Question Number 85789 by Rio Michael last updated on 24/Mar/20
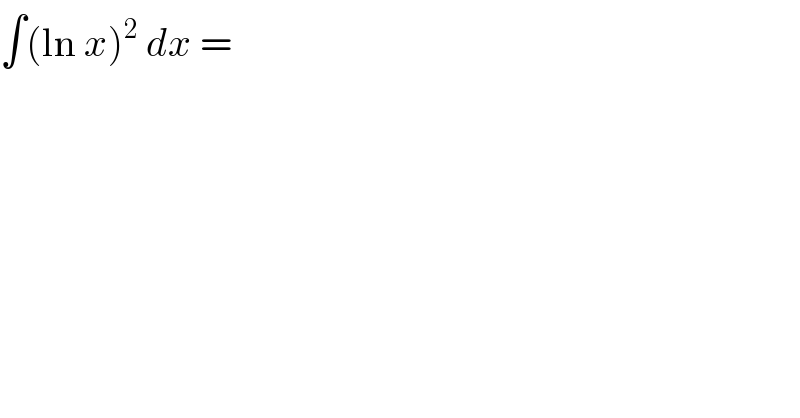
$$\int\left(\mathrm{ln}\:{x}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \:{dx}\:= \\ $$
Answered by sakeefhasan05@gmail.com last updated on 24/Mar/20
![=(ln x)^2 .x −∫x.2(ln x).(1/x)dx =x(ln x)^2 −2[(ln x).x−∫x.(1/x)dx] =x(ln x)^2 −2x(ln x))+2x+C](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q85792.png)
$$=\left(\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{x}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} .\mathrm{x}\:−\int\mathrm{x}.\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{x}\right).\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{x}}\mathrm{dx} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{x}\left(\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{x}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}\left[\left(\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{x}\right).\mathrm{x}−\int\mathrm{x}.\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{x}}\mathrm{dx}\right] \\ $$$$\left.=\mathrm{x}\left(\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{x}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2x}\left(\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{x}\right)\right)+\mathrm{2x}+\mathrm{C} \\ $$
