Question Number 171025 by Mastermind last updated on 06/Jun/22
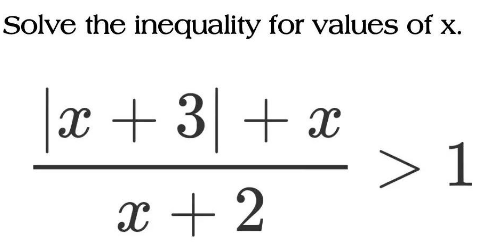
Answered by greougoury555 last updated on 06/Jun/22
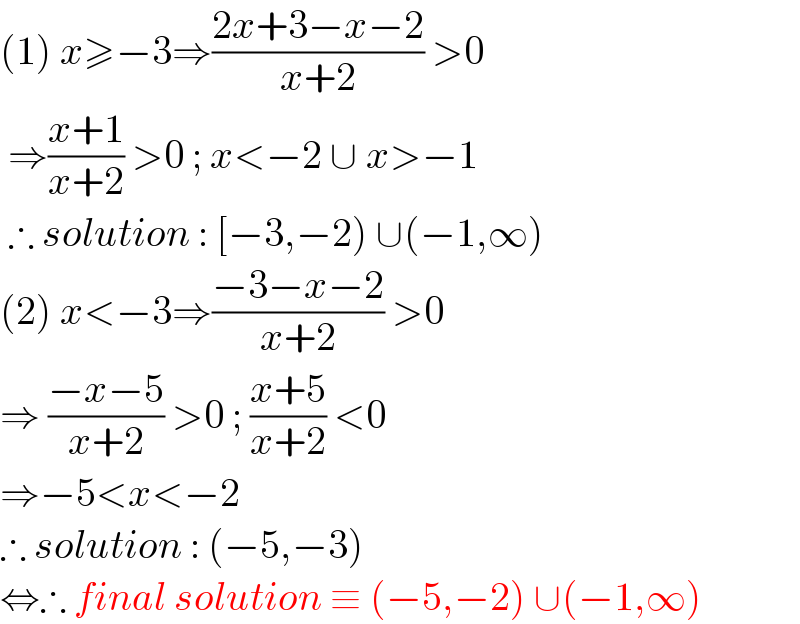
$$\left(\mathrm{1}\right)\:{x}\geqslant−\mathrm{3}\Rightarrow\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{3}−{x}−\mathrm{2}}{{x}+\mathrm{2}}\:>\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\:\Rightarrow\frac{{x}+\mathrm{1}}{{x}+\mathrm{2}}\:>\mathrm{0}\:;\:{x}<−\mathrm{2}\:\cup\:{x}>−\mathrm{1}\: \\ $$$$\:\therefore\:{solution}\::\:\left[−\mathrm{3},−\mathrm{2}\right)\:\cup\left(−\mathrm{1},\infty\right) \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\:{x}<−\mathrm{3}\Rightarrow\frac{−\mathrm{3}−{x}−\mathrm{2}}{{x}+\mathrm{2}}\:>\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\frac{−{x}−\mathrm{5}}{{x}+\mathrm{2}}\:>\mathrm{0}\:;\:\frac{{x}+\mathrm{5}}{{x}+\mathrm{2}}\:<\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow−\mathrm{5}<{x}<−\mathrm{2}\: \\ $$$$\therefore\:{solution}\::\:\left(−\mathrm{5},−\mathrm{3}\right) \\ $$$$\Leftrightarrow\therefore\:{final}\:{solution}\:\equiv\:\left(−\mathrm{5},−\mathrm{2}\right)\:\cup\left(−\mathrm{1},\infty\right) \\ $$
Commented by Tawa11 last updated on 07/Jun/22

$$\mathrm{Great}\:\mathrm{sir} \\ $$
Answered by thfchristopher last updated on 07/Jun/22
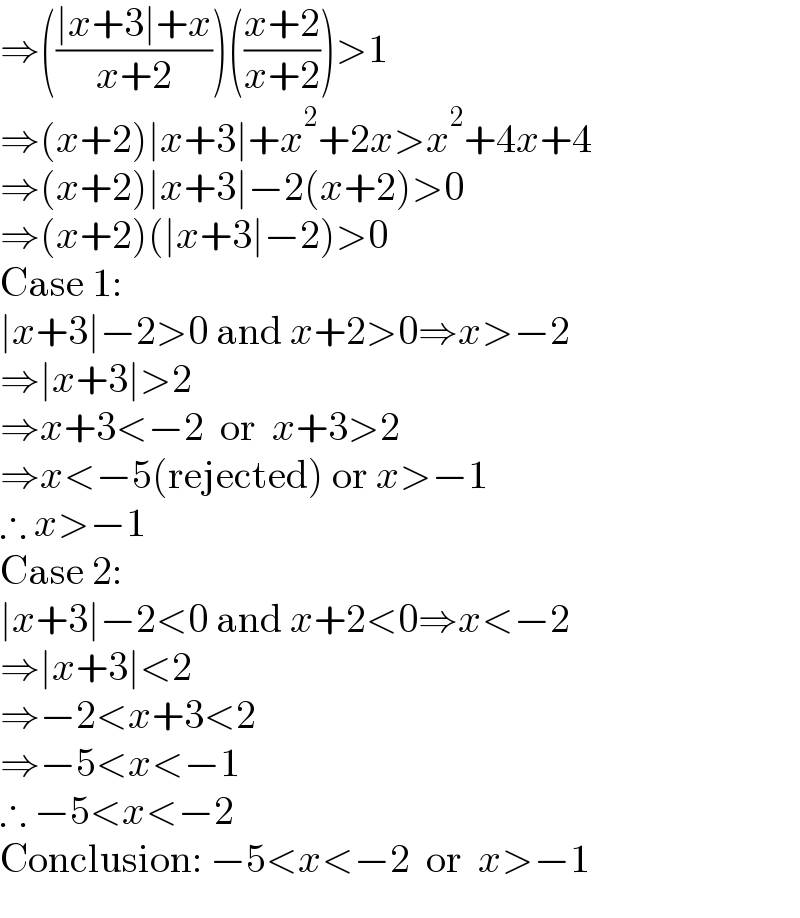
