Question Number 158186 by mkam last updated on 31/Oct/21

Answered by puissant last updated on 31/Oct/21
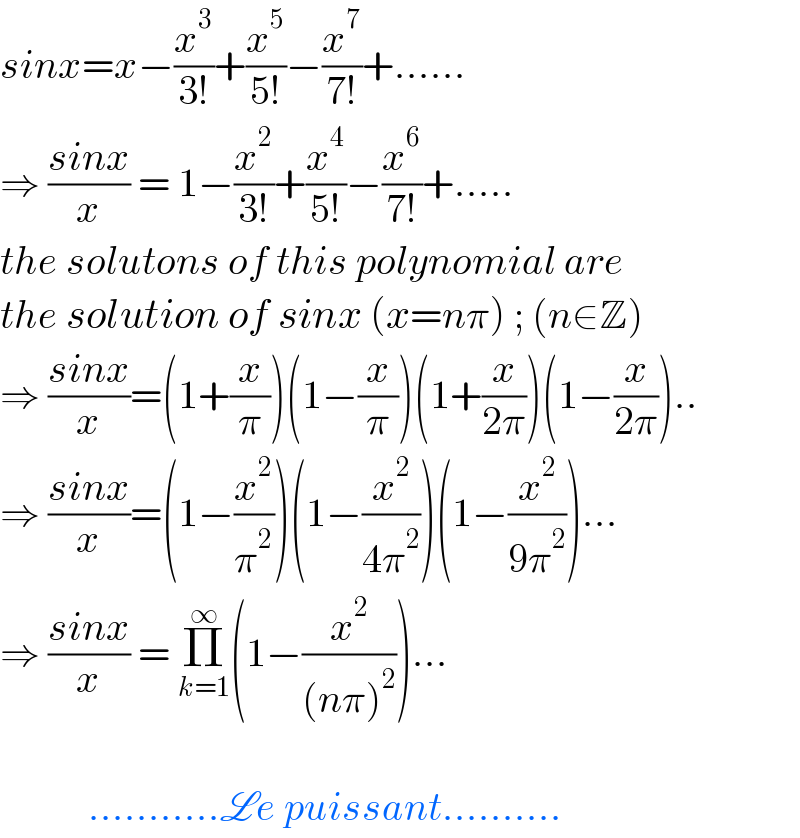
$${sinx}={x}−\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{3}!}+\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{5}} }{\mathrm{5}!}−\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{7}} }{\mathrm{7}!}+…… \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\frac{{sinx}}{{x}}\:=\:\mathrm{1}−\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{3}!}+\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{4}} }{\mathrm{5}!}−\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{6}} }{\mathrm{7}!}+….. \\ $$$${the}\:{solutons}\:{of}\:{this}\:{polynomial}\:{are}\: \\ $$$${the}\:{solution}\:{of}\:{sinx}\:\left({x}={n}\pi\right)\:;\:\left({n}\in\mathbb{Z}\right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\frac{{sinx}}{{x}}=\left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{{x}}{\pi}\right)\left(\mathrm{1}−\frac{{x}}{\pi}\right)\left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}\pi}\right)\left(\mathrm{1}−\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}\pi}\right).. \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\frac{{sinx}}{{x}}=\left(\mathrm{1}−\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\pi^{\mathrm{2}} }\right)\left(\mathrm{1}−\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{4}\pi^{\mathrm{2}} }\right)\left(\mathrm{1}−\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{9}\pi^{\mathrm{2}} }\right)… \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\frac{{sinx}}{{x}}\:=\:\underset{{k}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\prod}}\left(\mathrm{1}−\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\left({n}\pi\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }\right)… \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:………..\mathscr{L}{e}\:{puissant}………. \\ $$
