Question Number 119212 by help last updated on 23/Oct/20

Answered by Olaf last updated on 23/Oct/20
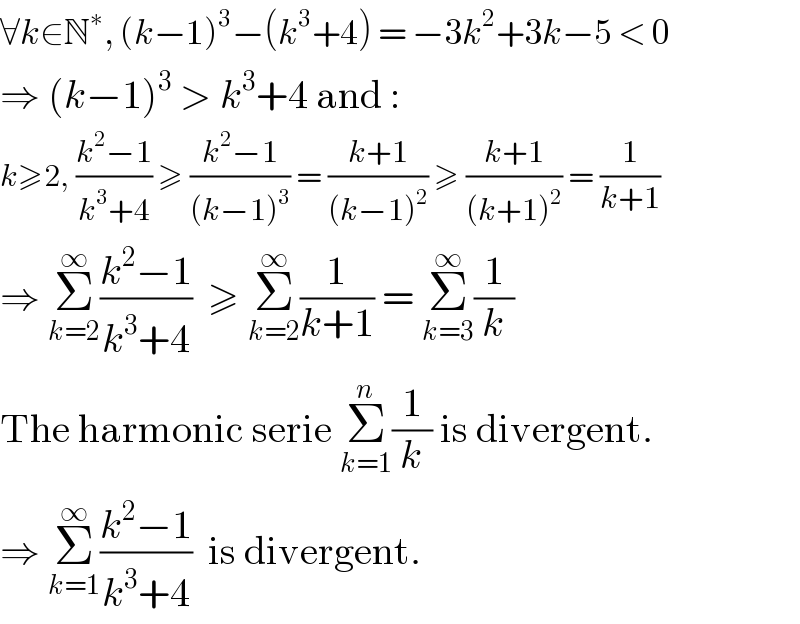
$$\forall{k}\in\mathbb{N}^{\ast} ,\:\left({k}−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{3}} −\left({k}^{\mathrm{3}} +\mathrm{4}\right)\:=\:−\mathrm{3}{k}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{3}{k}−\mathrm{5}\:<\:\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\left({k}−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{3}} \:>\:{k}^{\mathrm{3}} +\mathrm{4}\:\mathrm{and}\:: \\ $$$${k}\geqslant\mathrm{2},\:\frac{{k}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}}{{k}^{\mathrm{3}} +\mathrm{4}}\:\geqslant\:\frac{{k}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}}{\left({k}−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{3}} }\:=\:\frac{{k}+\mathrm{1}}{\left({k}−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\geqslant\:\frac{{k}+\mathrm{1}}{\left({k}+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{k}+\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\underset{{k}=\mathrm{2}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{{k}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}}{{k}^{\mathrm{3}} +\mathrm{4}}\:\:\geqslant\:\underset{{k}=\mathrm{2}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{k}+\mathrm{1}}\:=\:\underset{{k}=\mathrm{3}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{k}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{The}\:\mathrm{harmonic}\:\mathrm{serie}\:\underset{{k}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{{n}} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{k}}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{divergent}. \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\underset{{k}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{{k}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}}{{k}^{\mathrm{3}} +\mathrm{4}}\:\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{divergent}. \\ $$
