Question Number 160609 by cortano last updated on 03/Dec/21
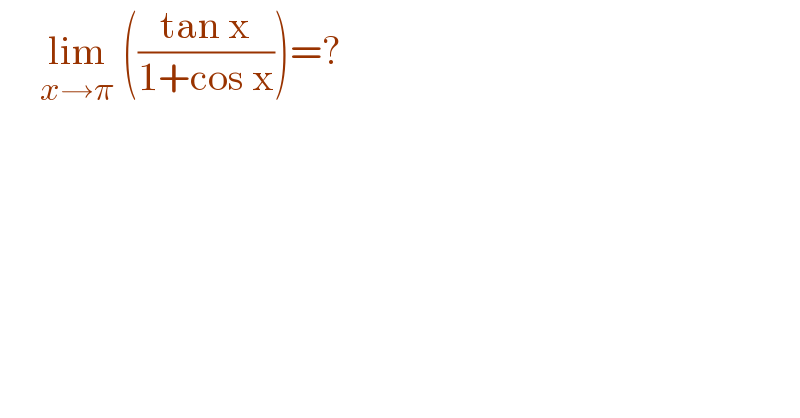
$$\:\:\:\:\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\pi} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\left(\frac{\mathrm{tan}\:\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{x}}\right)=? \\ $$
Answered by Ar Brandon last updated on 03/Dec/21
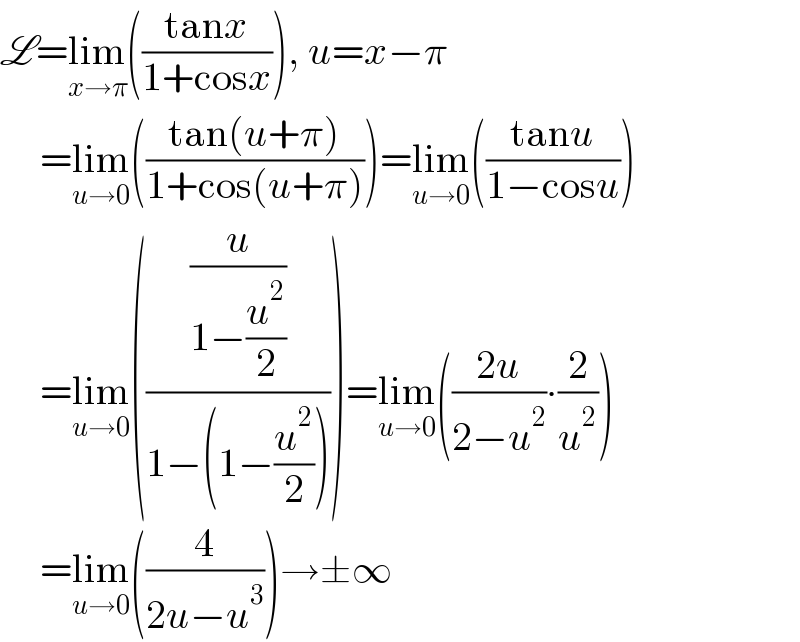
$$\mathscr{L}=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\pi} {\mathrm{lim}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{tan}{x}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{cos}{x}}\right),\:{u}={x}−\pi \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:=\underset{{u}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{tan}\left({u}+\pi\right)}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{cos}\left({u}+\pi\right)}\right)=\underset{{u}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{tan}{u}}{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{cos}{u}}\right) \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:=\underset{{u}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\left(\frac{\frac{{u}}{\mathrm{1}−\frac{{u}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}}}{\mathrm{1}−\left(\mathrm{1}−\frac{{u}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}\right)}\right)=\underset{{u}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{2}{u}}{\mathrm{2}−{u}^{\mathrm{2}} }\centerdot\frac{\mathrm{2}}{{u}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right) \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:=\underset{{u}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{2}{u}−{u}^{\mathrm{3}} }\right)\rightarrow\pm\infty \\ $$
