Question Number 27388 by macanudo last updated on 06/Jan/18

$$\underset{\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\:\frac{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{1}} }{\mathrm{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\: \\ $$
Commented by abdo imad last updated on 06/Jan/18
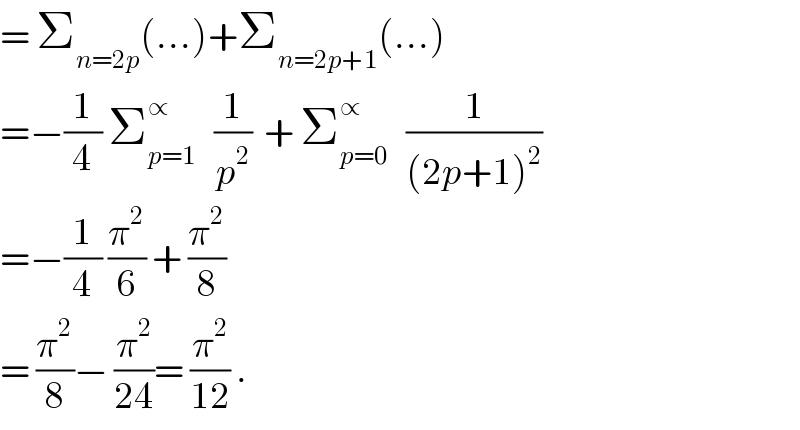
$$=\:\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{2}{p}} \left(…\right)+\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{2}{p}+\mathrm{1}} \left(…\right) \\ $$$$=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\:\sum_{{p}=\mathrm{1}} ^{\propto} \:\:\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{p}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\:+\:\sum_{{p}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\propto} \:\:\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left(\mathrm{2}{p}+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\:\frac{\pi^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{6}}\:+\:\frac{\pi^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{8}} \\ $$$$=\:\frac{\pi^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{8}}−\:\frac{\pi^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{24}}=\:\frac{\pi^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{12}}\:. \\ $$