$$\Rightarrow\left(\frac{\mid{x}+\mathrm{3}\mid+{x}}{{x}+\mathrm{2}}\right)\left(\frac{{x}+\mathrm{2}}{{x}+\mathrm{2}}\right)>\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\left({x}+\mathrm{2}\right)\mid{x}+\mathrm{3}\mid+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{x}>{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{4}{x}+\mathrm{4} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\left({x}+\mathrm{2}\right)\mid{x}+\mathrm{3}\mid−\mathrm{2}\left({x}+\mathrm{2}\right)>\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\left({x}+\mathrm{2}\right)\left(\mid{x}+\mathrm{3}\mid−\mathrm{2}\right)>\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\mathrm{Case}\:\mathrm{1}: \\ $$$$\mid{x}+\mathrm{3}\mid−\mathrm{2}>\mathrm{0}\:\mathrm{and}\:{x}+\mathrm{2}>\mathrm{0}\Rightarrow{x}>−\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mid{x}+\mathrm{3}\mid>\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{x}+\mathrm{3}<−\mathrm{2}\:\:\mathrm{or}\:\:{x}+\mathrm{3}>\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{x}<−\mathrm{5}\left(\mathrm{rejected}\right)\:\mathrm{or}\:{x}>−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\therefore\:{x}>−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\mathrm{Case}\:\mathrm{2}: \\ $$$$\mid{x}+\mathrm{3}\mid−\mathrm{2}<\mathrm{0}\:\mathrm{and}\:{x}+\mathrm{2}<\mathrm{0}\Rightarrow{x}<−\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mid{x}+\mathrm{3}\mid<\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow−\mathrm{2}<{x}+\mathrm{3}<\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow−\mathrm{5}<{x}<−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\therefore\:−\mathrm{5}<{x}<−\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\mathrm{Conclusion}:\:−\mathrm{5}<{x}<−\mathrm{2}\:\:\mathrm{or}\:\:{x}>−\mathrm{1} \\ $$
