Question Number 122109 by sdfg last updated on 14/Nov/20

Answered by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 14/Nov/20
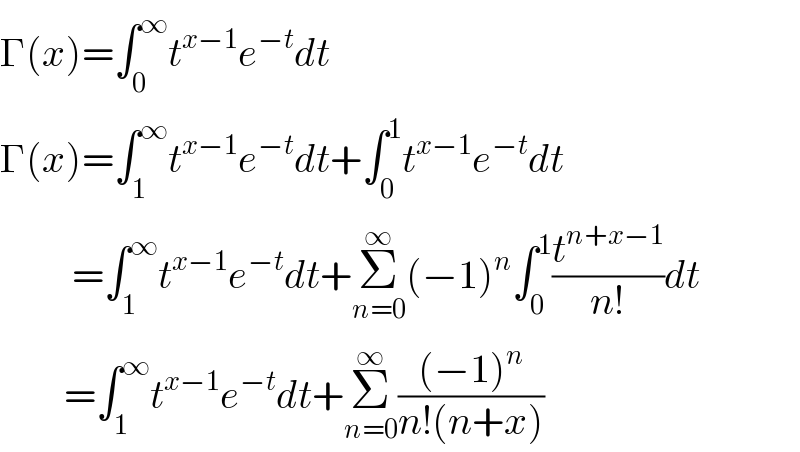
$$\Gamma\left({x}\right)=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} {t}^{{x}−\mathrm{1}} {e}^{−{t}} {dt} \\ $$$$\Gamma\left({x}\right)=\int_{\mathrm{1}} ^{\infty} {t}^{{x}−\mathrm{1}} {e}^{−{t}} {dt}+\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} {t}^{{x}−\mathrm{1}} {e}^{−{t}} {dt} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:=\int_{\mathrm{1}} ^{\infty} {t}^{{x}−\mathrm{1}} {e}^{−{t}} {dt}+\underset{{n}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} \int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \frac{{t}^{{n}+{x}−\mathrm{1}} }{{n}!}{dt} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:=\int_{\mathrm{1}} ^{\infty} {t}^{{x}−\mathrm{1}} {e}^{−{t}} {dt}+\underset{{n}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} }{{n}!\left({n}+{x}\right)} \\ $$
Answered by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 14/Nov/20
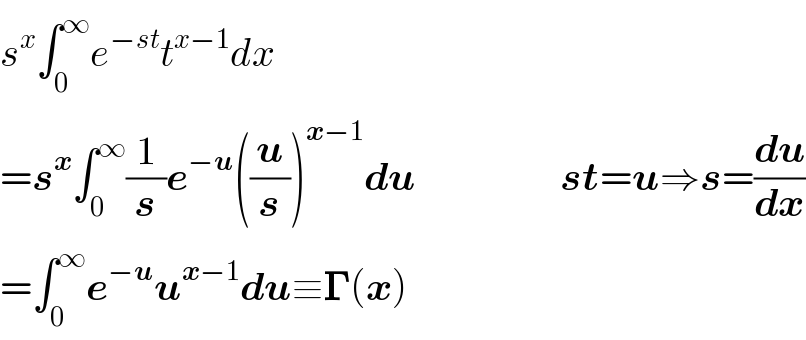
$${s}^{{x}} \int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} {e}^{−{st}} {t}^{{x}−\mathrm{1}} {dx} \\ $$$$=\boldsymbol{{s}}^{\boldsymbol{{x}}} \int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \frac{\mathrm{1}}{\boldsymbol{{s}}}\boldsymbol{{e}}^{−\boldsymbol{{u}}} \left(\frac{\boldsymbol{{u}}}{\boldsymbol{{s}}}\right)^{\boldsymbol{{x}}−\mathrm{1}} \boldsymbol{{du}}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\boldsymbol{{st}}=\boldsymbol{{u}}\Rightarrow\boldsymbol{{s}}=\frac{\boldsymbol{{du}}}{\boldsymbol{{dx}}} \\ $$$$=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \boldsymbol{{e}}^{−\boldsymbol{{u}}} \boldsymbol{{u}}^{\boldsymbol{{x}}−\mathrm{1}} \boldsymbol{{du}}\equiv\boldsymbol{\Gamma}\left(\boldsymbol{{x}}\right) \\ $$
