Question Number 123575 by bramlexs22 last updated on 26/Nov/20

Commented by liberty last updated on 26/Nov/20
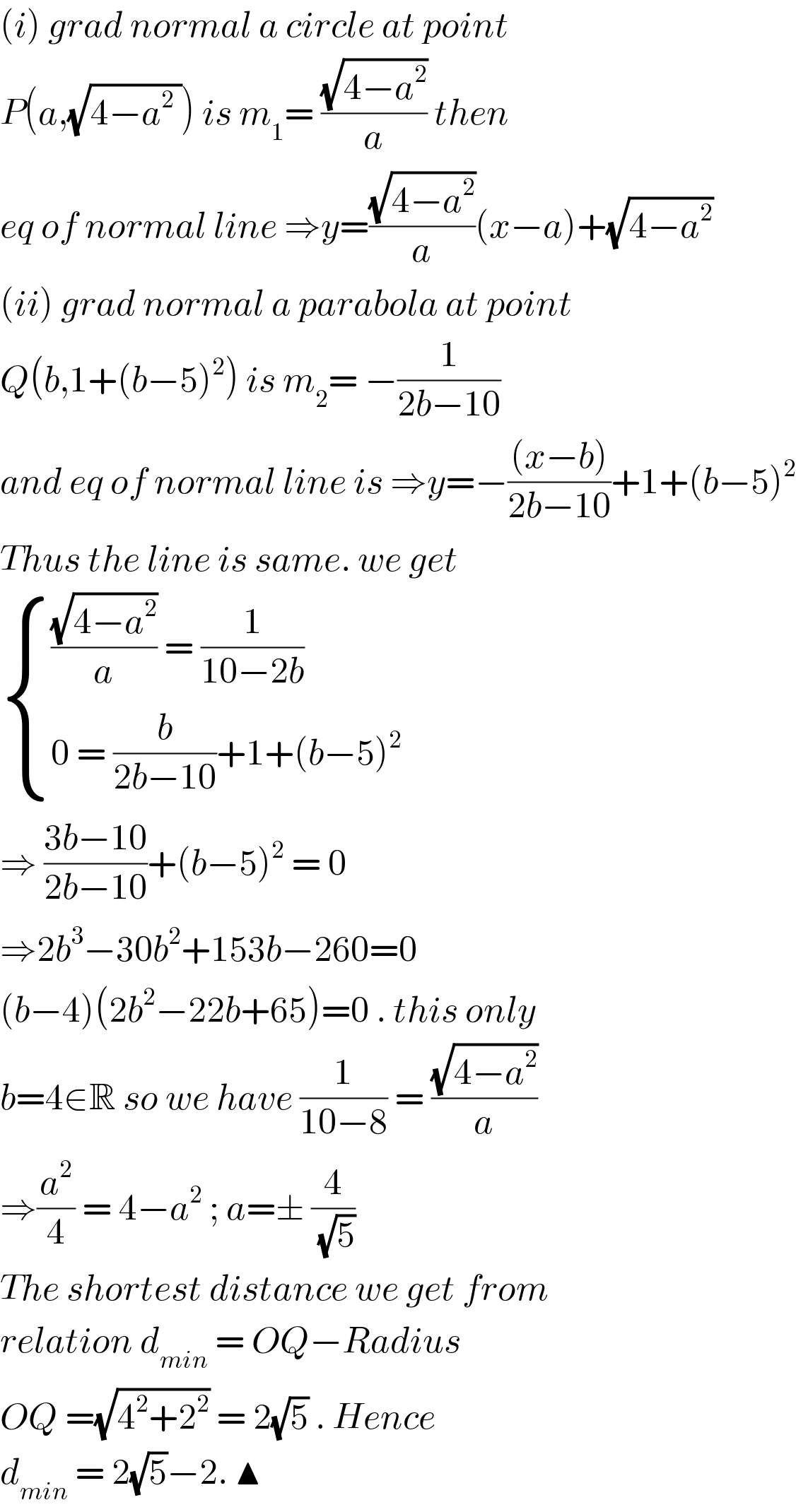
$$\left({i}\right)\:{grad}\:{normal}\:{a}\:{circle}\:{at}\:{point}\: \\ $$$${P}\left({a},\sqrt{\mathrm{4}−{a}^{\mathrm{2}} \:}\right)\:{is}\:{m}_{\mathrm{1}} =\:\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{4}−{a}^{\mathrm{2}} }}{{a}}\:{then}\: \\ $$$${eq}\:{of}\:{normal}\:{line}\:\Rightarrow{y}=\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{4}−{a}^{\mathrm{2}} }}{{a}}\left({x}−{a}\right)+\sqrt{\mathrm{4}−{a}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$\left({ii}\right)\:{grad}\:{normal}\:{a}\:{parabola}\:{at}\:{point} \\ $$$${Q}\left({b},\mathrm{1}+\left({b}−\mathrm{5}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\:{is}\:{m}_{\mathrm{2}} =\:−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{b}−\mathrm{10}} \\ $$$${and}\:{eq}\:{of}\:{normal}\:{line}\:{is}\:\Rightarrow{y}=−\frac{\left({x}−{b}\right)}{\mathrm{2}{b}−\mathrm{10}}+\mathrm{1}+\left({b}−\mathrm{5}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${Thus}\:{the}\:{line}\:{is}\:{same}.\:{we}\:{get}\: \\ $$$$\begin{cases}{\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{4}−{a}^{\mathrm{2}} }}{{a}}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{10}−\mathrm{2}{b}}}\\{\mathrm{0}\:=\:\frac{{b}}{\mathrm{2}{b}−\mathrm{10}}+\mathrm{1}+\left({b}−\mathrm{5}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }\end{cases} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\frac{\mathrm{3}{b}−\mathrm{10}}{\mathrm{2}{b}−\mathrm{10}}+\left({b}−\mathrm{5}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \:=\:\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{2}{b}^{\mathrm{3}} −\mathrm{30}{b}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{153}{b}−\mathrm{260}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\left({b}−\mathrm{4}\right)\left(\mathrm{2}{b}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{22}{b}+\mathrm{65}\right)=\mathrm{0}\:.\:{this}\:{only} \\ $$$${b}=\mathrm{4}\in\mathbb{R}\:{so}\:{we}\:{have}\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{10}−\mathrm{8}}\:=\:\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{4}−{a}^{\mathrm{2}} }}{{a}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\frac{{a}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{4}}\:=\:\mathrm{4}−{a}^{\mathrm{2}} \:;\:{a}=\pm\:\frac{\mathrm{4}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}\: \\ $$$${The}\:{shortest}\:{distance}\:{we}\:{get}\:{from}\: \\ $$$${relation}\:{d}_{{min}} \:=\:{OQ}−{Radius} \\ $$$${OQ}\:=\sqrt{\mathrm{4}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:=\:\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}\:.\:{Hence}\: \\ $$$${d}_{{min}} \:=\:\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}−\mathrm{2}.\:\blacktriangle \\ $$
