Question Number 119052 by shahria14 last updated on 21/Oct/20
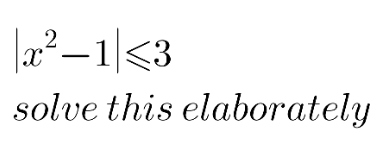
Answered by 1549442205PVT last updated on 22/Oct/20
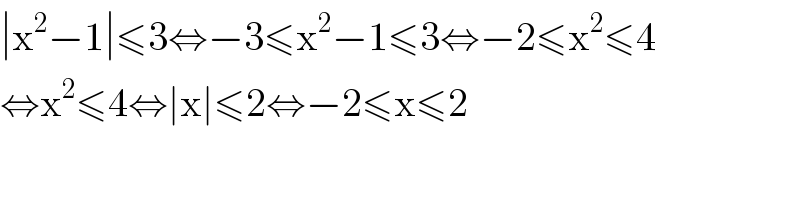
$$\mid\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}\mid\leqslant\mathrm{3}\Leftrightarrow−\mathrm{3}\leqslant\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}\leqslant\mathrm{3}\Leftrightarrow−\mathrm{2}\leqslant\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \leqslant\mathrm{4} \\ $$$$\Leftrightarrow\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \leqslant\mathrm{4}\Leftrightarrow\mid\mathrm{x}\mid\leqslant\mathrm{2}\Leftrightarrow−\mathrm{2}\leqslant\mathrm{x}\leqslant\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by MJS_new last updated on 22/Oct/20
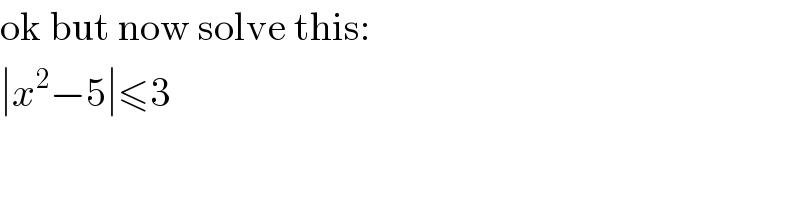
$$\mathrm{ok}\:\mathrm{but}\:\mathrm{now}\:\mathrm{solve}\:\mathrm{this}: \\ $$$$\mid{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{5}\mid\leqslant\mathrm{3} \\ $$
Commented by bemath last updated on 23/Oct/20
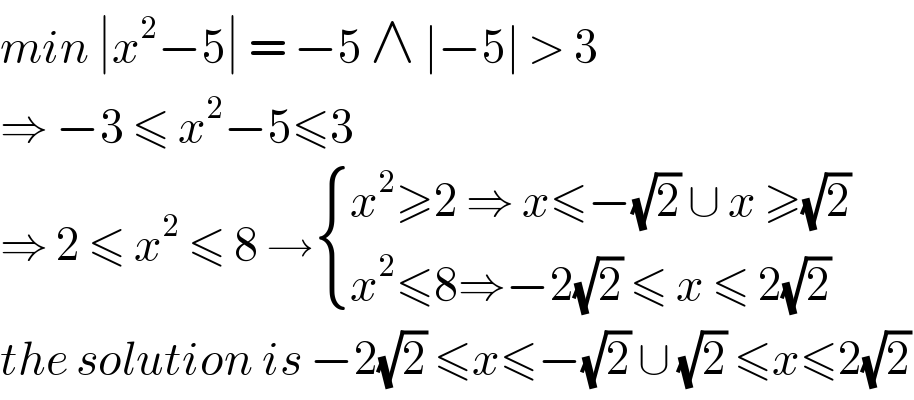
$${min}\:\mid{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{5}\mid\:=\:−\mathrm{5}\:\wedge\:\mid−\mathrm{5}\mid\:>\:\mathrm{3} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:−\mathrm{3}\:\leqslant\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{5}\leqslant\mathrm{3}\: \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\mathrm{2}\:\leqslant\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\leqslant\:\mathrm{8}\:\rightarrow\begin{cases}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \geqslant\mathrm{2}\:\Rightarrow\:{x}\leqslant−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\:\cup\:{x}\:\geqslant\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\\{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \leqslant\mathrm{8}\Rightarrow−\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\:\leqslant\:{x}\:\leqslant\:\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\end{cases} \\ $$$${the}\:{solution}\:{is}\:−\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\:\leqslant{x}\leqslant−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\:\cup\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\:\leqslant{x}\leqslant\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
Answered by MJS_new last updated on 22/Oct/20
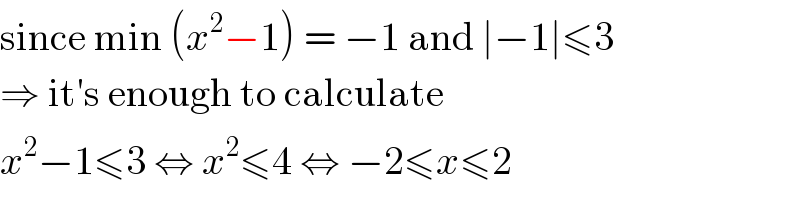
$$\mathrm{since}\:\mathrm{min}\:\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}\right)\:=\:−\mathrm{1}\:\mathrm{and}\:\mid−\mathrm{1}\mid\leqslant\mathrm{3} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\mathrm{it}'\mathrm{s}\:\mathrm{enough}\:\mathrm{to}\:\mathrm{calculate} \\ $$$${x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}\leqslant\mathrm{3}\:\Leftrightarrow\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \leqslant\mathrm{4}\:\Leftrightarrow\:−\mathrm{2}\leqslant{x}\leqslant\mathrm{2} \\ $$
Commented by bemath last updated on 22/Oct/20
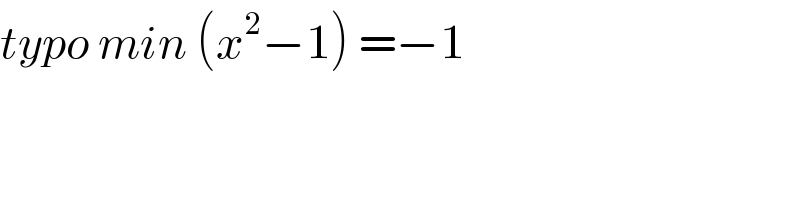
$${typo}\:{min}\:\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}\right)\:=−\mathrm{1} \\ $$
