Question Number 180066 by mr W last updated on 06/Nov/22
Commented by mr W last updated on 06/Nov/22
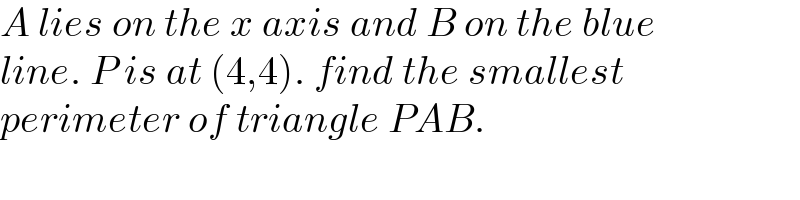
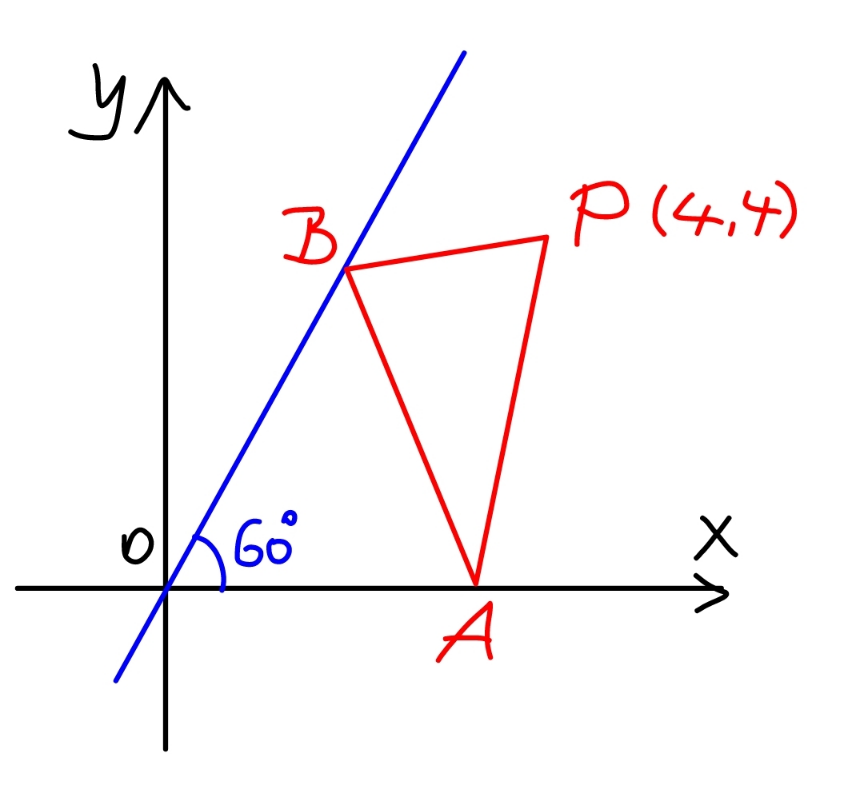
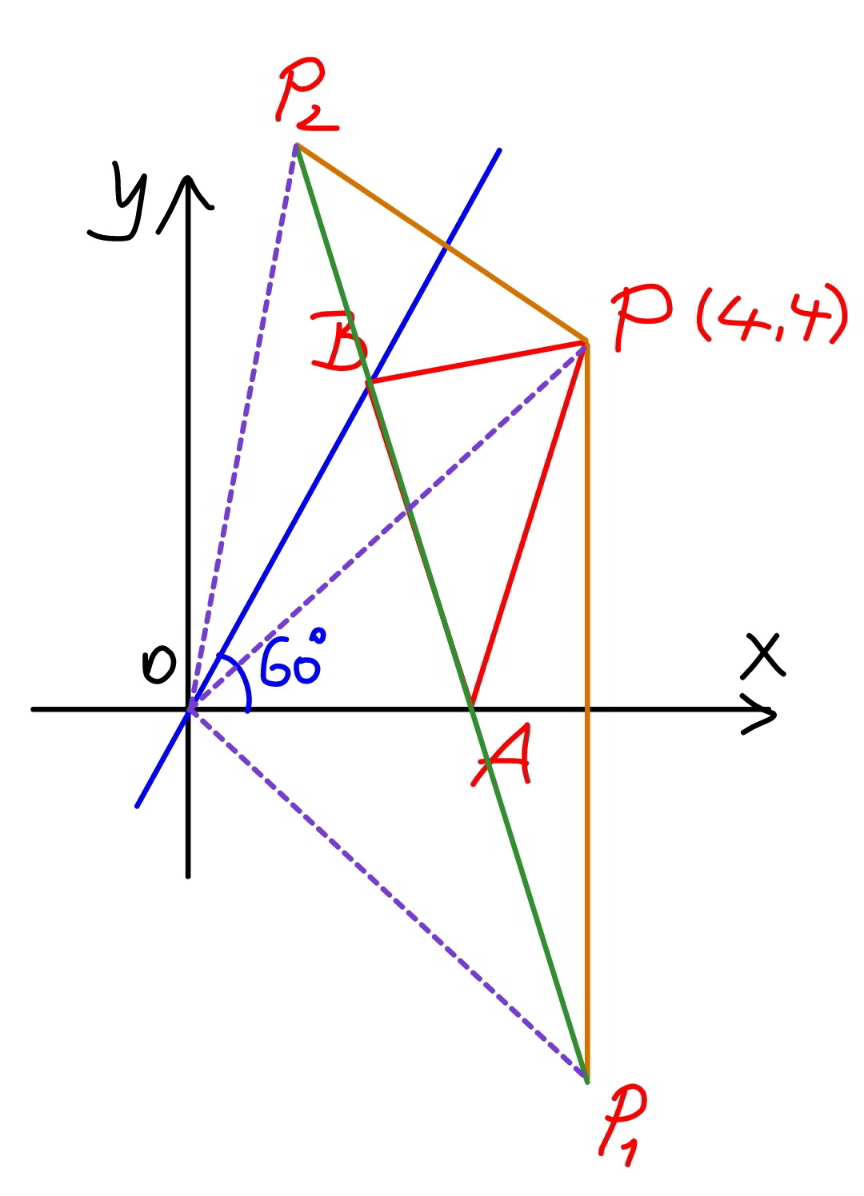
$${A}\:{lies}\:{on}\:{the}\:{x}\:{axis}\:{and}\:{B}\:{on}\:{the}\:{blue} \\ $$$${line}.\:{P}\:{is}\:{at}\:\left(\mathrm{4},\mathrm{4}\right).\:{find}\:{the}\:{smallest}\: \\ $$$${perimeter}\:{of}\:{triangle}\:{PAB}. \\ $$
Answered by aleks041103 last updated on 06/Nov/22
Commented by aleks041103 last updated on 06/Nov/22

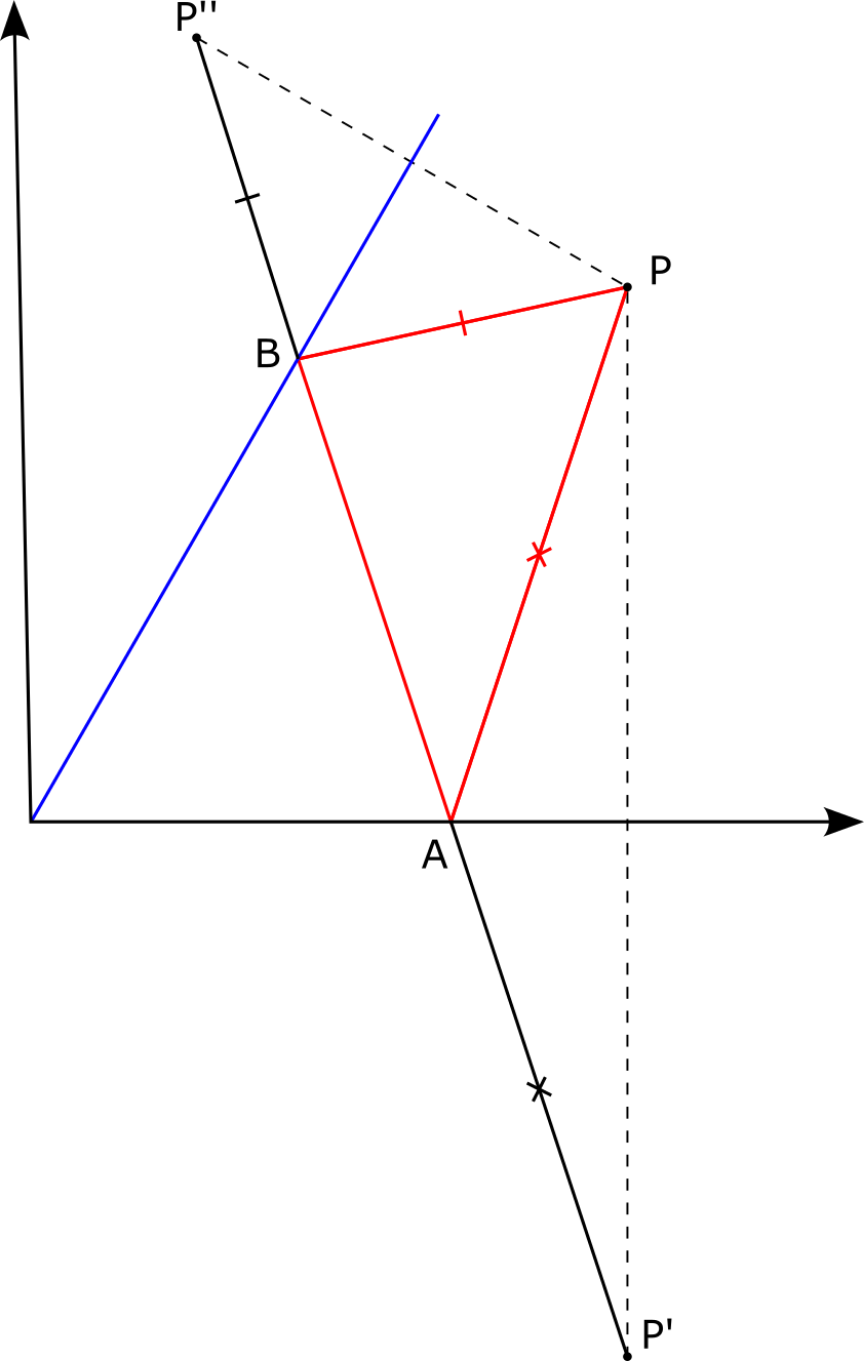
$${We}\:{can}\:{construct}\:{points}\:{P}\:'\:{and}\:{P}\:'',\:{which} \\ $$$${are}\:{the}\:{reflections}\:{of}\:{P}\:\:{with}\:{respect}\:{to} \\ $$$${the}\:{x}\:{axis}\:{and}\:{the}\:{blue}\:{line}. \\ $$$${Then}\:{by}\:{construction} \\ $$$${PA}={P}\:'{A}\:{and}\:{PB}={P}\:''{B}. \\ $$$${Therefore}\:{the}\:{triangle}'{s}\:{perimeter}\:{is} \\ $$$${p}={P}\:'{A}+{AB}+{P}\:''{B}. \\ $$$${obviously}\:{p}\:{is}\:{minimal},\:{when}\: \\ $$$${A},{B}\in{P}\:'{P}\:'' \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{min}\left({p}\right)={P}\:'{P}\:'' \\ $$$${But}\:{it}\:{is}\:{easy}\:{to}\:{see},\:{that}\:{then} \\ $$$${P}\:'{O}={P}\:''{O}={PO}={r} \\ $$$${and}\:\angle{P}\:'{OP}\:''=\mathrm{2}\alpha,\:{where}\:\alpha=\angle\left({Ox},\:{blue}\:{line}\right) \\ $$$$\left({this}\:{is}\:{true},\:{when}\:{P}\:{is}\:{between}\:{Ox}\:{and}\:{the}\right. \\ $$$$\left.{blue}\:{line}\right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{P}\:'{P}\:''=\mathrm{2}.{OP}.{sin}\alpha={p}_{{min}} \\ $$$${in}\:{our}\:{case}: \\ $$$${OP}=\mathrm{4}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\:{and}\:\alpha=\mathrm{60}° \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{p}_{{min}} =\mathrm{4}\sqrt{\mathrm{6}} \\ $$
Commented by mr W last updated on 07/Nov/22
$${perfect}!\:{thanks}\:{sir}! \\ $$
Commented by Acem last updated on 07/Nov/22

