Question Number 159852 by Tawa11 last updated on 21/Nov/21
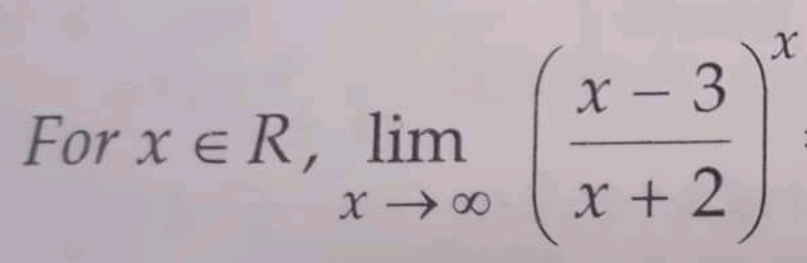
Answered by tounghoungko last updated on 21/Nov/21
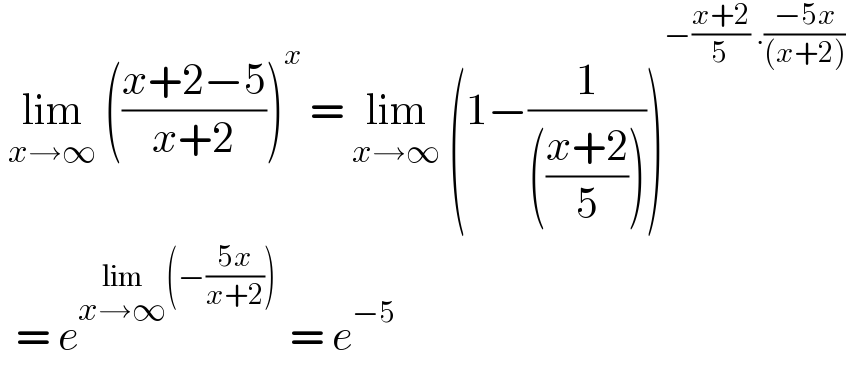
$$\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\left(\frac{{x}+\mathrm{2}−\mathrm{5}}{{x}+\mathrm{2}}\right)^{{x}} \:=\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\left(\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left(\frac{{x}+\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{5}}\right)}\right)^{−\frac{{x}+\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{5}}\:.\frac{−\mathrm{5}{x}}{\left({x}+\mathrm{2}\right)}} \\ $$$$\:\:=\:{e}^{\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\left(−\frac{\mathrm{5}{x}}{{x}+\mathrm{2}}\right)\:} \:=\:{e}^{−\mathrm{5}} \: \\ $$
Commented by Tawa11 last updated on 21/Nov/21

$$\mathrm{God}\:\mathrm{bless}\:\mathrm{you}\:\mathrm{sir}. \\ $$
Answered by LEKOUMA last updated on 21/Nov/21
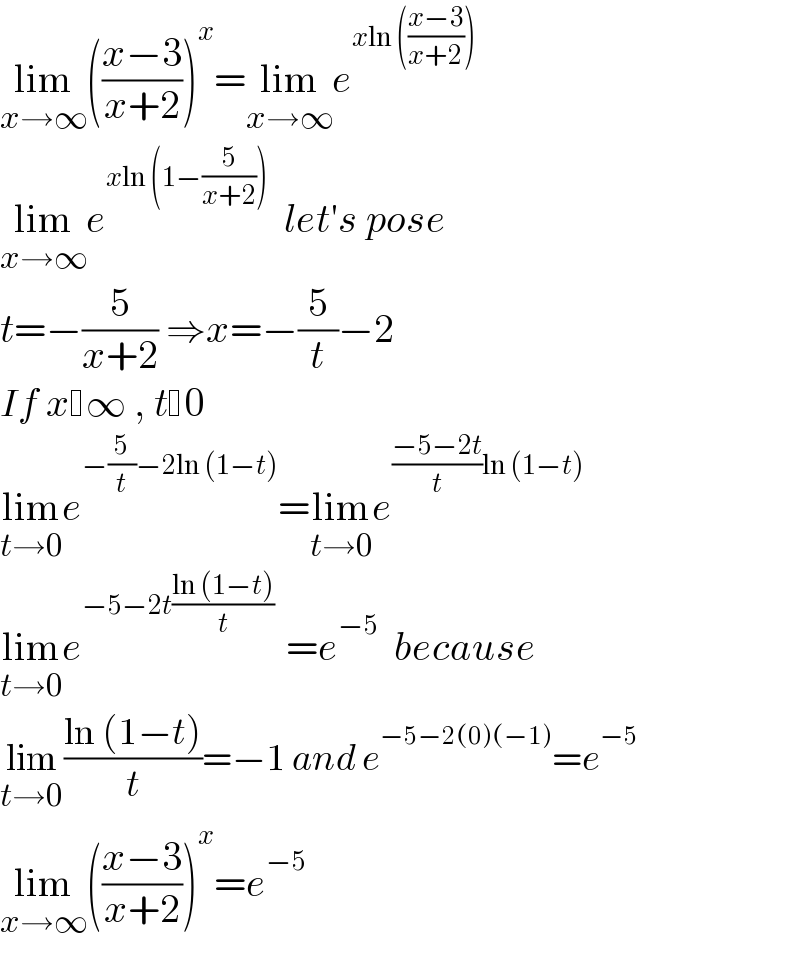
$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\left(\frac{{x}−\mathrm{3}}{{x}+\mathrm{2}}\right)^{{x}} =\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}{e}^{{x}\mathrm{ln}\:\left(\frac{{x}−\mathrm{3}}{{x}+\mathrm{2}}\right)} \\ $$$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}{e}^{{x}\mathrm{ln}\:\left(\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{5}}{{x}+\mathrm{2}}\right)} \:\:{let}'{s}\:{pose}\: \\ $$$${t}=−\frac{\mathrm{5}}{{x}+\mathrm{2}}\:\Rightarrow{x}=−\frac{\mathrm{5}}{{t}}−\mathrm{2}\: \\ $$$${If}\:{x} \infty\:,\:{t} \mathrm{0}\: \\ $$$$\underset{{t}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}{e}^{−\frac{\mathrm{5}}{{t}}−\mathrm{2ln}\:\left(\mathrm{1}−{t}\right)} =\underset{{t}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}{e}^{\frac{−\mathrm{5}−\mathrm{2}{t}}{{t}}\mathrm{ln}\:\left(\mathrm{1}−{t}\right)} \\ $$$$\underset{{t}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}{e}^{−\mathrm{5}−\mathrm{2}{t}\frac{\mathrm{ln}\:\left(\mathrm{1}−{t}\right)}{{t}}\:} \:={e}^{−\mathrm{5}} \:\:{because}\: \\ $$$$\underset{{t}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\mathrm{ln}\:\left(\mathrm{1}−{t}\right)}{{t}}=−\mathrm{1}\:{and}\:{e}^{−\mathrm{5}−\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{0}\right)\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)} ={e}^{−\mathrm{5}} \\ $$$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\left(\frac{{x}−\mathrm{3}}{{x}+\mathrm{2}}\right)^{{x}} ={e}^{−\mathrm{5}} \\ $$
