Question Number 111781 by mohammad17 last updated on 04/Sep/20
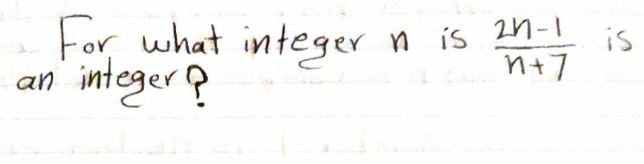
Commented by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 04/Sep/20
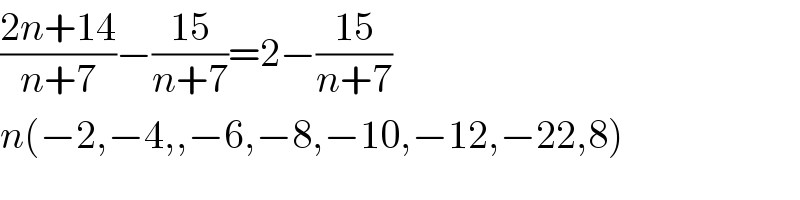
$$\frac{\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{14}}{{n}+\mathrm{7}}−\frac{\mathrm{15}}{{n}+\mathrm{7}}=\mathrm{2}−\frac{\mathrm{15}}{{n}+\mathrm{7}} \\ $$$${n}\left(−\mathrm{2},−\mathrm{4},,−\mathrm{6},−\mathrm{8},−\mathrm{10},−\mathrm{12},−\mathrm{22},\mathrm{8}\right) \\ $$
Commented by mohammad17 last updated on 04/Sep/20

$${thank}\:{you}\:{sir} \\ $$
Commented by Aziztisffola last updated on 04/Sep/20
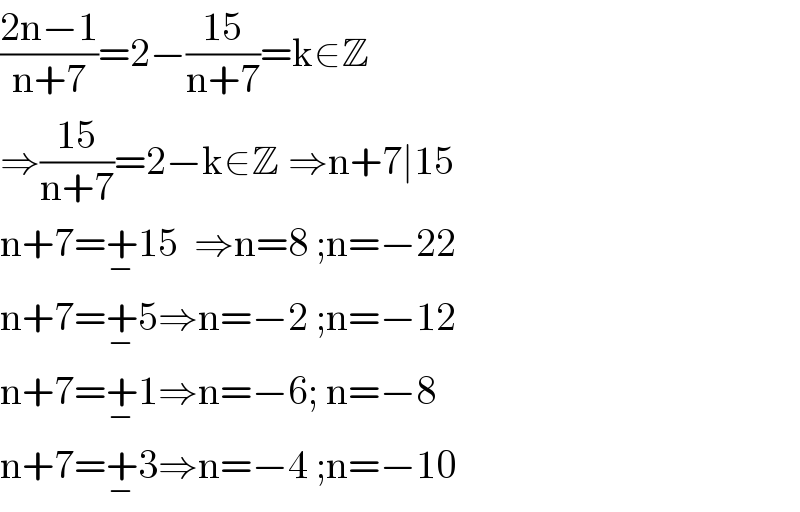
$$\frac{\mathrm{2n}−\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{7}}=\mathrm{2}−\frac{\mathrm{15}}{\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{7}}=\mathrm{k}\in\mathbb{Z} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\frac{\mathrm{15}}{\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{7}}=\mathrm{2}−\mathrm{k}\in\mathbb{Z}\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{7}\mid\mathrm{15} \\ $$$$\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{7}=\underset{−} {+}\mathrm{15}\:\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{8}\:;\mathrm{n}=−\mathrm{22} \\ $$$$\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{7}=\underset{−} {+}\mathrm{5}\Rightarrow\mathrm{n}=−\mathrm{2}\:;\mathrm{n}=−\mathrm{12} \\ $$$$\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{7}=\underset{−} {+}\mathrm{1}\Rightarrow\mathrm{n}=−\mathrm{6};\:\mathrm{n}=−\mathrm{8} \\ $$$$\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{7}=\underset{−} {+}\mathrm{3}\Rightarrow\mathrm{n}=−\mathrm{4}\:;\mathrm{n}=−\mathrm{10} \\ $$
