Question Number 113862 by Aina Samuel Temidayo last updated on 15/Sep/20
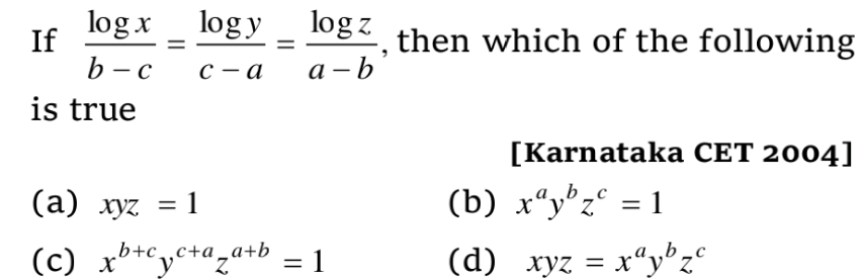
Answered by 1549442205PVT last updated on 16/Sep/20

$$\mathrm{From}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{hypotesis}\:\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{have} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{logx}}{\mathrm{b}−\mathrm{c}}=\frac{\mathrm{logy}}{\mathrm{c}−\mathrm{a}}=\frac{\mathrm{logz}}{\mathrm{a}−\mathrm{b}}=\mathrm{k}.\mathrm{Hence},\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{get} \\ $$$$\begin{cases}{\mathrm{logx}=\mathrm{k}\left(\mathrm{b}−\mathrm{c}\right)}\\{\mathrm{logy}=\mathrm{k}\left(\mathrm{c}−\mathrm{a}\right)}\\{\mathrm{logz}=\mathrm{k}\left(\mathrm{a}−\mathrm{b}\right)}\end{cases} \\ $$$$\mathrm{Adding}\:\mathrm{up}\:\mathrm{three}\:\mathrm{equalities}\:\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{obtain} \\ $$$$\mathrm{logx}+\mathrm{logy}+\mathrm{logz}=\mathrm{k}\left(\mathrm{b}−\mathrm{c}+\mathrm{c}−\mathrm{a}+\mathrm{a}−\mathrm{b}\right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{log}\left(\mathrm{xyz}\right)=\mathrm{k}.\mathrm{0}=\mathrm{0}\Rightarrow\mathrm{xyz}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{Therefore},\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{choose}\:\mathrm{a}\right) \\ $$
