Question Number 155450 by SANOGO last updated on 30/Sep/21
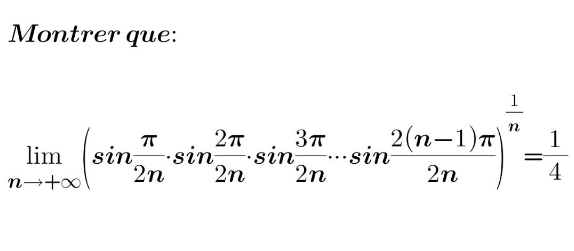
Answered by Kamel last updated on 30/Sep/21
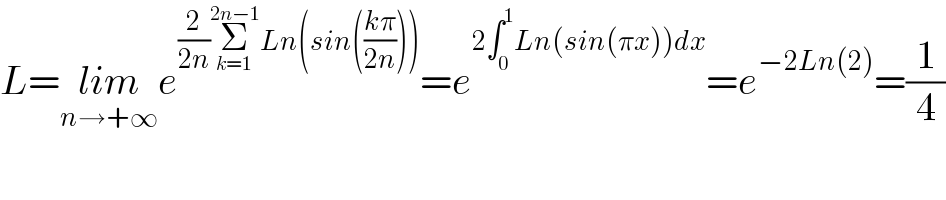
$${L}=\underset{{n}\rightarrow+\infty} {{lim}e}^{\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{2}{n}}\underset{{k}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\mathrm{2}{n}−\mathrm{1}} {\sum}}{Ln}\left({sin}\left(\frac{{k}\pi}{\mathrm{2}{n}}\right)\right)} ={e}^{\mathrm{2}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} {Ln}\left({sin}\left(\pi{x}\right)\right){dx}} ={e}^{−\mathrm{2}{Ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)} =\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$
Commented by SANOGO last updated on 01/Oct/21

$${merci}\:{bien} \\ $$
Answered by Ar Brandon last updated on 30/Sep/21
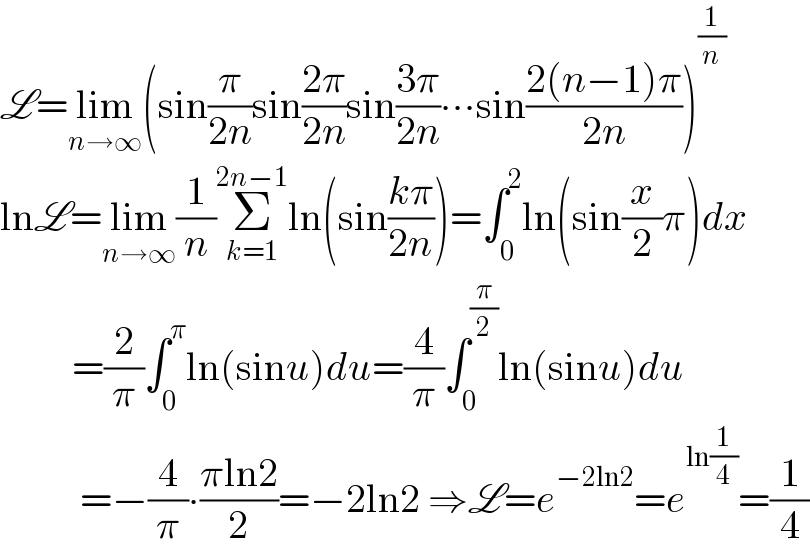
$$\mathscr{L}=\underset{{n}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\left(\mathrm{sin}\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}{n}}\mathrm{sin}\frac{\mathrm{2}\pi}{\mathrm{2}{n}}\mathrm{sin}\frac{\mathrm{3}\pi}{\mathrm{2}{n}}\centerdot\centerdot\centerdot\mathrm{sin}\frac{\mathrm{2}\left({n}−\mathrm{1}\right)\pi}{\mathrm{2}{n}}\right)^{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{ln}\mathscr{L}=\underset{{n}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}\underset{{k}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\mathrm{2}{n}−\mathrm{1}} {\sum}}\mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{sin}\frac{{k}\pi}{\mathrm{2}{n}}\right)=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{sin}\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\pi\right){dx} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:=\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\pi}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\pi} \mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{sin}{u}\right){du}=\frac{\mathrm{4}}{\pi}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{sin}{u}\right){du} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:=−\frac{\mathrm{4}}{\pi}\centerdot\frac{\pi\mathrm{ln2}}{\mathrm{2}}=−\mathrm{2ln2}\:\Rightarrow\mathscr{L}={e}^{−\mathrm{2ln2}} ={e}^{\mathrm{ln}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$
Commented by SANOGO last updated on 01/Oct/21

$${merci}\:{bien} \\ $$
