Question Number 148155 by Khalmohmmad last updated on 25/Jul/21

Answered by Rasheed.Sindhi last updated on 26/Jul/21
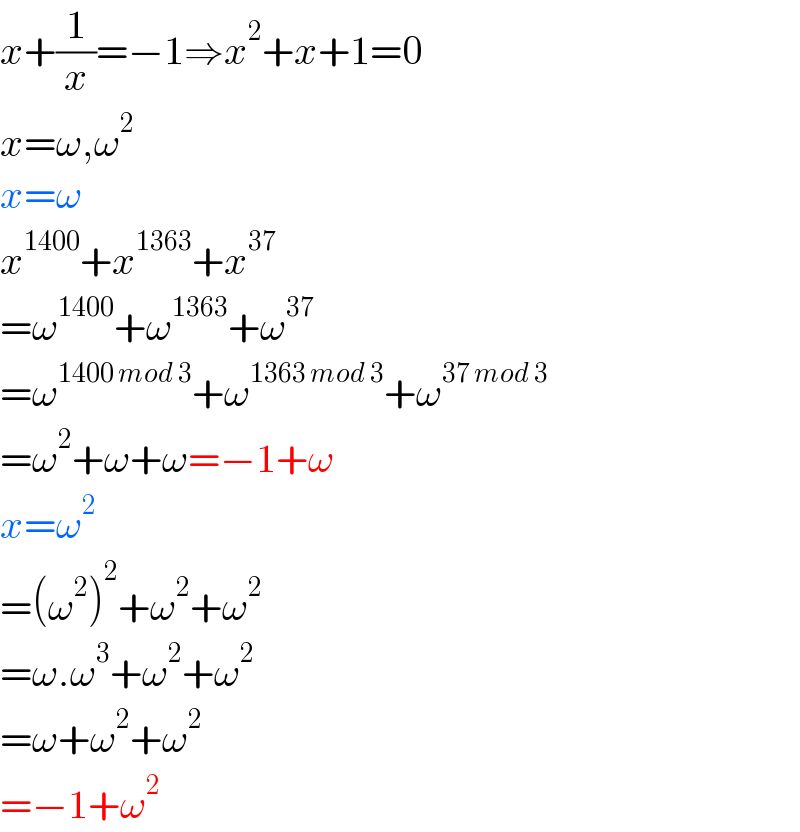
$${x}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}=−\mathrm{1}\Rightarrow{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{x}+\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${x}=\omega,\omega^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${x}=\omega \\ $$$${x}^{\mathrm{1400}} +{x}^{\mathrm{1363}} +{x}^{\mathrm{37}} \\ $$$$=\omega^{\mathrm{1400}} +\omega^{\mathrm{1363}} +\omega^{\mathrm{37}} \\ $$$$=\omega^{\mathrm{1400}\:{mod}\:\mathrm{3}} +\omega^{\mathrm{1363}\:{mod}\:\mathrm{3}} +\omega^{\mathrm{37}\:{mod}\:\mathrm{3}} \\ $$$$=\omega^{\mathrm{2}} +\omega+\omega=−\mathrm{1}+\omega \\ $$$${x}=\omega^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$=\left(\omega^{\mathrm{2}} \right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\omega^{\mathrm{2}} +\omega^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$=\omega.\omega^{\mathrm{3}} +\omega^{\mathrm{2}} +\omega^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$=\omega+\omega^{\mathrm{2}} +\omega^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$=−\mathrm{1}+\omega^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
