Question Number 147103 by mnjuly1970 last updated on 18/Jul/21
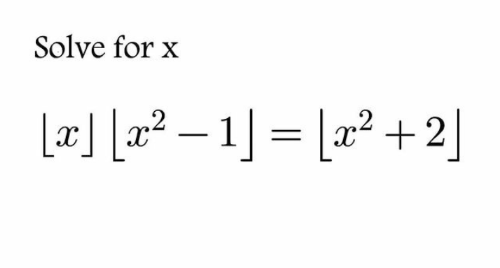
Answered by mr W last updated on 18/Jul/21
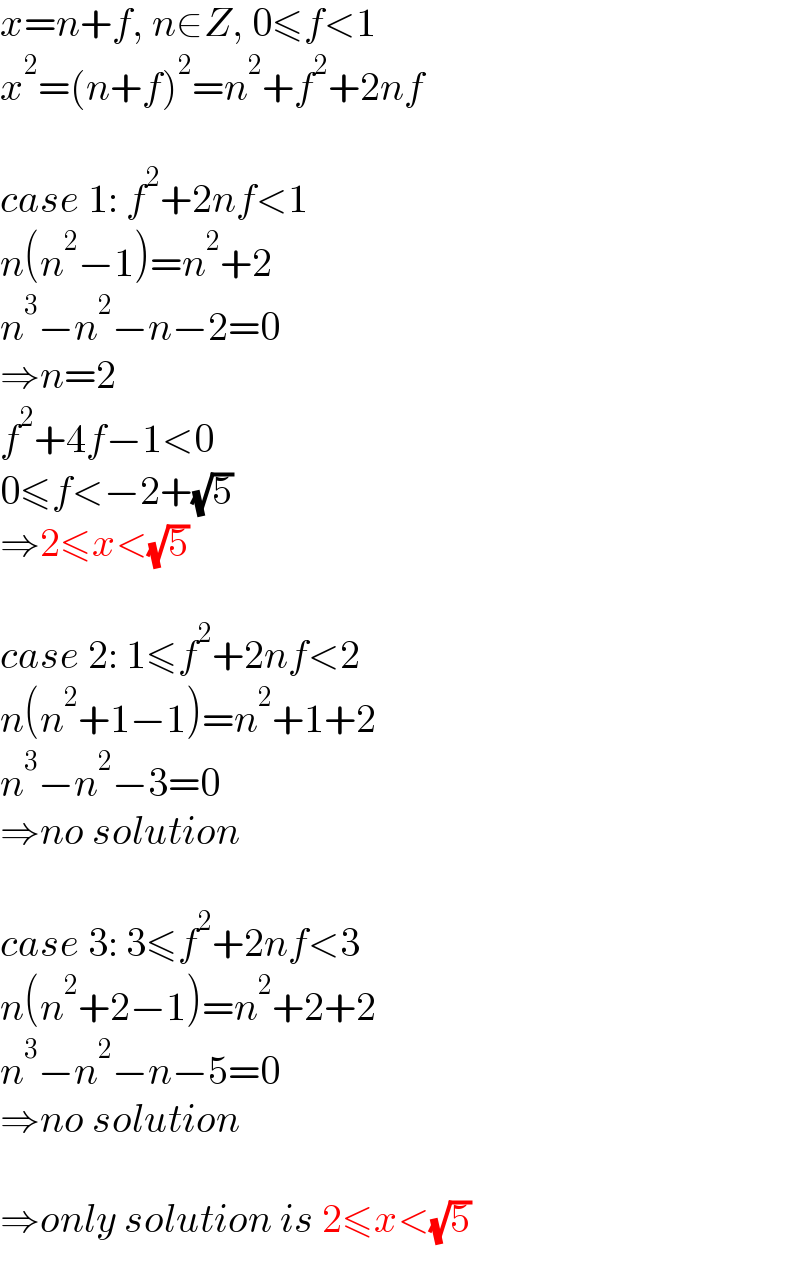
$${x}={n}+{f},\:{n}\in{Z},\:\mathrm{0}\leqslant{f}<\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${x}^{\mathrm{2}} =\left({n}+{f}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} ={n}^{\mathrm{2}} +{f}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{nf} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${case}\:\mathrm{1}:\:{f}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{nf}<\mathrm{1}\: \\ $$$${n}\left({n}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}\right)={n}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2} \\ $$$${n}^{\mathrm{3}} −{n}^{\mathrm{2}} −{n}−\mathrm{2}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{n}=\mathrm{2} \\ $$$${f}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{4}{f}−\mathrm{1}<\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\mathrm{0}\leqslant{f}<−\mathrm{2}+\sqrt{\mathrm{5}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{2}\leqslant{x}<\sqrt{\mathrm{5}} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${case}\:\mathrm{2}:\:\mathrm{1}\leqslant{f}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{nf}<\mathrm{2} \\ $$$${n}\left({n}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{1}\right)={n}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{2} \\ $$$${n}^{\mathrm{3}} −{n}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{3}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{no}\:{solution} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${case}\:\mathrm{3}:\:\mathrm{3}\leqslant{f}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{nf}<\mathrm{3} \\ $$$${n}\left({n}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}−\mathrm{1}\right)={n}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}+\mathrm{2} \\ $$$${n}^{\mathrm{3}} −{n}^{\mathrm{2}} −{n}−\mathrm{5}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{no}\:{solution} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{only}\:{solution}\:{is}\:\mathrm{2}\leqslant{x}<\sqrt{\mathrm{5}} \\ $$
Commented by mnjuly1970 last updated on 18/Jul/21
$$\:\:\:\:\:\:{thx}\:{sir}\:\mathrm{W}\:..{grateful}… \\ $$
