Question Number 163384 by amin96 last updated on 06/Jan/22
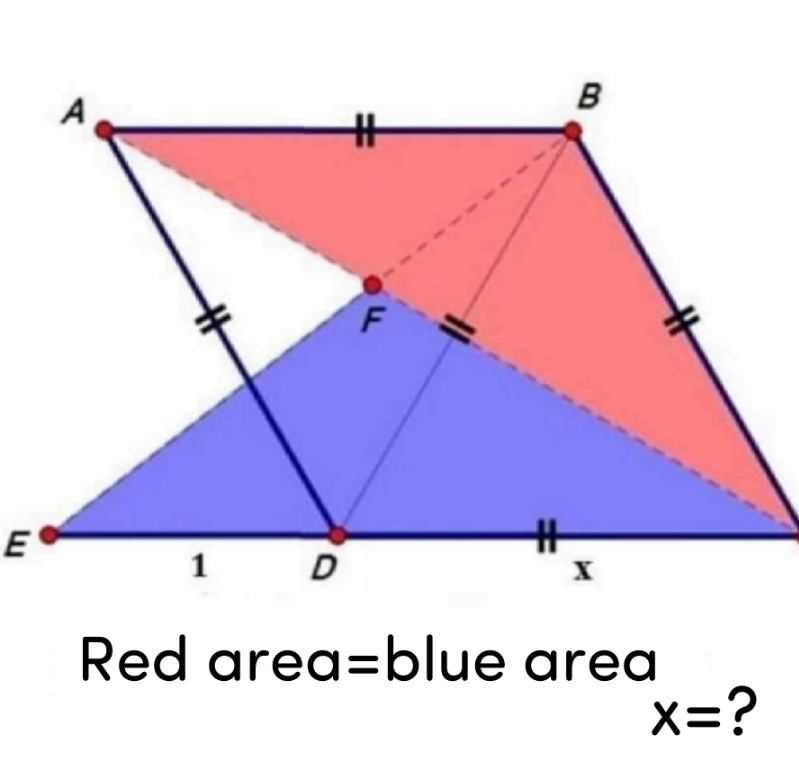
Answered by mr W last updated on 06/Jan/22
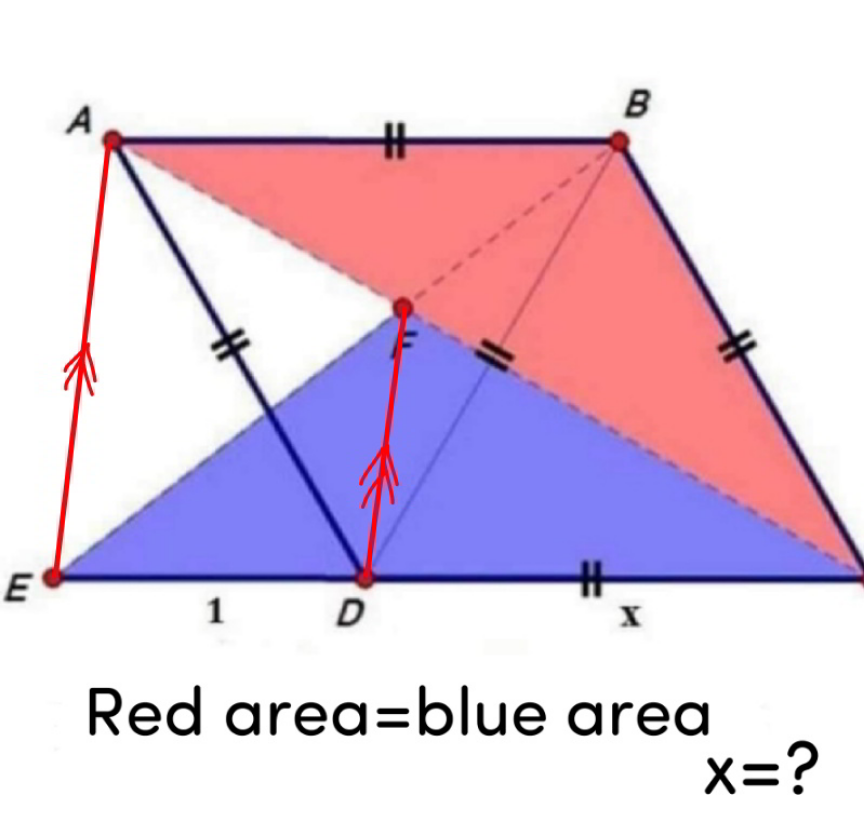
Commented by mr W last updated on 06/Jan/22
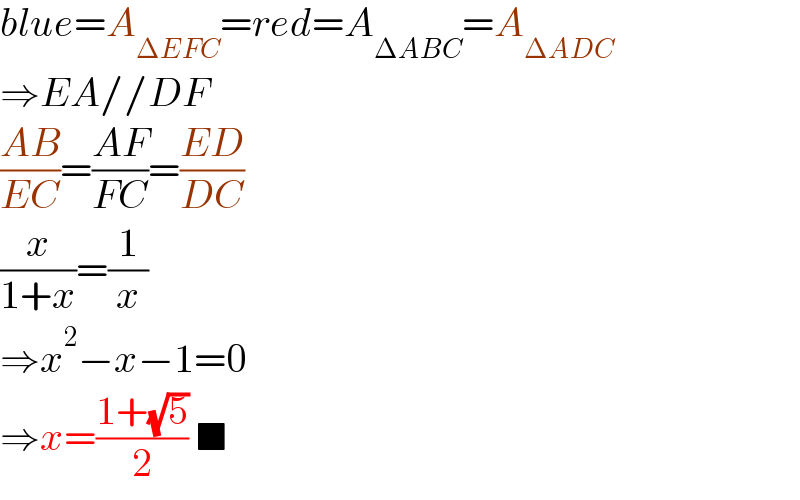
$${blue}={A}_{\Delta{EFC}} ={red}={A}_{\Delta{ABC}} ={A}_{\Delta{ADC}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{EA}//{DF} \\ $$$$\frac{{AB}}{{EC}}=\frac{{AF}}{{FC}}=\frac{{ED}}{{DC}} \\ $$$$\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −{x}−\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{x}=\frac{\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\blacksquare \\ $$
Commented by amin96 last updated on 06/Jan/22
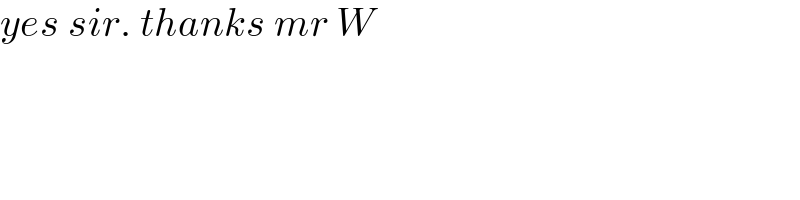
$${yes}\:{sir}.\:{thanks}\:{mr}\:{W} \\ $$
Commented by amin96 last updated on 06/Jan/22

