Question Number 154458 by mathdanisur last updated on 18/Sep/21

Answered by ARUNG_Brandon_MBU last updated on 18/Sep/21
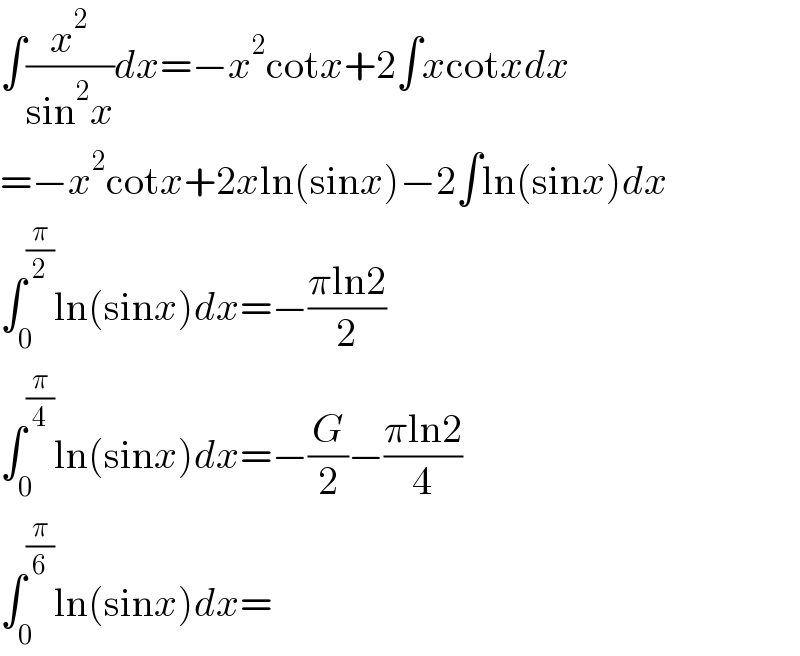
$$\int\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} {x}}{dx}=−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{cot}{x}+\mathrm{2}\int{x}\mathrm{cot}{xdx} \\ $$$$=−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{cot}{x}+\mathrm{2}{x}\mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{sin}{x}\right)−\mathrm{2}\int\mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{sin}{x}\right){dx} \\ $$$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{sin}{x}\right){dx}=−\frac{\pi\mathrm{ln2}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}} \mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{sin}{x}\right){dx}=−\frac{{G}}{\mathrm{2}}−\frac{\pi\mathrm{ln2}}{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{6}}} \mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{sin}{x}\right){dx}= \\ $$
