Question Number 115487 by 171 last updated on 26/Sep/20
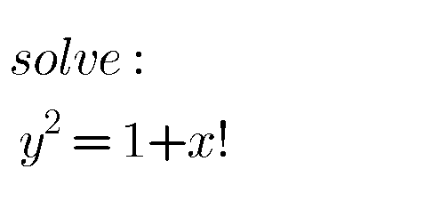
Commented by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 26/Sep/20
![y^2 =1+1 (x=1) y=±(√2) y^2 =1+2⇒y=±(√3) y^2 =1+6⇒y=±(√7) 0≤x<∞ y∈(−∞,−(√2)]∪[(√2),∞)](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q115488.png)
$$\mathrm{y}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{1}\:\left(\mathrm{x}=\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{y}=\pm\sqrt{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{y}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{2}\Rightarrow\mathrm{y}=\pm\sqrt{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{y}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{6}\Rightarrow\mathrm{y}=\pm\sqrt{\mathrm{7}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{0}\leqslant\mathrm{x}<\infty \\ $$$$\mathrm{y}\in\left(−\infty,−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\right]\cup\left[\sqrt{\mathrm{2}},\infty\right) \\ $$
Commented by mr W last updated on 26/Sep/20

$${i}\:{found}\:{following}\:{integer}\:{solutions}: \\ $$$$\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{4}!=\mathrm{25} \\ $$$$\mathrm{11}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{5}!=\mathrm{121} \\ $$$$\mathrm{71}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{7}!=\mathrm{5041} \\ $$$${i}\:{don}'{t}\:{know}\:{if}\:{there}\:{are}\:{more}. \\ $$
Commented by Olaf last updated on 26/Sep/20
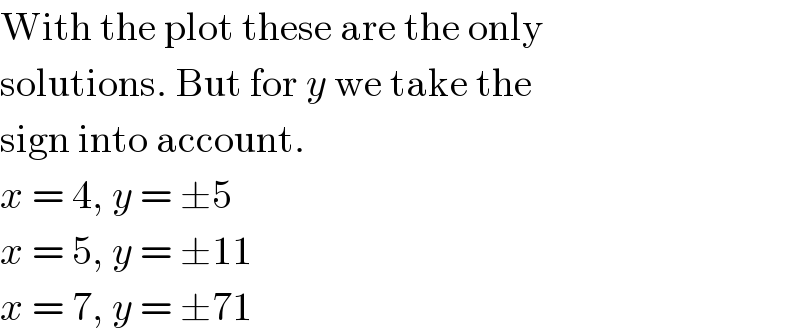
$$\mathrm{With}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{plot}\:\mathrm{these}\:\mathrm{are}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{only} \\ $$$$\mathrm{solutions}.\:\mathrm{But}\:\mathrm{for}\:{y}\:\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{take}\:\mathrm{the} \\ $$$$\mathrm{sign}\:\mathrm{into}\:\mathrm{account}. \\ $$$${x}\:=\:\mathrm{4},\:{y}\:=\:\pm\mathrm{5} \\ $$$${x}\:=\:\mathrm{5},\:{y}\:=\:\pm\mathrm{11} \\ $$$${x}\:=\:\mathrm{7},\:{y}\:=\:\pm\mathrm{71} \\ $$
