Question Number 189145 by mathlove last updated on 12/Mar/23
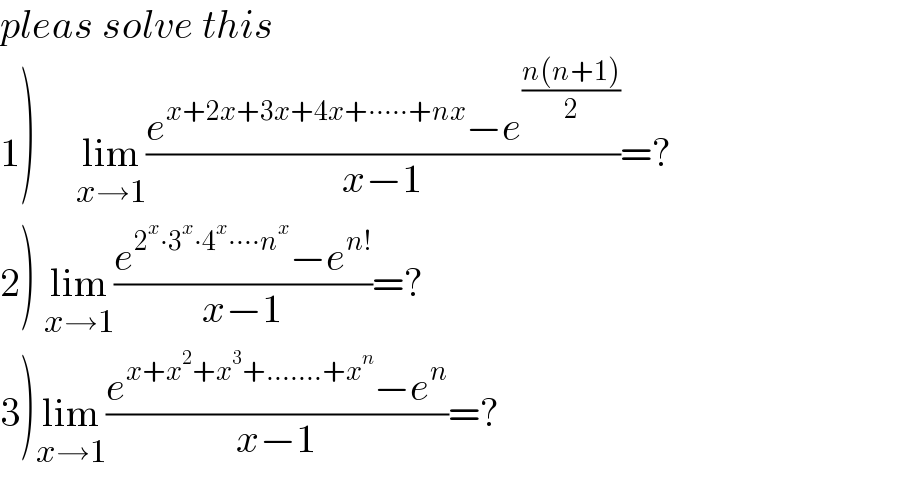
$${pleas}\:{solve}\:{this} \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{1}\right)\:\:\:\:\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{{e}^{{x}+\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{3}{x}+\mathrm{4}{x}+\centerdot\centerdot\centerdot\centerdot\centerdot+{nx}} −{e}^{\frac{{n}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}} }{{x}−\mathrm{1}}=? \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{2}\right)\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{{e}^{\mathrm{2}^{{x}} \centerdot\mathrm{3}^{{x}} \centerdot\mathrm{4}^{{x}} \centerdot\centerdot\centerdot\centerdot{n}^{{x}} } −{e}^{{n}!} }{{x}−\mathrm{1}}=? \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{3}\right)\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{{e}^{{x}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{x}^{\mathrm{3}} +…….+{x}^{{n}} } −{e}^{{n}} }{{x}−\mathrm{1}}=? \\ $$
Answered by Ar Brandon last updated on 12/Mar/23
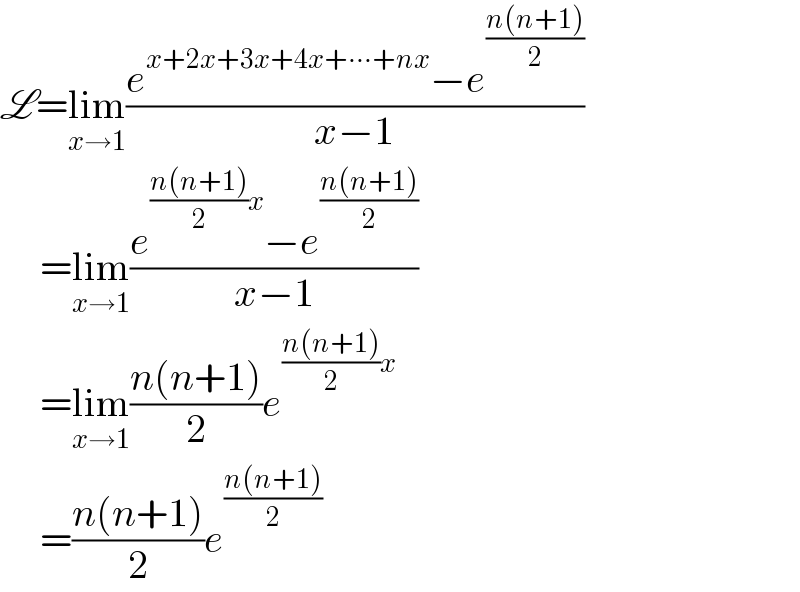
$$\mathscr{L}=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{{e}^{{x}+\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{3}{x}+\mathrm{4}{x}+\centerdot\centerdot\centerdot+{nx}} −{e}^{\frac{{n}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}} }{{x}−\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{{e}^{\frac{{n}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}{x}} −{e}^{\frac{{n}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}} }{{x}−\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{{n}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}{e}^{\frac{{n}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}{x}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:=\frac{{n}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}{e}^{\frac{{n}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}} \\ $$
Answered by Ar Brandon last updated on 12/Mar/23
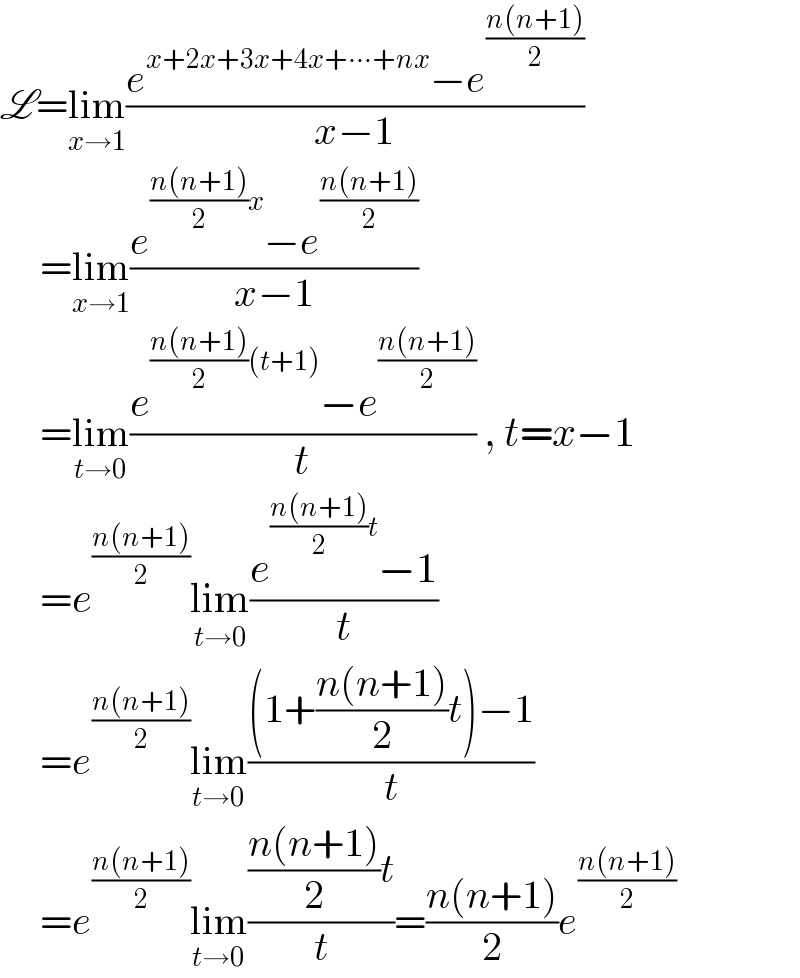
$$\mathscr{L}=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{{e}^{{x}+\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{3}{x}+\mathrm{4}{x}+\centerdot\centerdot\centerdot+{nx}} −{e}^{\frac{{n}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}} }{{x}−\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{{e}^{\frac{{n}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}{x}} −{e}^{\frac{{n}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}} }{{x}−\