Question Number 149268 by Samimsultani last updated on 04/Aug/21

Answered by dkenechukwu04 last updated on 04/Aug/21

$$\mathrm{Let}\:\mathrm{2}+\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}+\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}+\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}+…}}}={x} \\ $$$$\mathrm{5}+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{{x}}=\mathrm{5}+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{2}+\frac{\mathrm{3}}{{x}}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{5}+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{{x}}=\mathrm{5}+\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}}{\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{3}} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{5}{x}+\mathrm{2}}{{x}}=\frac{\mathrm{12}{x}+\mathrm{15}}{\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{3}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{10}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{19}{x}+\mathrm{6}=\mathrm{12}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{15}{x} \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4}{x}−\mathrm{6}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{3}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\left({x}−\mathrm{3}\right)\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\therefore{x}=\mathrm{3};\:{x}=-\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\mathrm{when}\:{x}=\mathrm{3} \\ $$$$\mathrm{5}+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{{x}}=\mathrm{5}+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:=\mathrm{5}.\mathrm{67} \\ $$$$\mathrm{when}\:{x}=-\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\mathrm{5}+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{{x}}=\mathrm{5}+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{-\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:=\mathrm{3} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Answered by nimnim last updated on 04/Aug/21
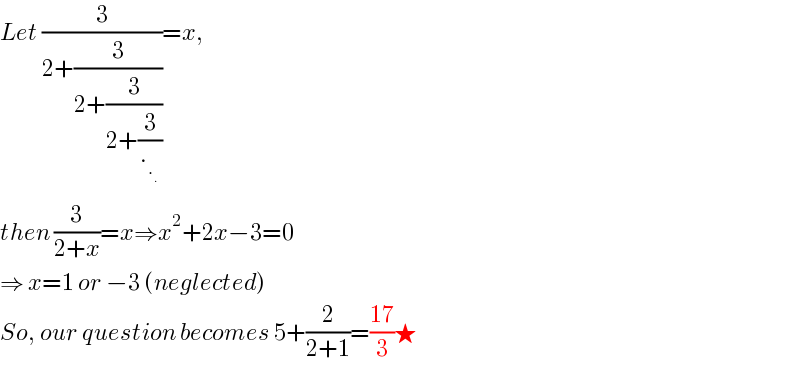
$${Let}\:\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}+\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}+\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}+\frac{\mathrm{3}}{._{._{.} } }}}}={x},\: \\ $$$${then}\:\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}+{x}}={x}\Rightarrow{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{3}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:{x}=\mathrm{1}\:{or}\:−\mathrm{3}\:\left({neglected}\right) \\ $$$${So},\:{our}\:{question}\:{becomes}\:\mathrm{5}+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{2}+\mathrm{1}}=\frac{\mathrm{17}}{\mathrm{3}}\bigstar \\ $$
Answered by john_santu last updated on 04/Aug/21

$$\mathrm{let}\:\mathrm{2}+\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}+\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}+\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\vdots}}}\:=\:\mathrm{x} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{x}\:=\:\mathrm{2}+\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{x}}\:;\:\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2x}−\mathrm{3}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\left(\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{3}\right)\left(\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{1}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{x}\:=\:\mathrm{3}\:\mathrm{or}\:\mathrm{x}=−\mathrm{1}\left(\mathrm{rejected}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{then}\:\mathrm{5}\:+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{x}}\:=\:\mathrm{5}+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}=\frac{\mathrm{17}}{\mathrm{3}}\: \\ $$
Answered by Ar Brandon last updated on 04/Aug/21
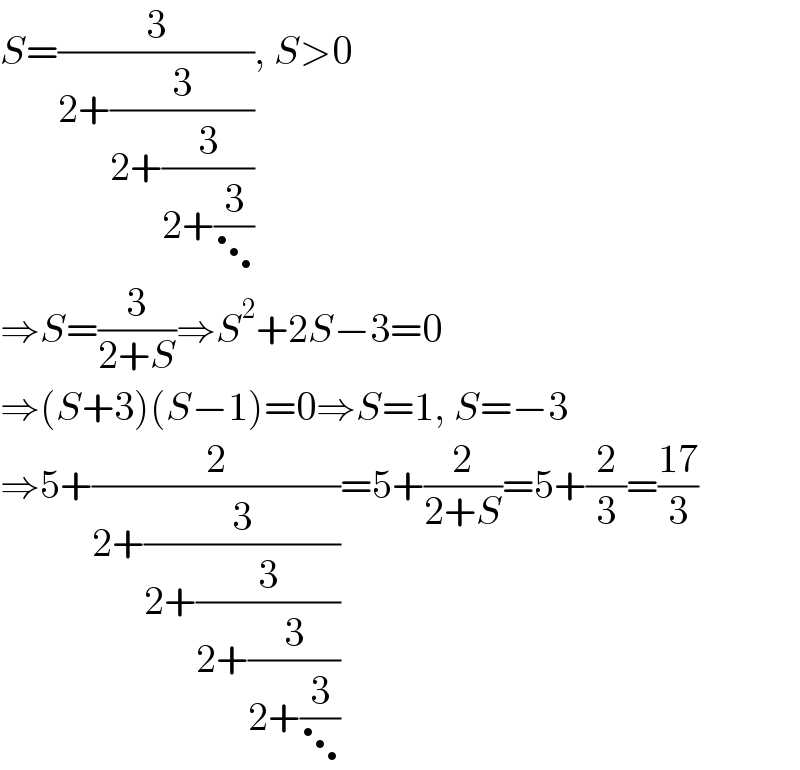
$${S}=\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}+\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}+\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}+\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\ddots}}}},\:{S}>\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{S}=\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}+{S}}\Rightarrow{S}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{S}−\mathrm{3}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\left({S}+\mathrm{3}\right)\left({S}−\mathrm{1}\right)=\mathrm{0}\Rightarrow{S}=\mathrm{1},\:{S}=−\mathrm{3} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{5}+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{2}+\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}+\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}+\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}+\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\ddots}}}}}=\mathrm{5}+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{2}+{S}}=\mathrm{5}+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}=\frac{\mathrm{17}}{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$