Answered by Kamel last updated on 18/Jul/21
=[x^2 ]−1+3⇔([x]−1)([x^2 ]−1)=3 3∈P⇔(1): { (([x]−1=±3)),(([x^2 ]−1=±1)) :}∨(2): { (([x]−1=±1)),(([x^2 ]−1=±3)) :} (1)⇔[x]=4∧[x^2 ]=2⇔4≤x<5 ∧ (√2)≤x<(√3) no solutions. (2)⇔[x]=2∧[x^2 ]=4⇔2≤x<(√5) ∧ 2≤x<3 ⇒2≤x<(√5). ∴ S={x∈R/2≤x<(√5)} No solutions for −1 and −3](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q147112.png)
$$\left[{x}\right]\left(\left[{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right]−\mathrm{1}\right)=\left[{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right]−\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{3}\Leftrightarrow\left(\left[{x}\right]−\mathrm{1}\right)\left(\left[{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right]−\mathrm{1}\right)=\mathrm{3} \\ $$$$\mathrm{3}\in\mathbb{P}\Leftrightarrow\left(\mathrm{1}\right):\begin{cases}{\left[{x}\right]−\mathrm{1}=\pm\mathrm{3}}\\{\left[{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right]−\mathrm{1}=\pm\mathrm{1}}\end{cases}\vee\left(\mathrm{2}\right):\begin{cases}{\left[{x}\right]−\mathrm{1}=\pm\mathrm{1}}\\{\left[{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right]−\mathrm{1}=\pm\mathrm{3}}\end{cases} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{1}\right)\Leftrightarrow\left[{x}\right]=\mathrm{4}\wedge\left[{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right]=\mathrm{2}\Leftrightarrow\mathrm{4}\leqslant{x}<\mathrm{5}\:\wedge\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\leqslant{x}<\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}\:{no}\:{solutions}. \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\Leftrightarrow\left[{x}\right]=\mathrm{2}\wedge\left[{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right]=\mathrm{4}\Leftrightarrow\mathrm{2}\leqslant{x}<\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}\:\wedge\:\mathrm{2}\leqslant{x}<\mathrm{3}\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{2}\leqslant{x}<\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}. \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\therefore\:\:{S}=\left\{{x}\in\mathbb{R}/\mathrm{2}\leqslant{x}<\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}\right\} \\ $$$${No}\:{solutions}\:{for}\:−\mathrm{1}\:{and}\:−\mathrm{3} \\ $$
