Question Number 163259 by SANOGO last updated on 05/Jan/22

Answered by TheSupreme last updated on 05/Jan/22
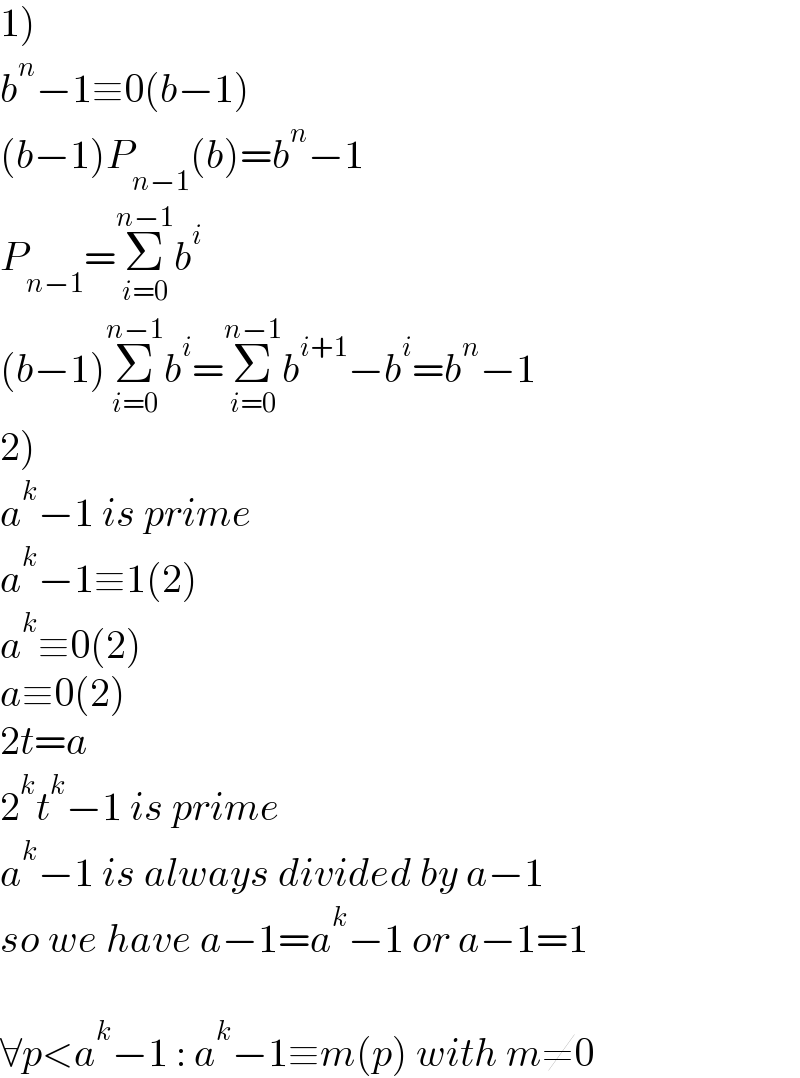
$$\left.\mathrm{1}\right)\: \\ $$$${b}^{{n}} −\mathrm{1}\equiv\mathrm{0}\left({b}−\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$$\left({b}−\mathrm{1}\right){P}_{{n}−\mathrm{1}} \left({b}\right)={b}^{{n}} −\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${P}_{{n}−\mathrm{1}} =\underset{{i}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{{n}−\mathrm{1}} {\sum}}{b}^{{i}} \\ $$$$\left({b}−\mathrm{1}\right)\underset{{i}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{{n}−\mathrm{1}} {\sum}}{b}^{{i}} =\underset{{i}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{{n}−\mathrm{1}} {\sum}}{b}^{{i}+\mathrm{1}} −{b}^{{i}} ={b}^{{n}} −\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{2}\right) \\ $$$${a}^{{k}} −\mathrm{1}\:{is}\:{prime} \\ $$$${a}^{{k}} −\mathrm{1}\equiv\mathrm{1}\left(\mathrm{2}\right) \\ $$$${a}^{{k}} \equiv\mathrm{0}\left(\mathrm{2}\right) \\ $$$${a}\equiv\mathrm{0}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}{t}={a} \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}^{{k}} {t}^{{k}} −\mathrm{1}\:{is}\:{prime} \\ $$$${a}^{{k}} −\mathrm{1}\:{is}\:{always}\:{divided}\:{by}\:{a}−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${so}\:{we}\:{have}\:{a}−\mathrm{1}={a}^{{k}} −\mathrm{1}\:{or}\:{a}−\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\forall{p}<{a}^{{k}} −\mathrm{1}\::\:{a}^{{k}} −\mathrm{1}\equiv{m}\left({p}\right)\:{with}\:{m}\neq\mathrm{0} \\ $$
Commented by SANOGO last updated on 06/Jan/22
$${merci}\:{bien} \\ $$
