Question Number 83842 by M±th+et£s last updated on 06/Mar/20
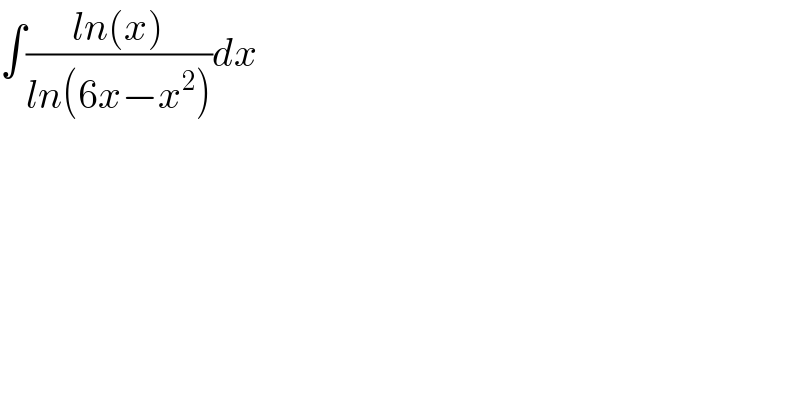
$$\int\frac{{ln}\left({x}\right)}{{ln}\left(\mathrm{6}{x}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)}{dx} \\ $$
Commented by Henri Boucatchou last updated on 06/Mar/20
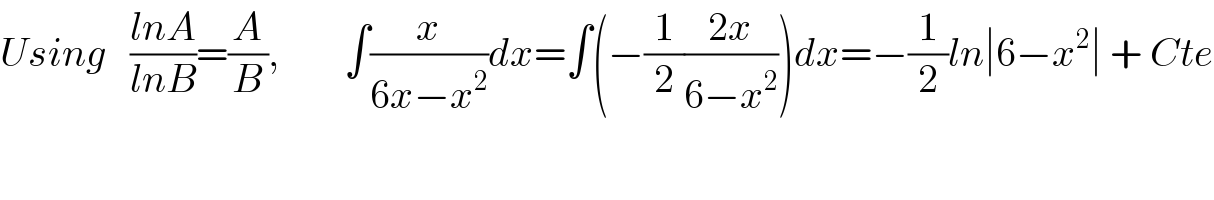
$${Using}\:\:\:\frac{{lnA}}{{lnB}}=\frac{{A}}{{B}},\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\int\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{6}{x}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{dx}=\int\left(−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}}{\mathrm{6}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right){dx}=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{ln}\mid\mathrm{6}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \mid\:+\:{Cte} \\ $$
Commented by MJS last updated on 06/Mar/20
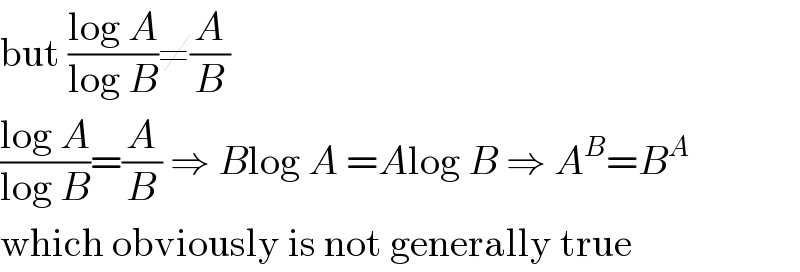
$$\mathrm{but}\:\frac{\mathrm{log}\:{A}}{\mathrm{log}\:{B}}\neq\frac{{A}}{{B}} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{log}\:{A}}{\mathrm{log}\:{B}}=\frac{{A}}{{B}}\:\Rightarrow\:{B}\mathrm{log}\:{A}\:={A}\mathrm{log}\:{B}\:\Rightarrow\:{A}^{{B}} ={B}^{{A}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{which}\:\mathrm{obviously}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{not}\:\mathrm{generally}\:\mathrm{true} \\ $$
Commented by M±th+et£s last updated on 06/Mar/20

$${thank}\:{you}\:{sir} \\ $$
Commented by MJS last updated on 07/Mar/20

$$\mathrm{I}\:\mathrm{tried}\:\mathrm{some}\:\mathrm{things}\:\mathrm{I}\:\mathrm{know}\:\mathrm{but}\:\mathrm{it}'\mathrm{s}\:\mathrm{not}\:\mathrm{possible} \\ $$$$\mathrm{for}\:\mathrm{me}\:\mathrm{to}\:\mathrm{solve}\:\mathrm{it} \\ $$
