Question Number 158410 by tebohlouis last updated on 03/Nov/21

Answered by MJS_new last updated on 03/Nov/21
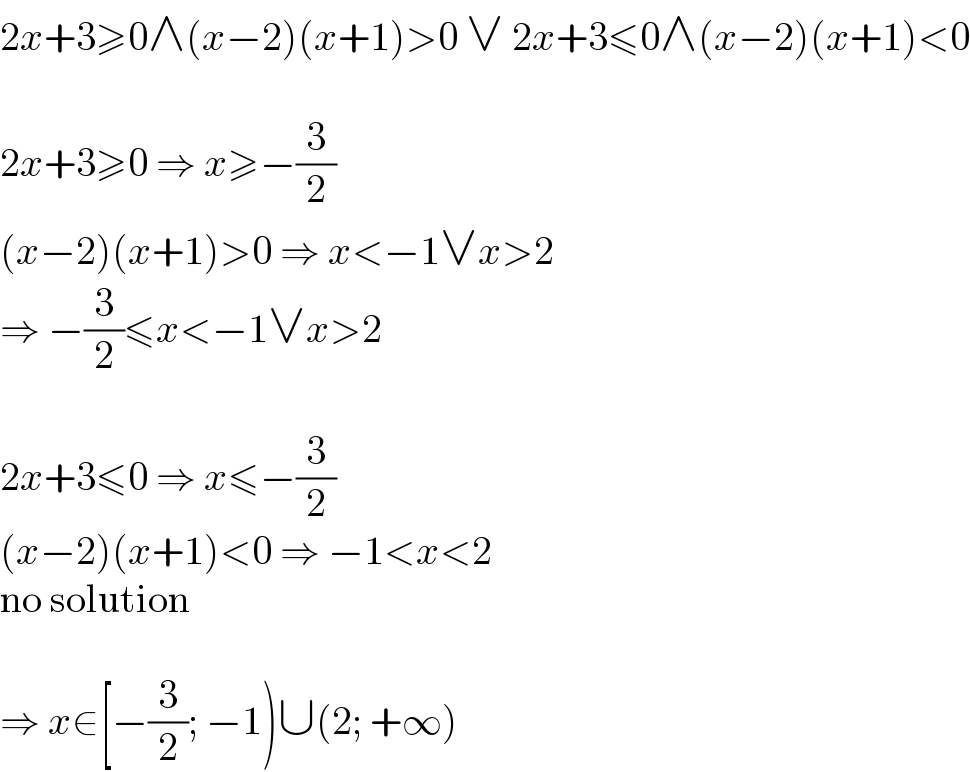
$$\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{3}\geqslant\mathrm{0}\wedge\left({x}−\mathrm{2}\right)\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right)>\mathrm{0}\:\vee\:\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{3}\leqslant\mathrm{0}\wedge\left({x}−\mathrm{2}\right)\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right)<\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{3}\geqslant\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow\:{x}\geqslant−\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\left({x}−\mathrm{2}\right)\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right)>\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow\:{x}<−\mathrm{1}\vee{x}>\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:−\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}\leqslant{x}<−\mathrm{1}\vee{x}>\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{3}\leqslant\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow\:{x}\leqslant−\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\left({x}−\mathrm{2}\right)\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right)<\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow\:−\mathrm{1}<{x}<\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\mathrm{no}\:\mathrm{solution} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:{x}\in\left[−\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}};\:−\mathrm{1}\right)\cup\left(\mathrm{2};\:+\infty\right) \\ $$
Answered by physicstutes last updated on 06/Nov/21

$$\mathrm{zero}'\mathrm{s} \\ $$$${x}−\mathrm{2}\:=\:\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow\:{x}\:=\:\mathrm{2} \\ $$$${x}+\mathrm{1}\:=\:\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow\:{x}\:=\:−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}{x}\:+\:\mathrm{3}\:=\:\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow\:{x}\:=\:−\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\begin{array}{|c|c|}{{x}<−\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}}&\hline{−\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}<{x}<−\mathrm{1}}&\hline{−\mathrm{1}<{x}<\mathrm{2}}&\hline{{x}>\mathrm{2}}\\{−}&\hline{+}&\hline{−}&\hline{+}\\\hline\end{array} \\ $$$${S}\:=\:\left\{\:{x}:\:−\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}\leqslant{x}<−\mathrm{1}\cup{x}>\mathrm{2}\right\} \\ $$