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:=\underset{{t}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{{e}^{\frac{{n}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}\left({t}+\mathrm{1}\right)} −{e}^{\frac{{n}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}} }{{t}}\:,\:{t}={x}−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:={e}^{\frac{{n}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}} \underset{{t}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{{e}^{\frac{{n}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}{t}} −\mathrm{1}}{{t}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:={e}^{\frac{{n}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}} \underset{{t}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{{n}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}{t}\right)−\mathrm{1}}{{t}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:={e}^{\frac{{n}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}} \underset{{t}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\frac{{n}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}{t}}{{t}}=\frac{{n}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}{e}^{\frac{{n}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}} \\ $$
Answered by CElcedricjunior last updated on 15/Mar/23
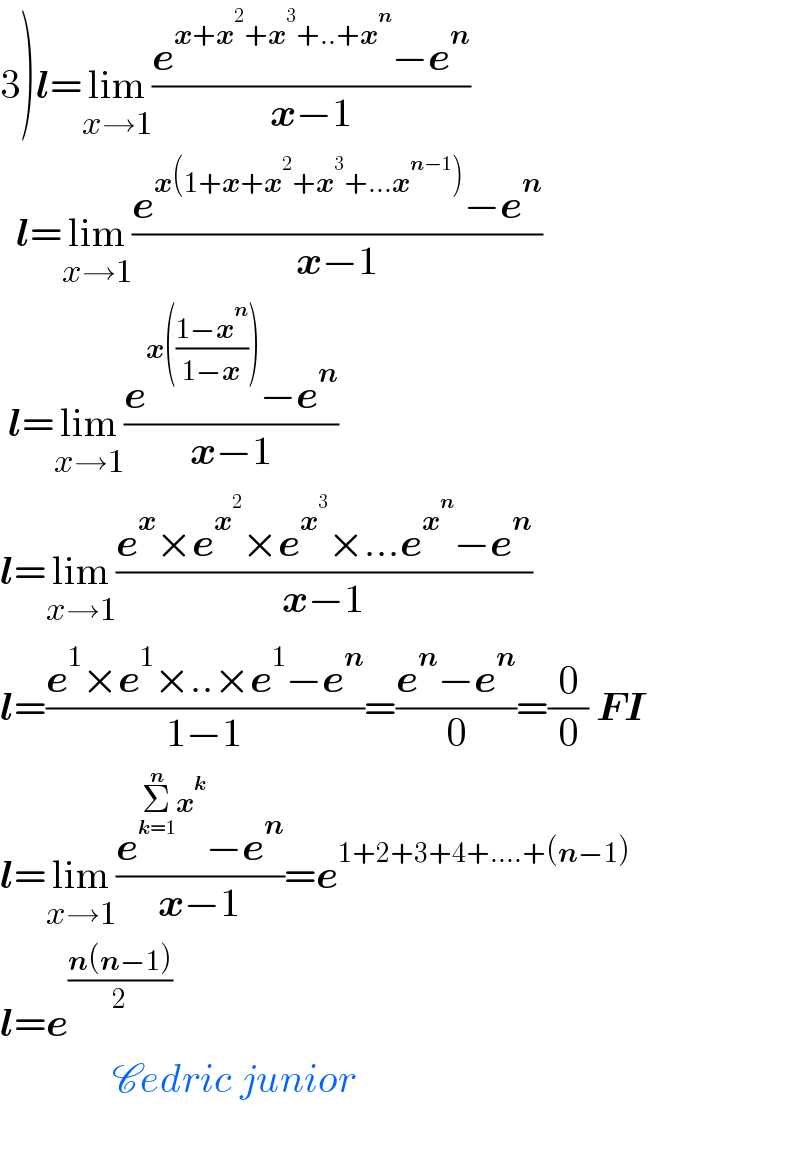
$$\left.\mathrm{3}\right)\boldsymbol{{l}}=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\boldsymbol{{x}}+\boldsymbol{{x}}^{\mathrm{2}} +\boldsymbol{{x}}^{\mathrm{3}} +..+\boldsymbol{{x}}^{\boldsymbol{{n}}} } −\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\boldsymbol{{n}}} }{\boldsymbol{{x}}−\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\:\:\boldsymbol{{l}}=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\boldsymbol{{x}}\left(\mathrm{1}+\boldsymbol{{x}}+\boldsymbol{{x}}^{\mathrm{2}} +\boldsymbol{{x}}^{\mathrm{3}} +…\boldsymbol{{x}}^{\boldsymbol{{n}}−\mathrm{1}} \right)} −\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\boldsymbol{{n}}} }{\boldsymbol{{x}}−\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\:\boldsymbol{{l}}=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\boldsymbol{{x}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}−\boldsymbol{{x}}^{\boldsymbol{{n}}} }{\mathrm{1}−\boldsymbol{{x}}}\right)} −\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\boldsymbol{{n}}} }{\boldsymbol{{x}}−\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\boldsymbol{{l}}=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\boldsymbol{{x}}} ×\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\boldsymbol{{x}}^{\mathrm{2}} } ×\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\boldsymbol{{x}}^{\mathrm{3}} } ×…\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\boldsymbol{{x}}^{\boldsymbol{{n}}} } −\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\boldsymbol{{n}}} }{\boldsymbol{{x}}−\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\boldsymbol{{l}}=\frac{\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\mathrm{1}} ×\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\mathrm{1}} ×..×\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\mathrm{1}} −\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\boldsymbol{{n}}} }{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{1}}=\frac{\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\boldsymbol{{n}}} −\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\boldsymbol{{n}}} }{\mathrm{0}}=\frac{\mathrm{0}}{\mathrm{0}}\:\boldsymbol{{FI}} \\ $$$$\boldsymbol{{l}}=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\underset{\boldsymbol{{k}}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\boldsymbol{{n}}} {\sum}}\boldsymbol{{x}}^{\boldsymbol{{k}}} } −\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\boldsymbol{{n}}} }{\boldsymbol{{x}}−\mathrm{1}}=\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{2}+\mathrm{3}+\mathrm{4}+….+\left(\boldsymbol{{n}}−\mathrm{1}\right)} \\ $$$$\boldsymbol{{l}}=\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\frac{\boldsymbol{{n}}\left(\boldsymbol{{n}}−\mathrm{1}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathscr{C}{edric}\:{junior}\: \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Answered by CElcedricjunior last updated on 14/Mar/23
![1)l=lim_(x→1) ((e^(x+2x+3x+4x+...+nx) −e^((n(n+1))/2) )/(x−1)) =lim_(x→1) ((e^(x(1+2+....+n)) −e^((n(n+1))/2) )/(x−1)) =lim_(x→1) ((e^(((n(n+1))/2)x) −e^((n(n+1))/2) )/(x−1))=lim_(x→1) ((f_n (x)−f_n (1))/(x−1)) =[f_n ′(1)] avec f_n (x)=e^(((n(n+1))/2)x) =((n(n+1))/2)e^((n(n+1))/2)](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q189311.png)
$$\left.\mathrm{1}\right){l}=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\boldsymbol{{x}}+\mathrm{2}\boldsymbol{{x}}+\mathrm{3}\boldsymbol{{x}}+\mathrm{4}\boldsymbol{{x}}+…+\boldsymbol{{nx}}} −\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\frac{\boldsymbol{{n}}\left(\boldsymbol{{n}}+\mathrm{1}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}} }{\boldsymbol{{x}}−\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\boldsymbol{{x}}\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{2}+….