$$ \\ $$Could you please tell me why is DF parallel to AE?
Commented by mr W last updated on 06/Jan/22
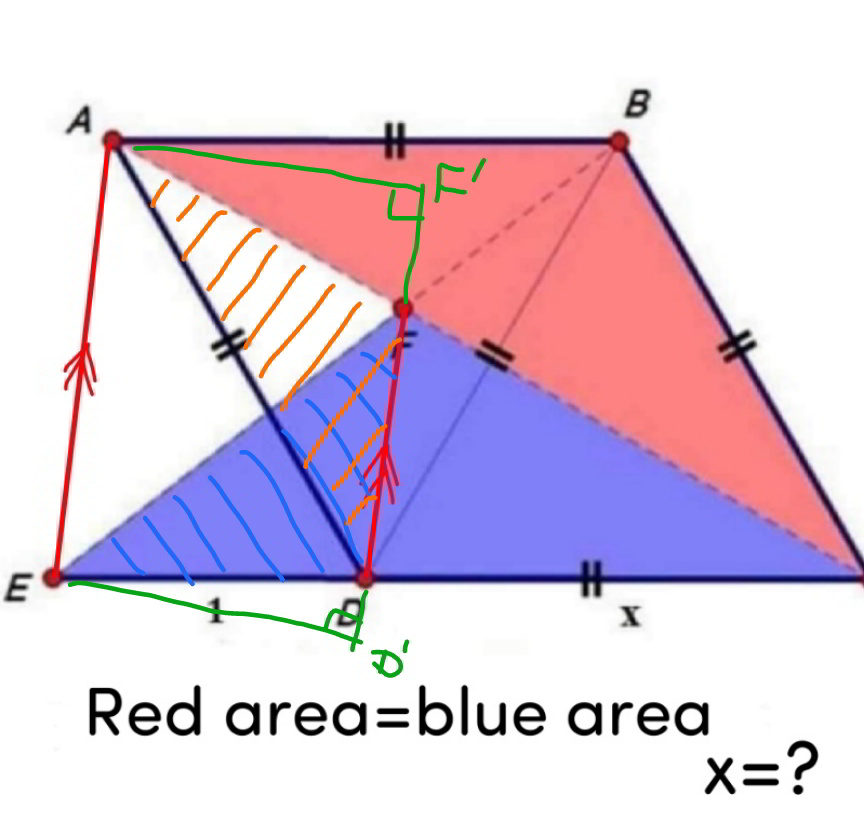
Commented by mr W last updated on 06/Jan/22
![[ΔEFC]=[ΔADC] ⇒[ΔEFD]+[ΔDFC]=[ΔADF]+[ΔDFC] ⇒[ΔEFD]=[ΔADF] ⇒(1/2)DF×ED′=(1/2)×DF×AF′ ⇒ED′=AF′ ⇒EA//DF](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q163407.png)
$$\left[\Delta{EFC}\right]=\left[\Delta{ADC}\right] \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\left[\Delta{EFD}\right]+\left[\Delta{DFC}\right]=\left[\Delta{ADF}\right]+\left[\Delta{DFC}\right] \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\left[\Delta{EFD}\right]=\left[\Delta{ADF}\right] \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{DF}×\mathrm{ED}'=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}×\mathrm{DF}×\mathrm{AF}' \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{ED}'=\mathrm{AF}' \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{EA}//{DF} \\ $$
