Question Number 122525 by mnjuly1970 last updated on 17/Nov/20
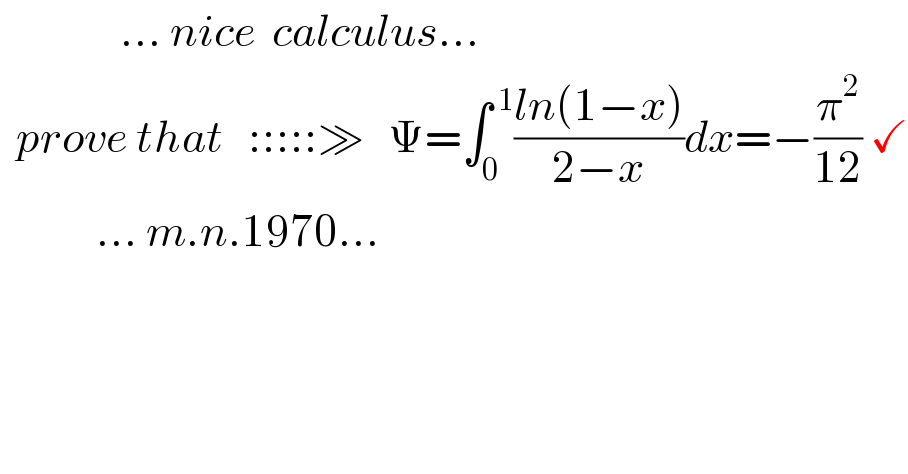
$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:…\:{nice}\:\:{calculus}… \\ $$$$\:\:{prove}\:{that}\:\:\::::::\gg\:\:\:\Psi=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\:\mathrm{1}} \frac{{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}−{x}\right)}{\mathrm{2}−{x}}{dx}=−\frac{\pi^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{12}}\:\checkmark \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:…\:{m}.{n}.\mathrm{1970}… \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\: \\ $$
Answered by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 17/Nov/20
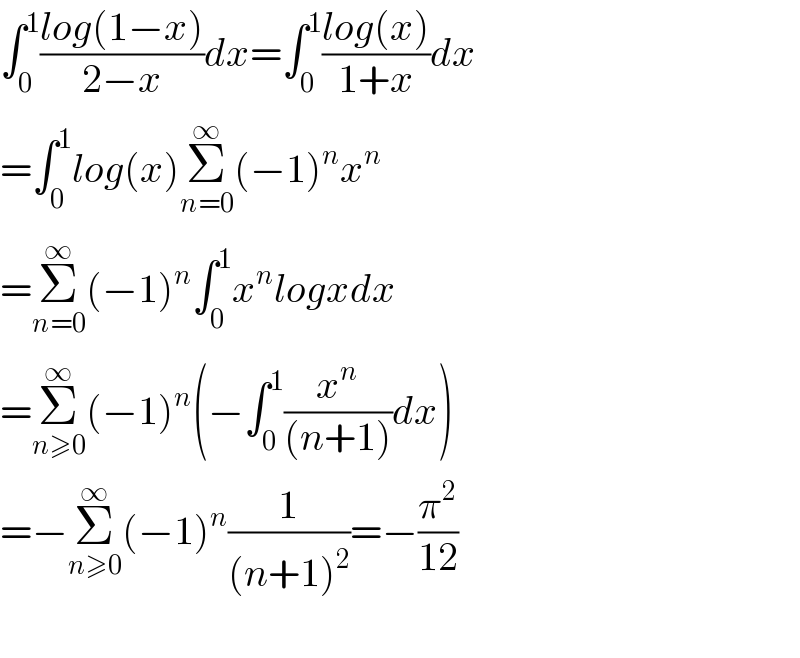
$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \frac{{log}\left(\mathrm{1}−{x}\right)}{\mathrm{2}−{x}}{dx}=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \frac{{log}\left({x}\right)}{\mathrm{1}+{x}}{dx} \\ $$$$=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} {log}\left({x}\right)\underset{{n}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} {x}^{{n}} \\ $$$$=\underset{{n}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} \int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} {x}^{{n}} {logxdx} \\ $$$$=\underset{{n}\geqslant\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} \left(−\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \frac{{x}^{{n}} }{\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)}{dx}\right) \\ $$$$=−\underset{{n}\geqslant\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} \frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }=−\frac{\pi^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{12}} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by mnjuly1970 last updated on 17/Nov/20

$${perfect}… \\ $$