+\boldsymbol{{n}}\right)} −\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\frac{\boldsymbol{{n}}\left(\boldsymbol{{n}}+\mathrm{1}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}} }{\boldsymbol{{x}}−\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\frac{\boldsymbol{{n}}\left(\boldsymbol{{n}}+\mathrm{1}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}\boldsymbol{{x}}} −\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\frac{\boldsymbol{{n}}\left(\boldsymbol{{n}}+\mathrm{1}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}} }{\boldsymbol{{x}}−\mathrm{1}}=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\boldsymbol{{f}}_{\boldsymbol{{n}}} \left(\boldsymbol{{x}}\right)−\boldsymbol{{f}}_{\boldsymbol{{n}}} \left(\mathrm{1}\right)}{\boldsymbol{{x}}−\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$=\left[\boldsymbol{{f}}_{{n}} '\left(\mathrm{1}\right)\right]\:\boldsymbol{{avec}}\:\boldsymbol{{f}}_{\boldsymbol{{n}}} \left(\boldsymbol{{x}}\right)=\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\frac{\boldsymbol{{n}}\left(\boldsymbol{{n}}+\mathrm{1}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}\boldsymbol{{x}}} \\ $$$$=\frac{\boldsymbol{{n}}\left(\boldsymbol{{n}}+\mathrm{1}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\frac{\boldsymbol{{n}}\left(\boldsymbol{{n}}+\mathrm{1}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Answered by CElcedricjunior last updated on 14/Mar/23

$$\left.\mathrm{2}\right)\boldsymbol{{l}}=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\mathrm{2}^{\boldsymbol{{x}}} .\mathrm{3}^{\boldsymbol{{x}}} ….\boldsymbol{{n}}^{\boldsymbol{{x}}} } −\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\boldsymbol{{n}}!} }{\boldsymbol{{x}}−\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\boldsymbol{{l}}=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\underset{\boldsymbol{{k}}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\boldsymbol{{n}}} {\prod}}\left(\boldsymbol{{k}}\right)^{\boldsymbol{{x}}} } −\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\boldsymbol{{n}}!} }{\boldsymbol{{x}}−\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\:\:\boldsymbol{{l}}=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\left(\boldsymbol{{n}}!\right)^{\boldsymbol{{x}}} } −\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\boldsymbol{{n}}!