${there}\:{is}\:{no}\:\infty\:{in}\:{question}… \\ $$