Commented by amin96 last updated on 06/Jan/22

$$\boldsymbol{{VERY}}\:\boldsymbol{{NICE}}\: \\ $$
Commented by Tawa11 last updated on 06/Jan/22

$$\mathrm{Great}\:\mathrm{sir} \\ $$
Answered by mr W last updated on 06/Jan/22
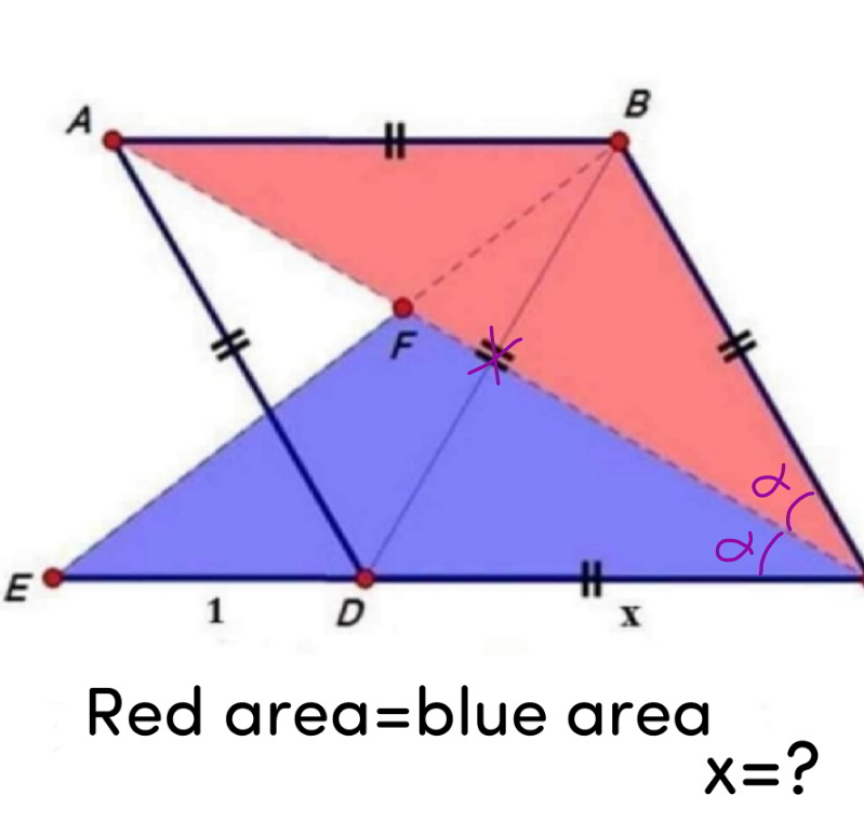
Commented by mr W last updated on 06/Jan/22
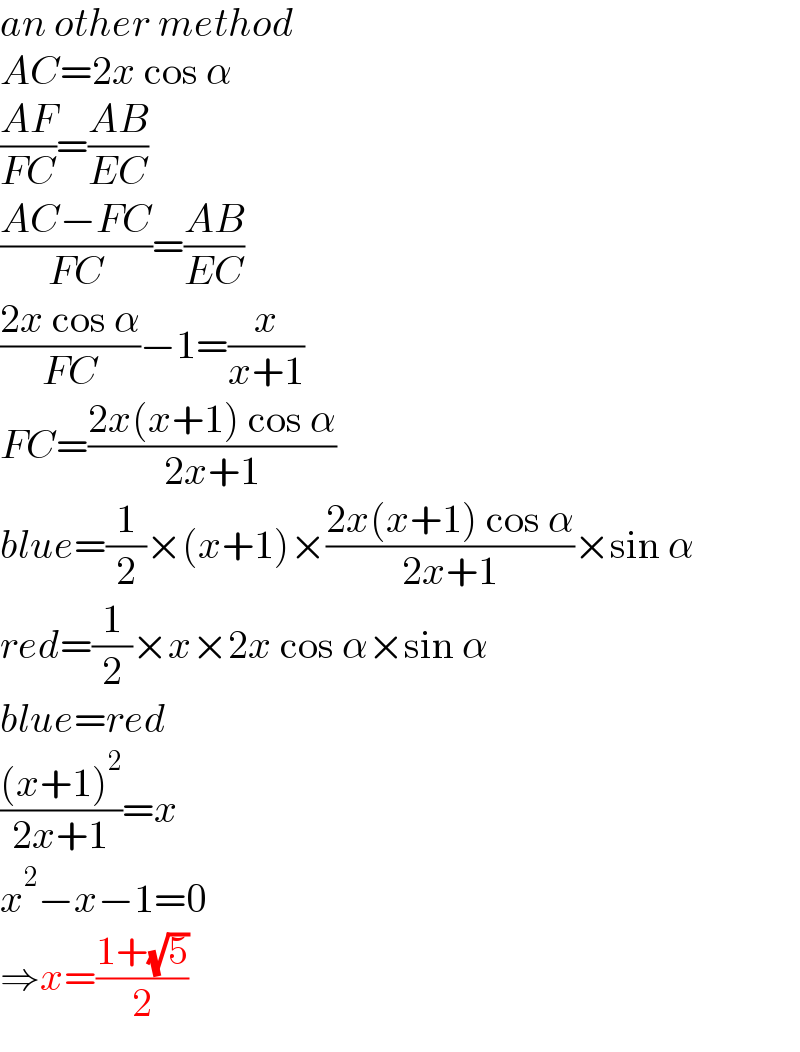
$${an}\:{other}\:{method} \\ $$$${AC}=\mathrm{2}{x}\:\mathrm{cos}\:\alpha \\ $$$$\frac{{AF}}{{FC}}=\frac{{AB}}{{EC}} \\ $$$$\frac{{AC}−{FC}}{{FC}}=\frac{{AB}}{{EC}} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}\:\mathrm{cos}\:\alpha}{{FC}}−\mathrm{1}=\frac{{x}}{{x}+\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$${FC}=\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right)\:\mathrm{cos}\:\alpha}{\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$${blue}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}×\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right)×\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right)\:\mathrm{cos}\:\alpha}{\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}}×\mathrm{sin}\:\alpha \\ $$$${red}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}×{x}×\mathrm{2}{x}\:\mathrm{cos}\:\alpha×\mathrm{sin}\:\alpha \\ $$$${blue}={red} \\ $$$$\frac{\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}}={x} \\ $$$${x}^{\mathrm{2}} −{x}−\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{x}=\frac{\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
Commented by Tawa11 last updated on 07/Jan/22

$$\mathrm{Great}\:\mathrm{sir} \\ $$
