Question Number 150596 by mr W last updated on 14/Aug/21
Commented by mr W last updated on 14/Aug/21

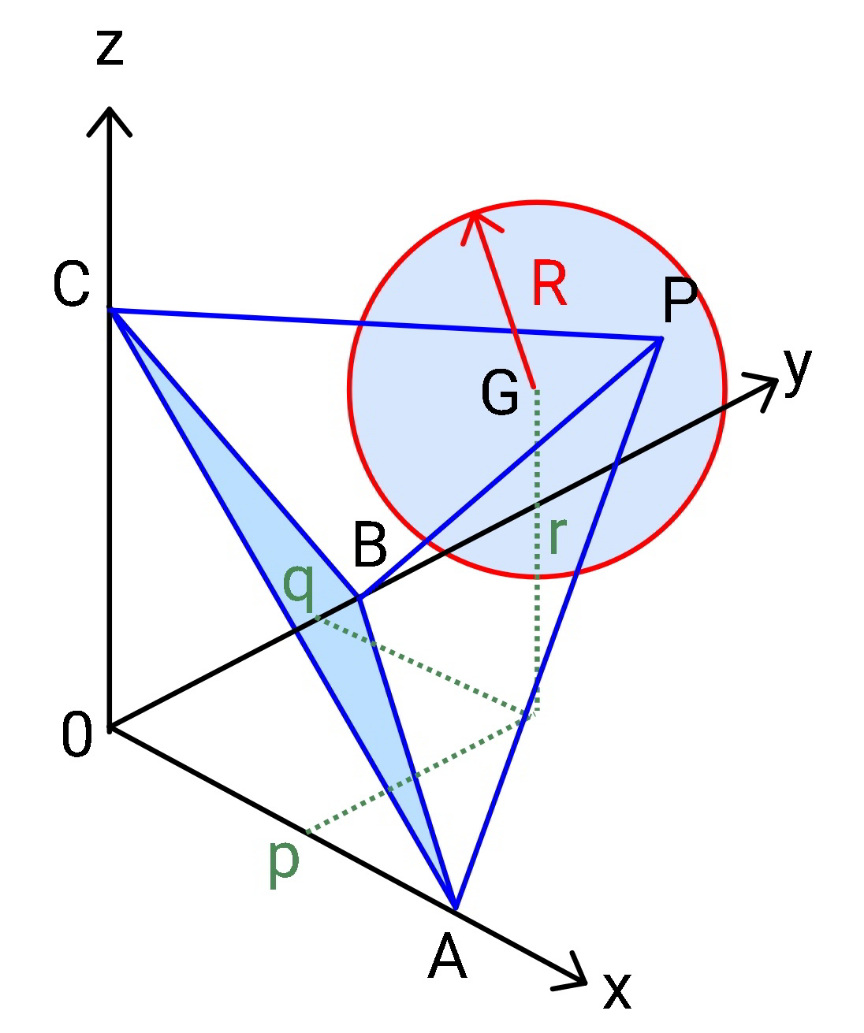
$${a}\:{more}\:{challenging}\:{case}:\:\mathrm{3}{D}\:{case} \\ $$$${three}\:{vertex}\:{of}\:{a}\:{tetrahedron}\:{lie}\:{on} \\ $$$${the}\:{coordinate}\:{axes}.\:{the}\:{fourth}\:{one} \\ $$$${lies}\:{on}\:{the}\:{sphere}\:{with}\:{radius}\:{R}\:{and} \\ $$$${center}\:{at}\:{G}\left({p},{q},{r}\right). \\ $$$${find}\:{the}\:{minimum}\:{and}\:{maximum} \\ $$$${volume}\:{of}\:{the}\:{tetrahedron}. \\ $$
Answered by ajfour last updated on 14/Aug/21
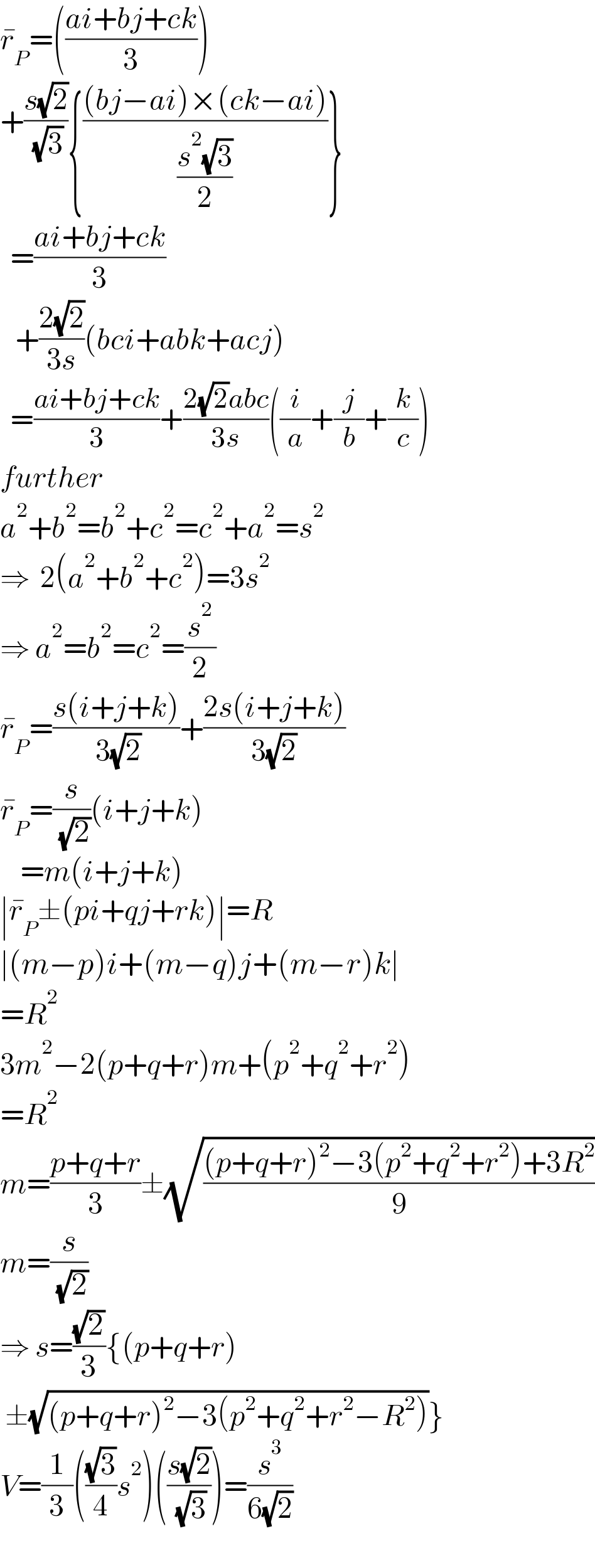
$$\bar {{r}}_{{P}} =\left(\frac{{ai}+{bj}+{ck}}{\mathrm{3}}\right) \\ $$$$+\frac{{s}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}\left\{\frac{\left({bj}−{ai}\right)×\left({ck}−{ai}\right)}{\frac{{s}^{\mathrm{2}} \sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}{\mathrm{2}}}\right\} \\ $$$$\:\:=\frac{{ai}+{bj}+{ck}}{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:+\frac{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}{\mathrm{3}{s}}\left({bci}+{abk}+{acj}\right) \\ $$$$\:\:=\frac{{ai}+{bj}+{ck}}{\mathrm{3}}+\frac{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}{abc}}{\mathrm{3}{s}}\left(\frac{{i}}{{a}}+\frac{{j}}{{b}}+\frac{{k}}{{c}}\right) \\ $$$${further} \\ $$$${a}^{\mathrm{2}} +{b}^{\mathrm{2}} ={b}^{\mathrm{2}} +{c}^{\mathrm{2}} ={c}^{\mathrm{2}} +{a}^{\mathrm{2}} ={s}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\:\mathrm{2}\left({a}^{\mathrm{2}} +{b}^{\mathrm{2}} +{c}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)=\mathrm{3}{s}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:{a}^{\mathrm{2}} ={b}^{\mathrm{2}} ={c}^{\mathrm{2}} =\frac{{s}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\bar {{r}}_{{P}} =\frac{{s}\left({i}+{j}+{k}\right)}{\:\mathrm{3}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}+\frac{\mathrm{2}{s}\left({i}+{j}+{k}\right)}{\mathrm{3}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}} \\ $$$$\bar {{r}}_{{P}} =\frac{{s}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\left({i}+{j}+{k}\right) \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:={m}\left({i}+{j}+{k}\right) \\ $$$$\mid\bar {{r}}_{{P}} \pm\left({pi}+{qj}+{rk}\right)\mid={R} \\ $$$$\mid\left({m}−{p}\right){i}+\left({m}−{q}\right){j}+\left({m}−{r}\right){k}\mid \\ $$$$={R}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{3}{m}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}\left({p}+{q}+{r}\right){m}+\left({p}^{\mathrm{2}} +{q}^{\mathrm{2}} +{r}^{\mathrm{2}} \right) \\ $$$$={R}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${m}=\frac{{p}+{q}+{r}}{\mathrm{3}}\pm\sqrt{\frac{\left({p}+{q}+{r}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{3}\left({p}^{\mathrm{2}} +{q}^{\mathrm{2}} +{r}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)+\mathrm{3}{R}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{9}}} \\ $$$${m}=\frac{{s}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:{s}=\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}{\mathrm{3}}\left\{\left({p}+{q}+{r}\right)\right. \\ $$$$\left.\:\pm\sqrt{\left({p}+{q}+{r}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{3}\left({p}^{\mathrm{2}} +{q}^{\mathrm{2}} +{r}^{\mathrm{2}} −{R}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)}\right\} \\ $$$${V}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\left(\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}{\mathrm{4}}{s}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\left(\frac{{s}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}\right)=\frac{{s}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{6}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Answered by mr W last updated on 14/Aug/21

$${say}\:{edge}\:{length}\:{of}\:{tetrahedron}\:{is}\:{s}. \\ $$$$\Delta{ABC}\:{is}\:{an}\:{equilateral}\:{triangle}\:{with} \\ $$$${side}\:{length}\:{s}. \\ $$$${A}\left({a},\mathrm{0},\mathrm{0}\right) \\ $$$${B}\left(\mathrm{0},{b},\mathrm{0}\right) \\ $$$${C}\left(\mathrm{0},\mathrm{0},{c}\right) \\ $$$${since}\:{AB}={BC}={CA}={s}, \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{a}={b}={c}=\frac{{s}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}} \\ $$$${eqn}.\:{of}\:{plane}\:{ABC}\:{is} \\ $$$${x}+{y}+{z}=\frac{{s}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}} \\ $$$${the}\:{fourth}\:{vertex}\:{lies}\:{on}\:{the}\:{line} \\ $$$${x}={y}={z}={k},\:{say} \\ $$$${since}\:{it}\:{lies}\:{also}\:{on}\:{the}\:{sphere} \\ $$$$\left({x}−{p}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\left({y}−{q}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\left({z}−{r}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} ={R}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\left({k}−{p}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\left({k}−{q}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\left({k}−{r}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} ={R}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{3}{k}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}\left({p}+{q}+{r}\right){k}+{p}^{\mathrm{2}} +{q}^{\mathrm{2}} +{r}^{\mathrm{2}} −{R}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{k}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\left\{{p}+{q}+{r}\pm\sqrt{\left({p}+{q}+{r}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{3}\left({p}^{\mathrm{2}} +{q}^{\mathrm{2}} +{r}^{\mathrm{2}} −{R}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)}\right\} \\ $$$${solution}\:{exists}\:{only}\:{if}\: \\ $$$$\left({p}+{q}+{r}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{3}\left({p}^{\mathrm{2}} +{q}^{\mathrm{2}} +{r}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\geqslant\mathrm{3}{R}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${the}\:{distance}\:{from}\:{intersection}\:{point} \\ $$$${P}\left({k},{k},{k}\right)\:{to}\:{the}\:{plane}\:{ABC}\:{is}\:{the} \\ $$$${heigth}\:{of}\:{the}\:{tetrahedron},\:{which}\:{is} \\ $$$$\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{6}}{s}}{\mathrm{3}}. \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{3}{k}−\frac{{s}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}=\pm\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{6}}{s}}{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{3}{k}=\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\left(\mathrm{1}\pm\mathrm{2}\right){s}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{s}=\frac{\mathrm{3}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}{k}}{\mathrm{1}\pm\mathrm{2}}>\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{s}=\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}{\mathrm{1}\pm\mathrm{2}}\left\{{p}+{q}+{r}\pm\sqrt{\left({p}+{q}+{r}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{3}\left({p}^{\mathrm{2}} +{q}^{\mathrm{2}} +{r}^{\mathrm{2}} −{R}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)}\right\} \\ $$$${the}\:{volume}\:{of}\:{tetrahedron}\:{is} \\ $$$${V}=\frac{{s}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{6}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}} \\ $$$${in}\:{general}\:{there}\:{exist}\:\mathrm{2}\:{tetrahedrons}. \\ $$
