Question Number 128736 by mnjuly1970 last updated on 09/Jan/21
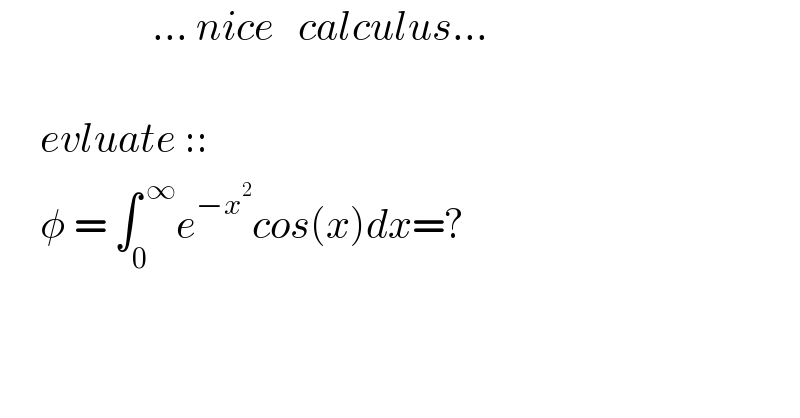
$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:…\:{nice}\:\:\:{calculus}… \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:{evluate}\::: \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\phi\:=\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\:\infty} {e}^{−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } {cos}\left({x}\right){dx}=? \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by Lordose last updated on 10/Jan/21

Answered by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 09/Jan/21
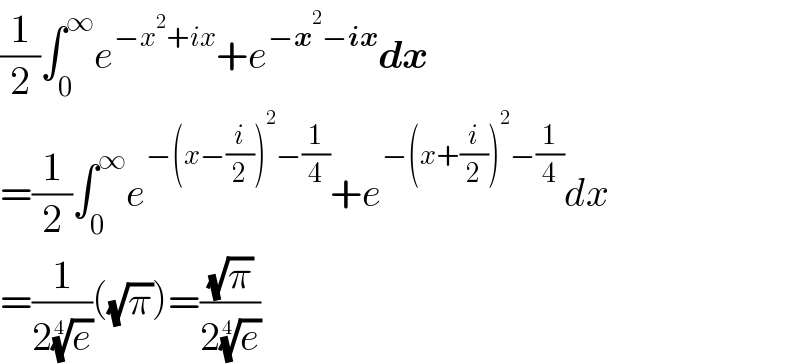
$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} {e}^{−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{ix}} +{e}^{−\boldsymbol{{x}}^{\mathrm{2}} −\boldsymbol{{ix}}} \boldsymbol{{dx}} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} {e}^{−\left({x}−\frac{{i}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} −\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}} +{e}^{−\left({x}+\frac{{i}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} −\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}} {dx} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}\sqrt[{\mathrm{4}}]{{e}}}\left(\sqrt{\pi}\right)=\frac{\sqrt{\pi}}{\mathrm{2}\sqrt[{\mathrm{4}}]{{e}}} \\ $$
