Question Number 31106 by abdo imad last updated on 02/Mar/18
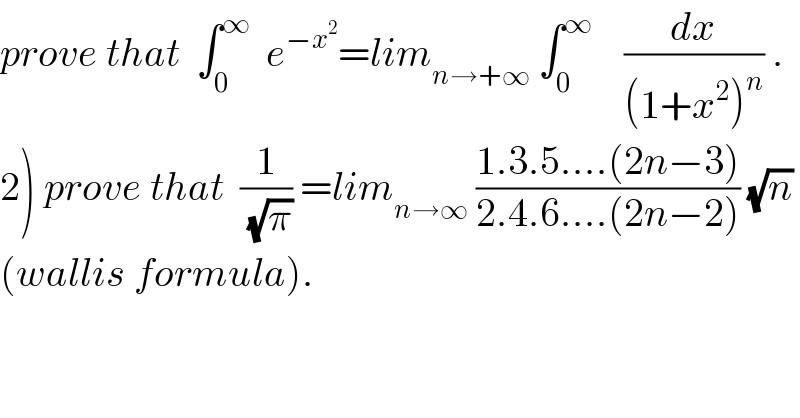
$${prove}\:{that}\:\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\:{e}^{−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } ={lim}_{{n}\rightarrow+\infty} \:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\:\:\:\frac{{dx}}{\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)^{{n}} }\:. \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{2}\right)\:{prove}\:{that}\:\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\:\sqrt{\pi}}\:={lim}_{{n}\rightarrow\infty} \:\frac{\mathrm{1}.\mathrm{3}.\mathrm{5}….\left(\mathrm{2}{n}−\mathrm{3}\right)}{\mathrm{2}.\mathrm{4}.\mathrm{6}….\left(\mathrm{2}{n}−\mathrm{2}\right)}\:\sqrt{{n}} \\ $$$$\left({wallis}\:{formula}\right). \\ $$
