Question Number 36707 by rahul 19 last updated on 04/Jun/18

$$\mathrm{P}=\mathrm{i}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{R}\:\mathrm{then}\:\mathrm{how}\:\frac{\mathrm{dP}}{\mathrm{P}}\:=\:\mathrm{2}\:\frac{\mathrm{dI}}{\mathrm{I}}\:? \\ $$$$\mathrm{Similarly}\:\mathrm{P}=\:\frac{\mathrm{V}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{R}}\:\mathrm{then}\:\mathrm{how}\:\frac{\mathrm{dP}}{\mathrm{P}}=\mathrm{2}\frac{\mathrm{dV}}{\mathrm{V}}? \\ $$
Commented by rahul 19 last updated on 04/Jun/18
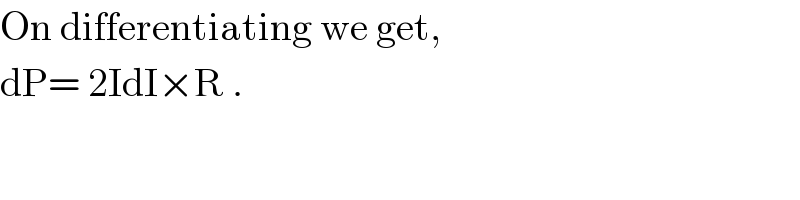
$$\mathrm{On}\:\mathrm{differentiating}\:\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{get}, \\ $$$$\mathrm{dP}=\:\mathrm{2IdI}×\mathrm{R}\:. \\ $$
Answered by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 04/Jun/18

$${P}={I}^{\mathrm{2}} {R} \\ $$$$\frac{{dP}}{{dI}}=\mathrm{2}{IR} \\ $$$${dP}=\mathrm{2}{IRdI} \\ $$$$\frac{{dP}}{{P}}=\frac{\mathrm{2}{IRdI}}{{I}^{\mathrm{2}} {R}} \\ $$$$\frac{{dP}}{{P}}=\frac{\mathrm{2}{dI}}{{I}}\:\:{proved} \\ $$
Commented by rahul 19 last updated on 04/Jun/18

$$\mathrm{thanks}\:\mathrm{sir}. \\ $$
Answered by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 04/Jun/18

$${P}=\frac{{V}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{R}} \\ $$$$\frac{{dP}}{{dV}}=\frac{\mathrm{2}{V}}{{R}} \\ $$$${dP}=\frac{\mathrm{2}{VdV}}{{R}} \\ $$$$\frac{{dP}}{{P}}=\frac{\mathrm{2}{VdV}×{R}}{{R}×{V}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$\frac{{dP}}{{P}}=\frac{\mathrm{2}{dV}}{{V}}\:{proved} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$