Commented by MJS_new last updated on 22/Oct/20
$$\mathrm{yes}…\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{display}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{my}\:\mathrm{smartphone}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{too} \\ $$$$\mathrm{narrow},\:\mathrm{so}\:\mathrm{sometimes}\:\mathrm{I}\:\mathrm{hit}\:\mathrm{2}\:\mathrm{keys}\:\mathrm{at}\:\mathrm{the} \\ $$$$\mathrm{same}\:\mathrm{time}… \\ $$
Answered by Bird last updated on 21/Oct/20
![∣x^2 −1∣≤3 ⇒∣x^2 −1∣−3≤0 ⇒f(x)≤0 sith f(x)=∣x^2 −1∣−3 x −∞ −1 1 +∞ ∣x^2 −1∣ x^2 −1 0 1−x^2 0 x^2 −1 f(x) x^2 −4 −2−x^2 x^2 −4 if x≤−1 f(x)≤0 ⇒x^2 −4 ≤0 ⇒ −2≤x≤2 ⇒S_1 =[−2,−1] if x∈[−1,1] f(x)≤0 ⇒−2−x^2 ≤0 ⇒ 2+x^2 ≥0 ⇒S_2 =[−1,1] if x≥1 f(x)≤0 ⇒x^2 −4≤0 ⇒ −2≤x≤2 ⇒S_3 =[1,2] ⇒ S=∪S_i =[−2,2]](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q119063.png)
$$\mid{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}\mid\leqslant\mathrm{3}\:\Rightarrow\mid{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}\mid−\mathrm{3}\leqslant\mathrm{0}\: \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{f}\left({x}\right)\leqslant\mathrm{0}\:\:{sith}\:{f}\left({x}\right)=\mid{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}\mid−\mathrm{3} \\ $$$${x}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:−\infty\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:−\mathrm{1}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{1}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:+\infty \\ $$$$\mid{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}\mid\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{0}\:\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\mathrm{0}\:\:\:\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${f}\left({x}\right)\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:−\mathrm{2}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\:\:\:\:\:\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4} \\ $$$${if}\:{x}\leqslant−\mathrm{1}\:\:\:{f}\left({x}\right)\leqslant\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4}\:\leqslant\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$−\mathrm{2}\leqslant{x}\leqslant\mathrm{2}\:\:\Rightarrow{S}_{\mathrm{1}} =\left[−\mathrm{2},−\mathrm{1}\right] \\ $$$${if}\:{x}\in\left[−\mathrm{1},\mathrm{1}\right]\:\:{f}\left({x}\right)\leqslant\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow−\mathrm{2}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \leqslant\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \geqslant\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow{S}_{\mathrm{2}} =\left[−\mathrm{1},\mathrm{1}\right] \\ $$$${if}\:{x}\geqslant\mathrm{1}\:\:{f}\left({x}\right)\leqslant\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4}\leqslant\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$−\mathrm{2}\leqslant{x}\leqslant\mathrm{2}\:\Rightarrow{S}_{\mathrm{3}} =\left[\mathrm{1},\mathrm{2}\right]\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${S}=\cup{S}_{{i}} =\left[−\mathrm{2},\mathrm{2}\right] \\ $$$$ \\ $$
