Question Number 81853 by jagoll last updated on 16/Feb/20
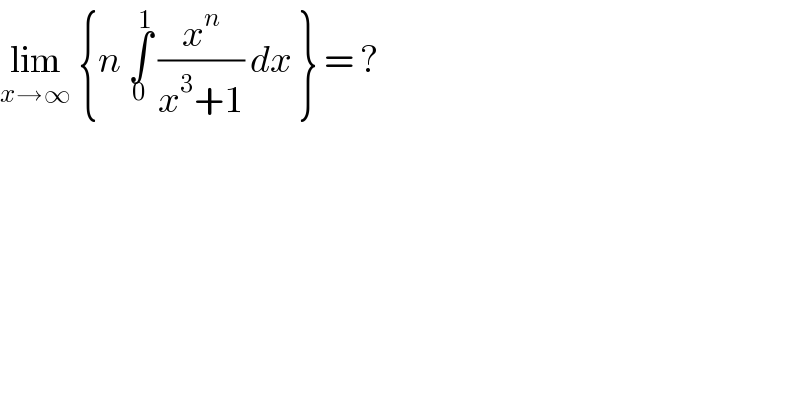
$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\left\{{n}\:\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\mathrm{1}} {\int}}\:\frac{{x}^{{n}} }{{x}^{\mathrm{3}} +\mathrm{1}}\:{dx}\:\right\}\:=\:? \\ $$
Commented by john santu last updated on 16/Feb/20

$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:{is}\:{the}\:{answer} \\ $$
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 16/Feb/20
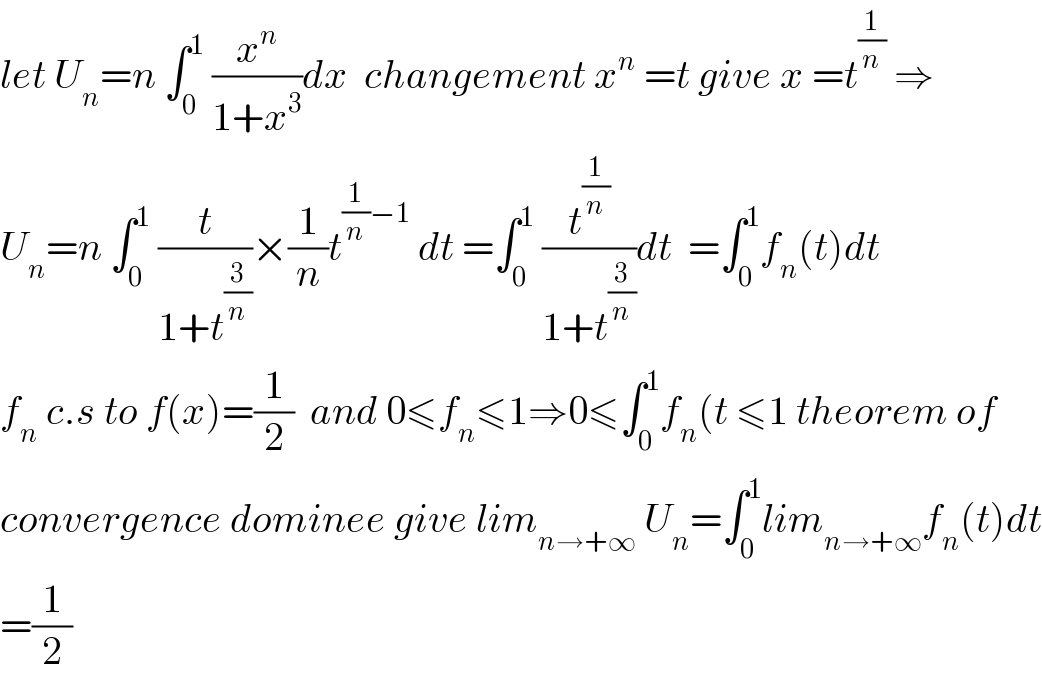
$${let}\:{U}_{{n}} ={n}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\frac{{x}^{{n}} }{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{3}} }{dx}\:\:{changement}\:{x}^{{n}} \:={t}\:{give}\:{x}\:={t}^{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}} \:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${U}_{{n}} ={n}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\frac{{t}}{\mathrm{1}+{t}^{\frac{\mathrm{3}}{{n}}} }×\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}{t}^{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}−\mathrm{1}} \:{dt}\:=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\frac{{t}^{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}} }{\mathrm{1}+{t}^{\frac{\mathrm{3}}{{n}}} }{dt}\:\:=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} {f}_{{n}} \left({t}\right){dt} \\ $$$${f}_{{n}} \:{c}.{s}\:{to}\:{f}\left({x}\right)=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\:{and}\:\mathrm{0}\leqslant{f}_{{n}} \leqslant\mathrm{1}\Rightarrow\mathrm{0}\leqslant\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} {f}_{{n}} \left({t}\:\leqslant\mathrm{1}\:{theorem}\:{of}\right. \\ $$$${convergence}\:{dominee}\:{give}\:{lim}_{{n}\rightarrow+\infty} \:{U}_{{n}} =\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} {lim}_{{n}\rightarrow+\infty} {f}_{{n}} \left({t}\right){dt} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
