Question Number 171442 by mnjuly1970 last updated on 15/Jun/22
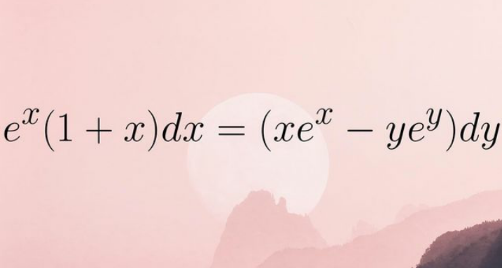
Commented by infinityaction last updated on 15/Jun/22
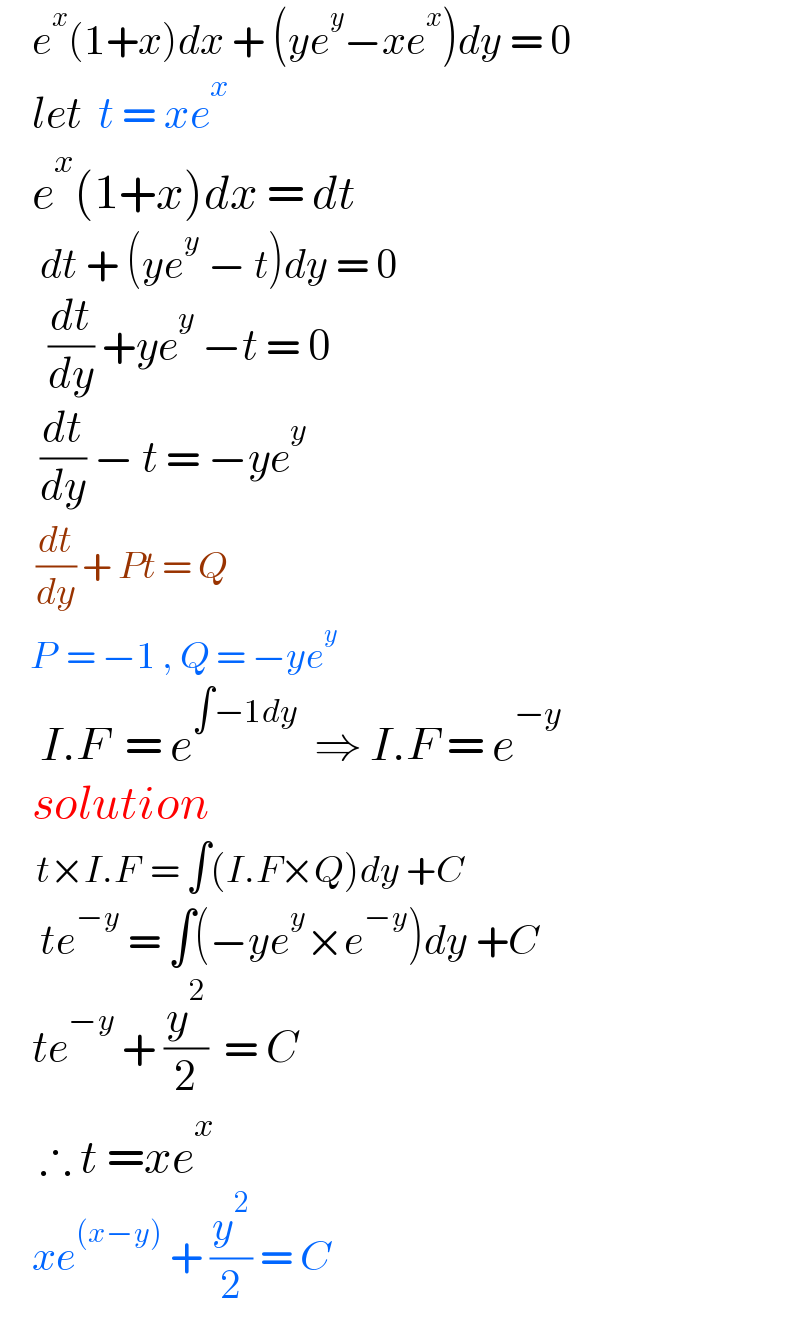
$$\:\:\:\:{e}^{{x}} \left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right){dx}\:+\:\left({ye}^{{y}} −{xe}^{{x}} \right){dy}\:=\:\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:{let}\:\:{t}\:=\:{xe}^{{x}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:{e}^{{x}} \left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right){dx}\:=\:{dt} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:{dt}\:+\:\left({ye}^{{y}} \:−\:{t}\right){dy}\:=\:\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\frac{{dt}}{{dy}}\:+{ye}^{{y}} \:−{t}\:=\:\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\frac{{dt}}{{dy}}\:−\:{t}\:=\:−{ye}^{{y}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\frac{{dt}}{{dy}}\:+\:{Pt}\:=\:{Q} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:{P}\:\:=\:−\mathrm{1}\:,\:{Q}\:=\:−{ye}^{{y}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:{I}.{F}\:\:=\:{e}^{\int−\mathrm{1}{dy}} \:\:\Rightarrow\:{I}.{F}\:=\:{e}^{−{y}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:{solution} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:{t}×{I}.{F}\:\:=\:\int\left({I}.{F}×{Q}\right){dy}\:+{C} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:{te}^{−{y}} \:=\:\int\left(−{ye}^{{y}} ×{e}^{−{y}} \right){dy}\:+{C} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:{te}^{−{y}} \:+\:\frac{{y}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}\:\:=\:{C} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\therefore\:{t}\:={xe}^{{x}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:{xe}^{\left({x}−{y}\right)} \:+\:\frac{{y}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}\:=\:{C} \\ $$
