Question Number 160333 by cortano last updated on 27/Nov/21

Commented by blackmamba last updated on 28/Nov/21
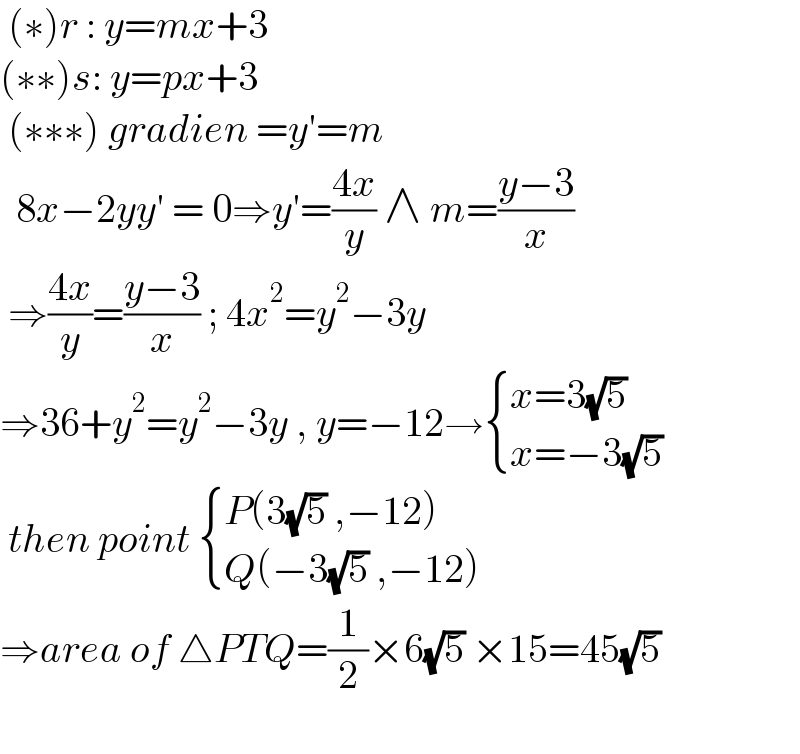
$$\:\left(\ast\right){r}\::\:{y}={mx}+\mathrm{3} \\ $$$$\left(\ast\ast\right){s}:\:{y}={px}+\mathrm{3} \\ $$$$\:\left(\ast\ast\ast\right)\:{gradien}\:={y}'={m} \\ $$$$\:\:\mathrm{8}{x}−\mathrm{2}{yy}'\:=\:\mathrm{0}\Rightarrow{y}'=\frac{\mathrm{4}{x}}{{y}}\:\wedge\:{m}=\frac{{y}−\mathrm{3}}{{x}} \\ $$$$\:\Rightarrow\frac{\mathrm{4}{x}}{{y}}=\frac{{y}−\mathrm{3}}{{x}}\:;\:\mathrm{4}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} ={y}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{3}{y} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{36}+{y}^{\mathrm{2}} ={y}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{3}{y}\:,\:{y}=−\mathrm{12}\rightarrow\begin{cases}{{x}=\mathrm{3}\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}\\{{x}=−\mathrm{3}\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}\end{cases} \\ $$$$\:{then}\:{point}\:\begin{cases}{{P}\left(\mathrm{3}\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}\:,−\mathrm{12}\right)}\\{{Q}\left(−\mathrm{3}\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}\:,−\mathrm{12}\right)}\end{cases} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{area}\:{of}\:\bigtriangleup{PTQ}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}×\mathrm{6}\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}\:×\mathrm{15}=\mathrm{45}\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}\: \\ $$$$ \\ $$