Answered by MJS_new last updated on 26/Nov/20
![we need the point of the parabola with the shortest distance to the center of the circle. the center of the circle is ((0),(0) ) , its radius is 2 the points of the parabola are ((x),(((x−5)^2 +1)) ) ⇒ the square of the distance to ((0),(0) ) is (x)^2 +((x−5)^2 +1)^2 = =x^4 −20x^3 +153x^2 −520x+676 (d/dx)[x^4 −20x^3 +153x^2 −520x+676]=0 4x^3 −60x^2 +306x−520=0 ⇒ x=4 ⇒ distance is 2(√5) to the origin and 2(√5)−2 to the line of the circle answer 2(√5)−2](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q123579.png)
$$\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{need}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{point}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{parabola}\:\mathrm{with}\:\mathrm{the} \\ $$$$\mathrm{shortest}\:\mathrm{distance}\:\mathrm{to}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{center}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{circle}. \\ $$$$\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{center}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{circle}\:\mathrm{is}\:\begin{pmatrix}{\mathrm{0}}\\{\mathrm{0}}\end{pmatrix}\:,\:\mathrm{its}\:\mathrm{radius}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{points}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{parabola}\:\mathrm{are}\:\begin{pmatrix}{{x}}\\{\left({x}−\mathrm{5}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}\end{pmatrix} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{square}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{distance}\:\mathrm{to}\:\begin{pmatrix}{\mathrm{0}}\\{\mathrm{0}}\end{pmatrix}\:\mathrm{is} \\ $$$$\left({x}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\left(\left({x}−\mathrm{5}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} = \\ $$$$={x}^{\mathrm{4}} −\mathrm{20}{x}^{\mathrm{3}} +\mathrm{153}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{520}{x}+\mathrm{676} \\ $$$$\frac{{d}}{{dx}}\left[{x}^{\mathrm{4}} −\mathrm{20}{x}^{\mathrm{3}} +\mathrm{153}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{520}{x}+\mathrm{676}\right]=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\mathrm{4}{x}^{\mathrm{3}} −\mathrm{60}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{306}{x}−\mathrm{520}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:{x}=\mathrm{4} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\mathrm{distance}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}\:\mathrm{to}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{origin}\:\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}−\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\mathrm{to}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{line}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{circle} \\ $$$$\mathrm{answer}\:\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}−\mathrm{2} \\ $$
