Question Number 124421 by Ar Brandon last updated on 03/Dec/20
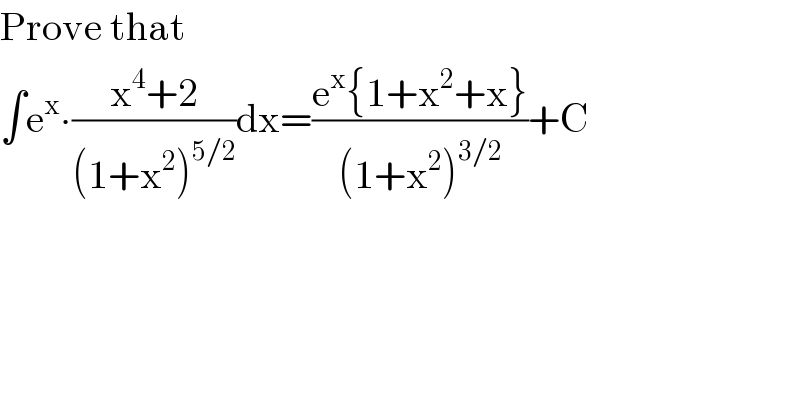
$$\mathrm{Prove}\:\mathrm{that} \\ $$$$\int\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} \centerdot\frac{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{4}} +\mathrm{2}}{\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)^{\mathrm{5}/\mathrm{2}} }\mathrm{dx}=\frac{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} \left\{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{x}\right\}}{\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)^{\mathrm{3}/\mathrm{2}} }+\mathrm{C} \\ $$
Commented by Ar Brandon last updated on 03/Dec/20

Commented by Ar Brandon last updated on 03/Dec/20
I don't understand the third line
Commented by Ar Brandon last updated on 03/Dec/20
Alright ! I got it ✋