} }{\boldsymbol{{x}}−\mathrm{1}}=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\boldsymbol{{g}}_{\boldsymbol{{n}}} \left(\boldsymbol{{x}}\right)−\boldsymbol{{g}}_{\boldsymbol{{n}}} \left(\mathrm{1}\right)}{\boldsymbol{{x}}−\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\boldsymbol{{avec}}\:\:\boldsymbol{{g}}_{\boldsymbol{{n}}} \left(\boldsymbol{{x}}\right)=\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\left(\boldsymbol{{n}}!\right)^{\boldsymbol{{x}}} } \\ $$$$\:\:\:\boldsymbol{{l}}=\boldsymbol{{g}}_{\boldsymbol{{n}}} '\left(\mathrm{1}\right)=\boldsymbol{{ln}}\left(\boldsymbol{{n}}!\right){n}!\:\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\boldsymbol{{n}}!} \\ $$
Answered by TUN last updated on 14/Mar/23
![3)lim_(x→1) ((e^(x+x^2 +x^3 +...+x^n ) −e^n )/(x−1))=lim_(x→1) ((e^(x.((x^n −1)/(x−1))) −e^n )/(x−1)) =lim_(x→1) ((e^(x.(x^(n−1) +x^(n−2) +...+x^1 +1)) −e^n )/(x−1)) =lim_(x→1) ((e^((x^n +x^(n−1) +...+x^2 +x)) −e^n )/(x−1))=lim_(x→1) [nx^(n−1) +(n−1)x^(n−2) +...+2x+1]e^((x^n +x^(n−1) +...+x^2 +x)) =lim_(x→1) (n+n−1+n−2+...+2+1)e^n =[n+((n(n−1))/2)].e^n =((n(n+1))/2).e^n](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q189322.png)
$$ \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{3}\right)\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{{e}^{{x}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{x}^{\mathrm{3}} +…+{x}^{{n}} } −{e}^{{n}} }{{x}−\mathrm{1}}=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{{e}^{{x}.\frac{{x}^{{n}} −\mathrm{1}}{{x}−\mathrm{1}}} −{e}^{{n}} }{{x}−\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{{e}^{{x}.\left({x}^{{n}−\mathrm{1}} +{x}^{{n}−\mathrm{2}} +…+{x}^{\mathrm{1}} +\mathrm{1}\right)} −{e}^{{n}} }{{x}−\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{{e}^{\left({x}^{{n}} +{x}^{{n}−\mathrm{1}} +…+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{x}\right)} −{e}^{{n}} }{{x}−\mathrm{1}}=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {\mathrm{lim}}\left[{nx}^{{n}−\mathrm{1}} +\left({n}−\mathrm{1}\right){x}^{{n}−\mathrm{2}} +…+\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}\right]{e}^{\left({x}^{{n}} +{x}^{{n}−\mathrm{1}} +…+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{x}\right)} \\ $$$$=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {\mathrm{lim}}\left({n}+{n}−\mathrm{1}+{n}−\mathrm{2}+…+\mathrm{2}+\mathrm{1}\right){e}^{{n}} =\left[{n}+\frac{{n}\left({n}−\mathrm{1}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}\right].{e}^{{n}} \\ $$$$=\frac{{n}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}.{e}^{{n}} \\ $$