$${The}\:{development}\:{of}\:{prograning}\:{and}\:{engineering} \\ $$$$\:{graphic}\:{programs}\:{made}\:{us}\:{rely}\:{on}\:{them}\:{and} \\ $$$$\:{forgot}\:{simplest}\:{things}\:{in}\:{descriptive}\:{geometry}! \\ $$$$\:{My}\:{grades}\:{at}\:{it}\:{were}\:{all}\:\mathrm{100}/\mathrm{100} \\ $$$$\:{Yesterday}\:,\:{i}\:{was}\:{helpless}\:{in}\:{front}\:{of}\:{this}\:{question} \\ $$$${Thank}\:{you}\:{Sir}\:{for}\:{refresh}\:{our}\:{mind}, \\ $$$$\:{and}\:{thank}\:{you}\:{Sir}\:{Aleks}\:{too} \\ $$
Answered by mr W last updated on 07/Nov/22
Commented by mr W last updated on 07/Nov/22
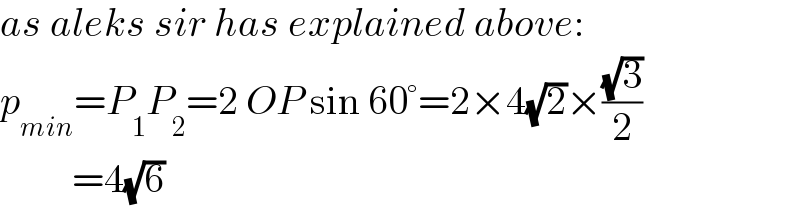
$${as}\:{aleks}\:{sir}\:{has}\:{explained}\:{above}: \\ $$$${p}_{{min}} ={P}_{\mathrm{1}} {P}_{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{2}\:{OP}\:\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{60}°=\mathrm{2}×\mathrm{4}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}×\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:=\mathrm{4}\sqrt{\mathrm{6}} \\ $$
