Question Number 174566 by RajiYusuf last updated on 04/Aug/22

Answered by aleks041103 last updated on 05/Aug/22
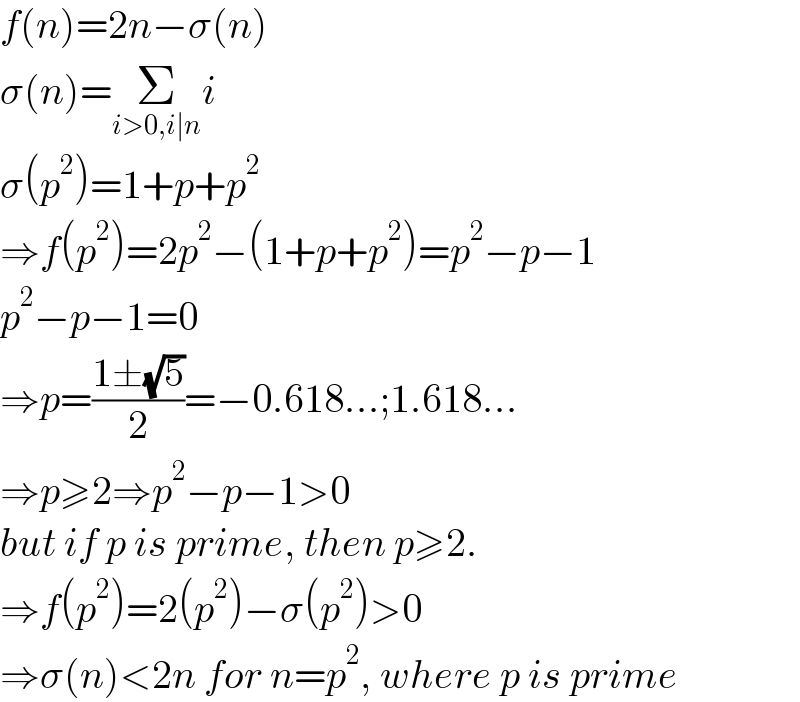
$${f}\left({n}\right)=\mathrm{2}{n}−\sigma\left({n}\right) \\ $$$$\sigma\left({n}\right)=\underset{{i}>\mathrm{0},{i}\mid{n}} {\sum}{i} \\ $$$$\sigma\left({p}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)=\mathrm{1}+{p}+{p}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{f}\left({p}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)=\mathrm{2}{p}^{\mathrm{2}} −\left(\mathrm{1}+{p}+{p}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)={p}^{\mathrm{2}} −{p}−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${p}^{\mathrm{2}} −{p}−\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{p}=\frac{\mathrm{1}\pm\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{2}}=−\mathrm{0}.\mathrm{618}…;\mathrm{1}.\mathrm{618}… \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{p}\geqslant\mathrm{2}\Rightarrow{p}^{\mathrm{2}} −{p}−\mathrm{1}>\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${but}\:{if}\:{p}\:{is}\:{prime},\:{then}\:{p}\geqslant\mathrm{2}. \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{f}\left({p}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)=\mathrm{2}\left({p}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)−\sigma\left({p}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)>\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\sigma\left({n}\right)<\mathrm{2}{n}\:{for}\:{n}={p}^{\mathrm{2}} ,\:{where}\:{p}\:{is}\:{prime} \\ $$