Answered by alephzero last updated on 03/Dec/21
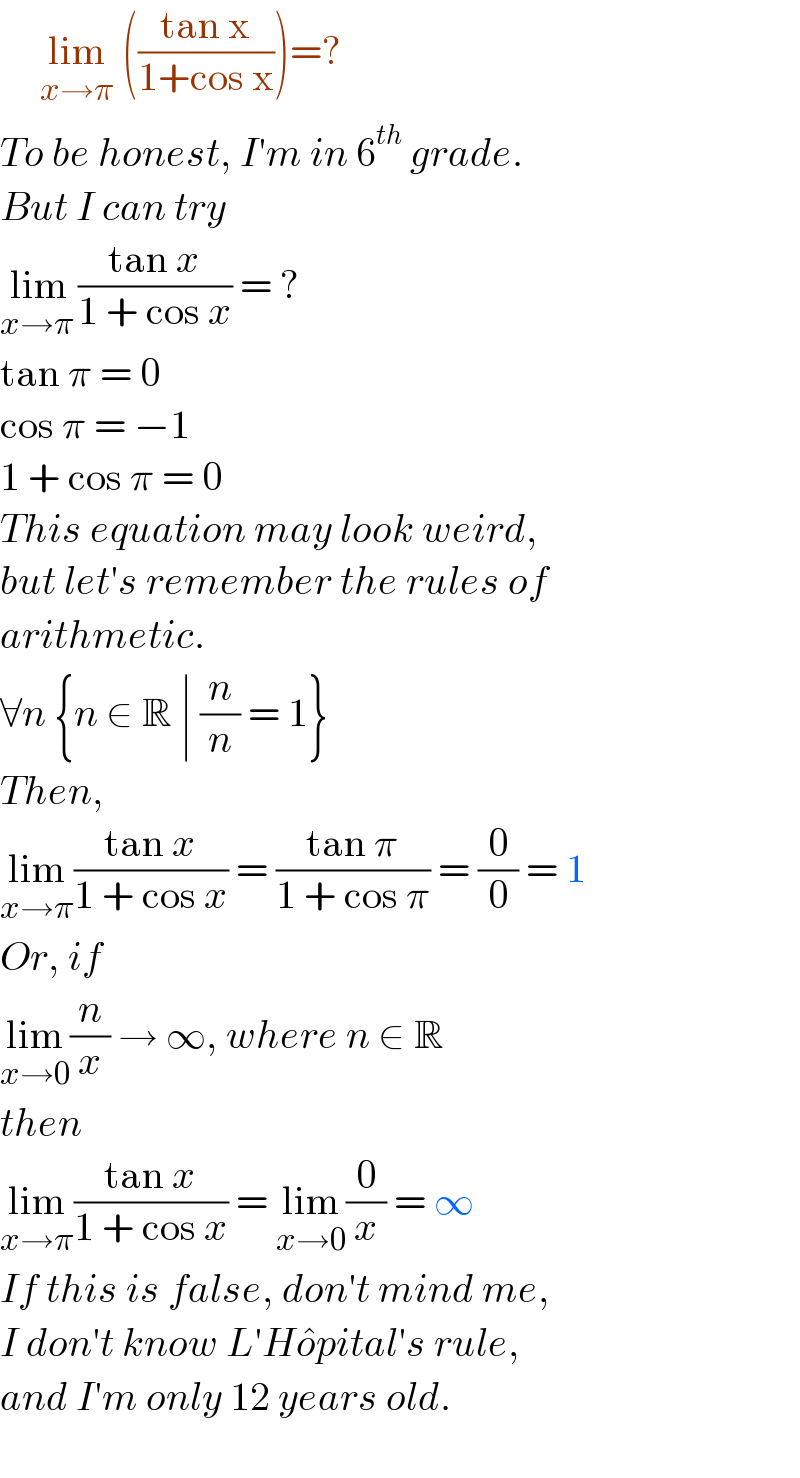
$$\:\:\:\:\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\pi} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\left(\frac{\mathrm{tan}\:\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{x}}\right)=? \\ $$$${To}\:{be}\:{honest},\:{I}'{m}\:{in}\:\mathrm{6}^{{th}} \:{grade}. \\ $$$${But}\:{I}\:{can}\:{try} \\ $$$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\pi\:} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\mathrm{tan}\:{x}}{\mathrm{1}\:+\:\mathrm{cos}\:{x}}\:=\:? \\ $$$$\mathrm{tan}\:\pi\:=\:\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\mathrm{cos}\:\pi\:=\:−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\mathrm{1}\:+\:\mathrm{cos}\:\pi\:=\:\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${This}\:{equation}\:{may}\:{look}\:{weird}, \\ $$$${but}\:{let}'{s}\:{remember}\:{the}\:{rules}\:{of} \\ $$$${arithmetic}. \\ $$$$\forall{n}\:\left\{{n}\:\in\:\mathbb{R}\:\mid\:\frac{{n}}{{n}}\:=\:\mathrm{1}\right\} \\ $$$${Then}, \\ $$$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\pi} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\mathrm{tan}\:{x}}{\mathrm{1}\:+\:\mathrm{cos}\:{x}}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{tan}\:\pi}{\mathrm{1}\:+\:\mathrm{cos}\:\pi}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{0}}{\mathrm{0}}\:=\:\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${Or},\:{if} \\ $$$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{{n}}{{x}}\:\rightarrow\:\infty,\:{where}\:{n}\:\in\:\mathbb{R} \\ $$$${then} \\ $$$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\pi} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\mathrm{tan}\:{x}}{\mathrm{1}\:+\:\mathrm{cos}\:{x}}\:=\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\mathrm{0}}{{x}}\:=\:\infty \\ $$$${If}\:{this}\:{is}\:{false},\:{don}'{t}\:{mind}\:{me}, \\ $$$${I}\:{don}'{t}\:{know}\:{L}'{H}\hat {{o}pital}'{s}\:{rule}, \\ $$$${and}\:{I}'{m}\:{only}\:\mathrm{12}\:{years}\:{old}. \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Answered by tounghoungko last updated on 03/Dec/21
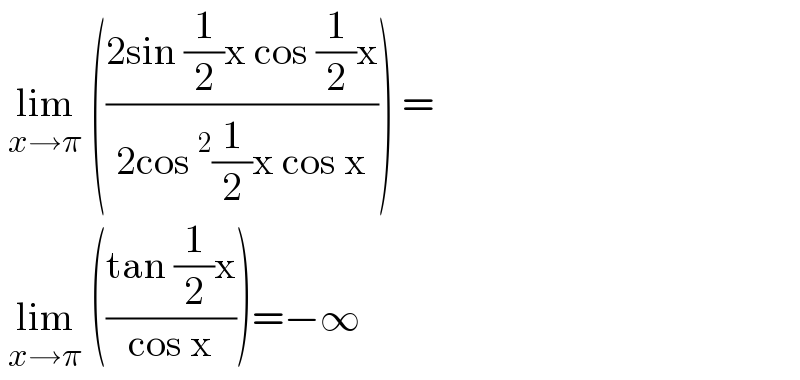
$$\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\pi} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\left(\frac{\mathrm{2sin}\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{x}\:\mathrm{cos}\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{2cos}\:^{\mathrm{2}} \frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{x}\:\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{x}}\right)\:= \\ $$$$\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\pi} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\left(\frac{\mathrm{tan}\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{x}}\right)=−\infty \\ $$
Answered by Mathspace last updated on 03/Dec/21
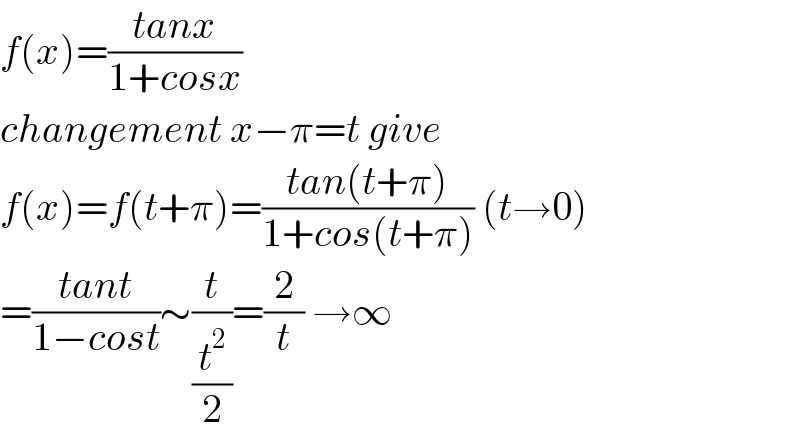
$${f}\left({x}\right)=\frac{{tanx}}{\mathrm{1}+{cosx}} \\ $$$${changement}\:{x}−\pi={t}\:{give} \\ $$$${f}\left({x}\right)={f}\left({t}+\pi\right)=\frac{{tan}\left({t}+\pi\right)}{\mathrm{1}+{cos}\left({t}+\pi\right)}\:\left({t}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}\right) \\ $$$$=\frac{{tant}}{\mathrm{1}−{cost}}\sim\frac{{t}}{\frac{{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}}=\frac{\mathrm{2}}{{t}}\:\rightarrow\infty \\ $$