Answered by mind is power last updated on 16/Feb/20
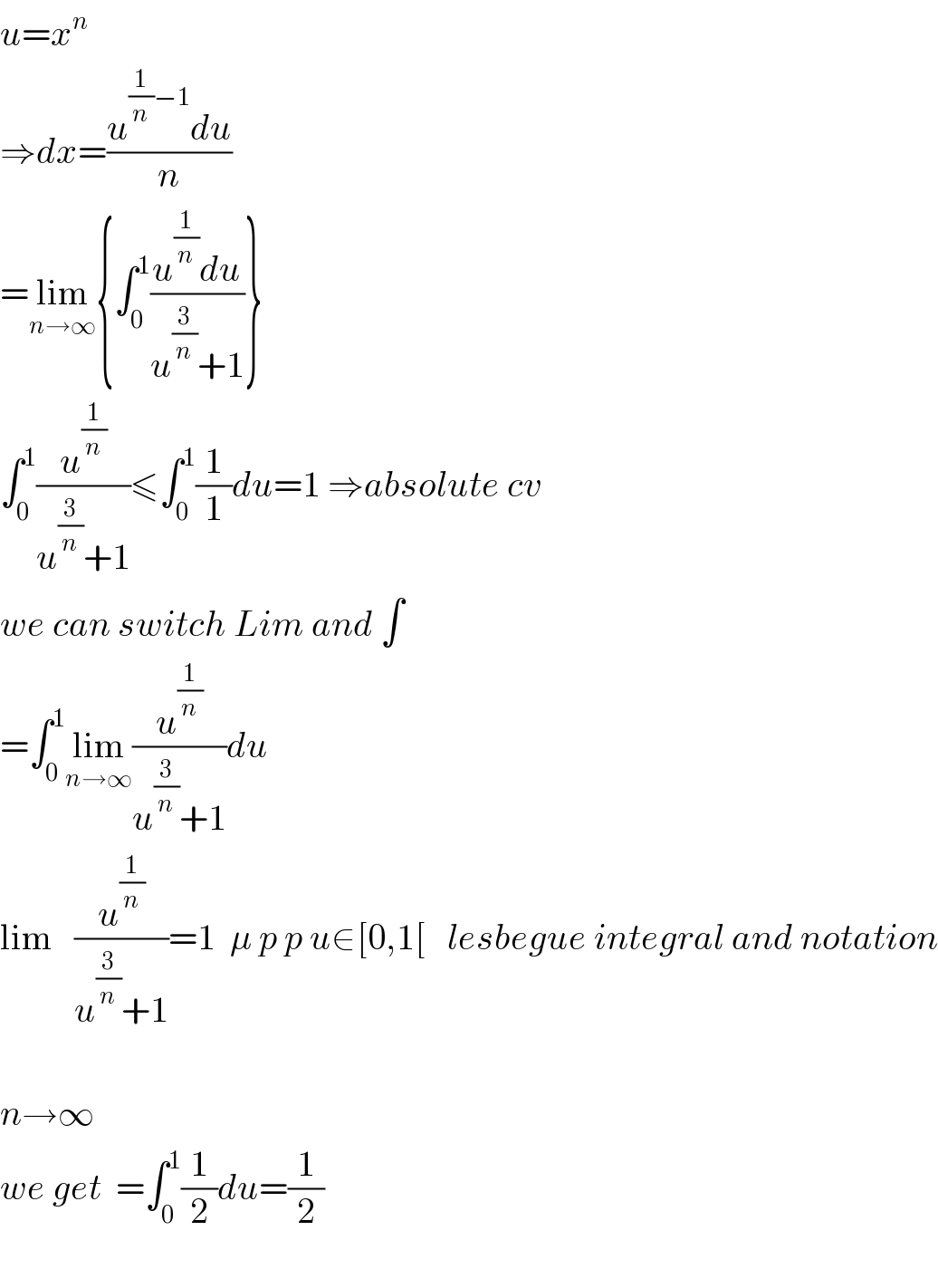
$${u}={x}^{{n}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{dx}=\frac{{u}^{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}−\mathrm{1}} {du}}{{n}} \\ $$$$=\underset{{n}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\left\{\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \frac{{u}^{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}} {du}}{{u}^{\frac{\mathrm{3}}{{n}}} +\mathrm{1}}\right\} \\ $$$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \frac{{u}^{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}} }{{u}^{\frac{\mathrm{3}}{{n}}} +\mathrm{1}}\leqslant\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}}{du}=\mathrm{1}\:\Rightarrow{absolute}\:{cv} \\ $$$${we}\:{can}\:{switch}\:{Lim}\:{and}\:\int \\ $$$$=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \underset{{n}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{{u}^{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}} }{{u}^{\frac{\mathrm{3}}{{n}}} +\mathrm{1}}{du} \\ $$$$\mathrm{lim}\:\:\:\frac{{u}^{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}} }{{u}^{\frac{\mathrm{3}}{{n}}} +\mathrm{1}}=\mathrm{1}\:\:\mu\:{p}\:{p}\:{u}\in\left[\mathrm{0},\mathrm{1}\left[\:\:\:{lesbegue}\:{integral}\:{and}\:{notation}\right.\right. \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${n}\rightarrow\infty \\ $$$${we}\:{get}\:\:=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{du}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
