Question Number 16803 by ajfour last updated on 26/Jun/17

Commented by ajfour last updated on 26/Jun/17

$$\mathrm{Prove}\:\mathrm{that}\:\mathrm{in}\:\mathrm{an}\:\mathrm{equilateral}\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{triangle}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{sum}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{distances} \\ $$$$\mathrm{from}\:\mathrm{any}\:\mathrm{point}\:\mathrm{to}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{three}\:\mathrm{sides} \\ $$$$\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{a}\:\mathrm{constant}. \\ $$
Answered by mrW1 last updated on 26/Jun/17
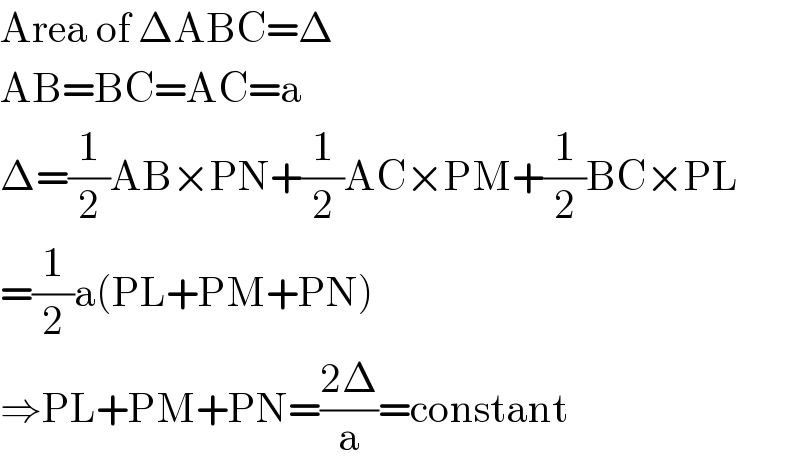
$$\mathrm{Area}\:\mathrm{of}\:\Delta\mathrm{ABC}=\Delta \\ $$$$\mathrm{AB}=\mathrm{BC}=\mathrm{AC}=\mathrm{a} \\ $$$$\Delta=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{AB}×\mathrm{PN}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{AC}×\mathrm{PM}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{BC}×\mathrm{PL} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{a}\left(\mathrm{PL}+\mathrm{PM}+\mathrm{PN}\right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{PL}+\mathrm{PM}+\mathrm{PN}=\frac{\mathrm{2}\Delta}{\mathrm{a}}=\mathrm{constant} \\ $$
Commented by ajfour last updated on 26/Jun/17
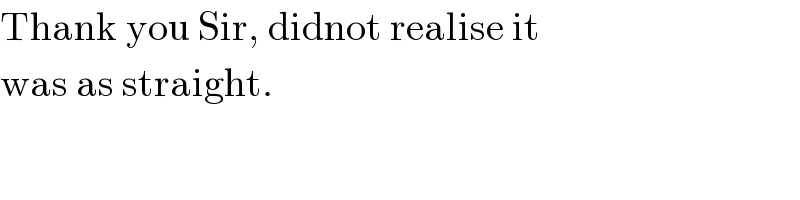
$$\mathrm{Thank}\:\mathrm{you}\:\mathrm{Sir},\:\mathrm{didnot}\:\mathrm{realise}\:\mathrm{it} \\ $$$$\mathrm{was}\:\mathrm{as}\:\mathrm{straight}. \\ $$
