Question Number 168446 by amin96 last updated on 10/Apr/22
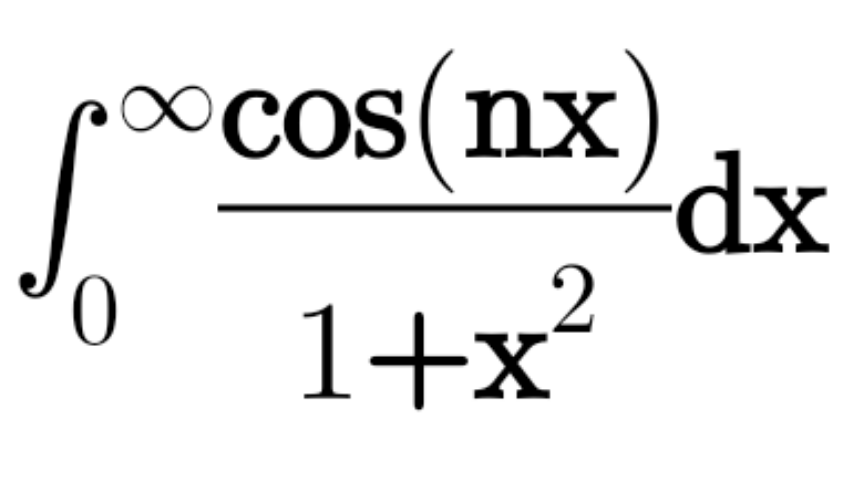
Answered by Mathspace last updated on 11/Apr/22
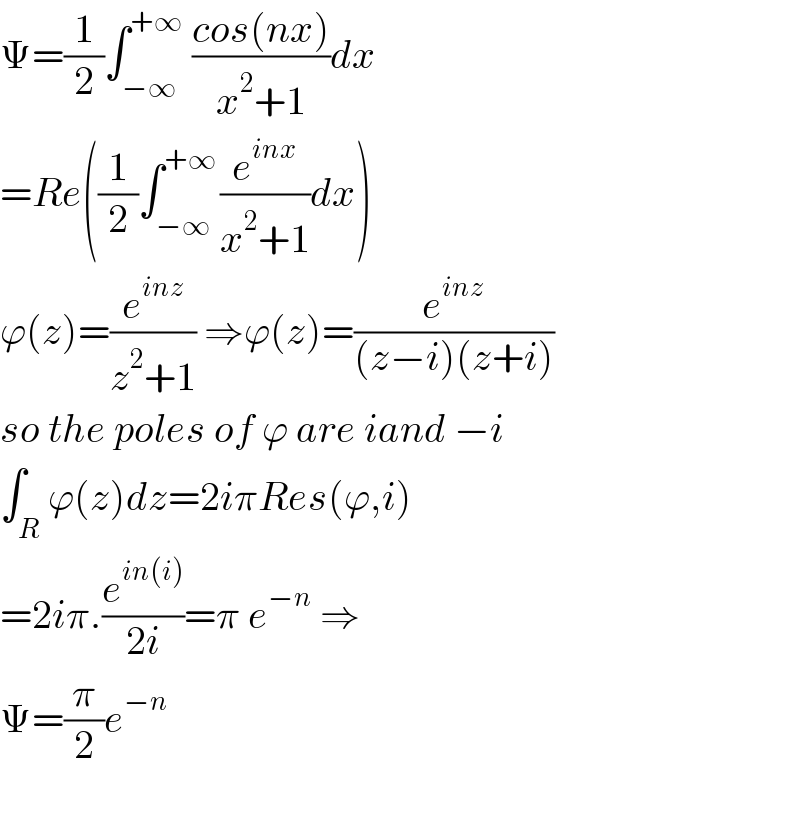
$$\Psi=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int_{−\infty} ^{+\infty} \:\frac{{cos}\left({nx}\right)}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}{dx} \\ $$$$={Re}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int_{−\infty} ^{+\infty\:} \frac{{e}^{{inx}} }{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}{dx}\right) \\ $$$$\varphi\left({z}\right)=\frac{{e}^{{inz}} }{{z}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}\:\Rightarrow\varphi\left({z}\right)=\frac{{e}^{{inz}} }{\left({z}−{i}\right)\left({z}+{i}\right)} \\ $$$${so}\:{the}\:{poles}\:{of}\:\varphi\:{are}\:{iand}\:−{i} \\ $$$$\int_{{R}} \varphi\left({z}\right){dz}=\mathrm{2}{i}\pi{Res}\left(\varphi,{i}\right) \\ $$$$=\mathrm{2}{i}\pi.\frac{{e}^{{in}\left({i}\right)} }{\mathrm{2}{i}}=\pi\:{e}^{−{n}} \:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\Psi=\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}{e}^{−{n}} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
