Question Number 128245 by mnjuly1970 last updated on 05/Jan/21
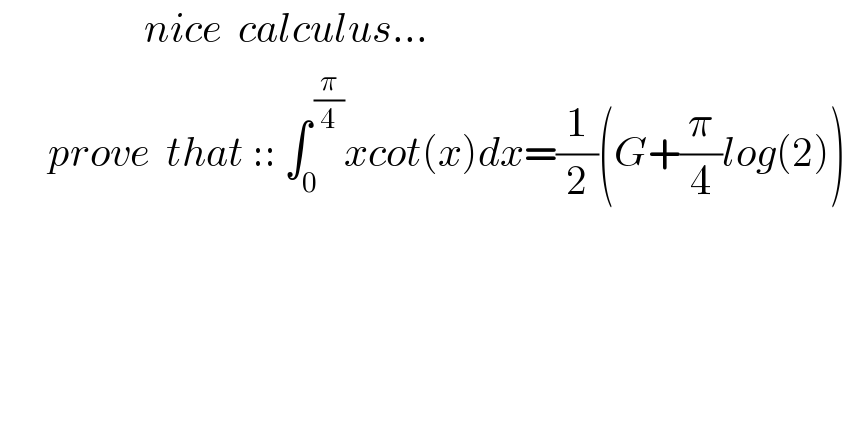
$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:{nice}\:\:{calculus}… \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:{prove}\:\:{that}\:::\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\:\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}} {xcot}\left({x}\right){dx}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left({G}+\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}{log}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\right) \\ $$
Answered by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 05/Jan/21
![∫_0 ^(π/4) xcotxdx=[xlog(sinx)]_0 ^(π/4) −∫_0 ^(π/4) log(sinx)dx = −(π/8)log(2)+(π/4)log(2)+(G/2)log(2) (Has been proved earliar) = (π/8)log(2)+(G/2)log(2) Q128244](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q128249.png)
$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}} {xcotxdx}=\left[{xlog}\left({sinx}\right)\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}} −\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}} {log}\left({sinx}\right){dx} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:=\:−\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{8}}{log}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)+\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}{log}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)+\frac{{G}}{\mathrm{2}}{log}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\:\:\left({Has}\:{been}\:{proved}\:{earliar}\right) \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:=\:\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{8}}{log}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)+\frac{{G}}{\mathrm{2}}{log}\left(\mathrm{2}\right) \\ $$$${Q}\mathrm{128244} \\ $$
Commented by mnjuly1970 last updated on 05/Jan/21
$${grateful}\:{mr}\:{payan}…{mercey}… \\ $$
