Question Number 169559 by TOTTI last updated on 03/May/22
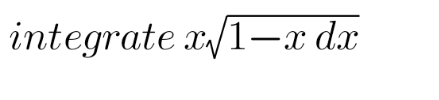
Commented by cortano1 last updated on 03/May/22
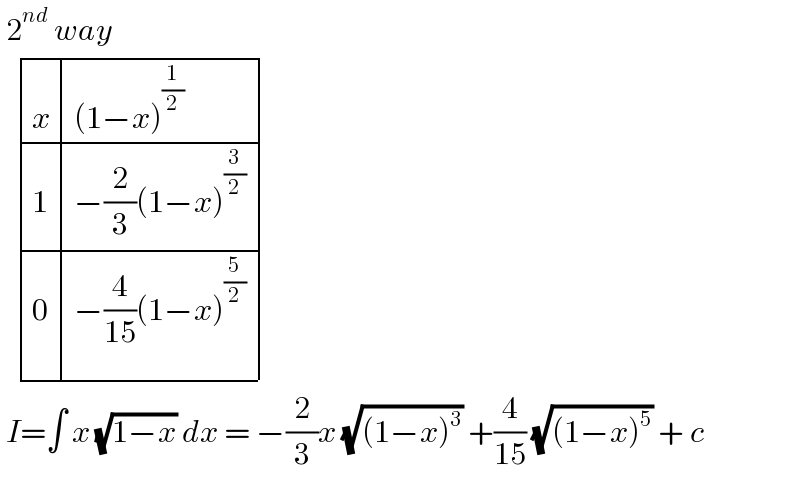
$$\:\mathrm{2}^{{nd}} \:{way}\: \\ $$$$\:\:\begin{array}{|c|c|c|}{{x}}&\hline{\left(\mathrm{1}−{x}\right)^{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}} }\\{\mathrm{1}}&\hline{−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}\left(\mathrm{1}−{x}\right)^{\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}} }\\{\mathrm{0}}&\hline{−\frac{\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{15}}\left(\mathrm{1}−{x}\right)^{\frac{\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{2}}} }\\\hline\end{array} \\ $$$$\:{I}=\int\:{x}\:\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−{x}}\:{dx}\:=\:−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}{x}\:\sqrt{\left(\mathrm{1}−{x}\right)^{\mathrm{3}} }\:+\frac{\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{15}}\:\sqrt{\left(\mathrm{1}−{x}\right)^{\mathrm{5}} }\:+\:{c} \\ $$
Answered by greougoury555 last updated on 03/May/22
![∫ x(√(1−x)) dx let (√(1−x)) = u → { ((x=1−u^2 )),((dx=−2u du)) :} I=∫ (1−u^2 )(u)(−2u)du =−2∫(1−u^2 )u^2 du =−2∫(u^2 −u^4 )du =−2[ (1/3)u^3 −(1/5)u^5 ]+c =−(2/(15))u^3 (5−3u^2 )+c =−(2/(15)) (√((1−x)^3 )) (5−3(1−x))+c =−(2/(15)) (3x+2)(√((1−x)^3 )) + c](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q169560.png)
$$\:\int\:{x}\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−{x}}\:{dx}\: \\ $$$$\:{let}\:\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−{x}}\:=\:{u}\:\rightarrow\begin{cases}{{x}=\mathrm{1}−{u}^{\mathrm{2}} }\\{{dx}=−\mathrm{2}{u}\:{du}}\end{cases} \\ $$$$\:{I}=\int\:\left(\mathrm{1}−{u}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\left({u}\right)\left(−\mathrm{2}{u}\right){du} \\ $$$$\:\:=−\mathrm{2}\int\left(\mathrm{1}−{u}^{\mathrm{2}} \right){u}^{\mathrm{2}} \:{du} \\ $$$$\:\:=−\mathrm{2}\int\left({u}^{\mathrm{2}} −{u}^{\mathrm{4}} \right){du} \\ $$$$\:\:=−\mathrm{2}\left[\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}{u}^{\mathrm{3}} −\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}{u}^{\mathrm{5}} \:\right]+{c} \\ $$$$\:\:=−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{15}}{u}^{\mathrm{3}} \left(\mathrm{5}−\mathrm{3}{u}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)+{c} \\ $$$$\:=−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{15}}\:\sqrt{\left(\mathrm{1}−{x}\right)^{\mathrm{3}} }\:\left(\mathrm{5}−\mathrm{3}\left(\mathrm{1}−{x}\right)\right)+{c} \\ $$$$\:=−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{15}}\:\left(\mathrm{3}{x}+\mathrm{2}\right)\sqrt{\left(\mathrm{1}−{x}\right)^{\mathrm{3}} }\:+\:{c} \\ $$
