Question Number 182441 by mathlove last updated on 09/Dec/22
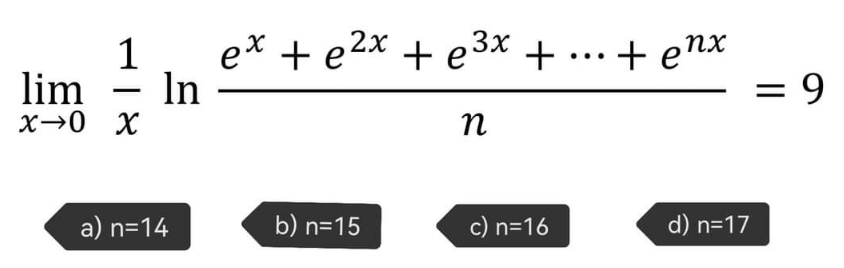
Answered by JDamian last updated on 09/Dec/22
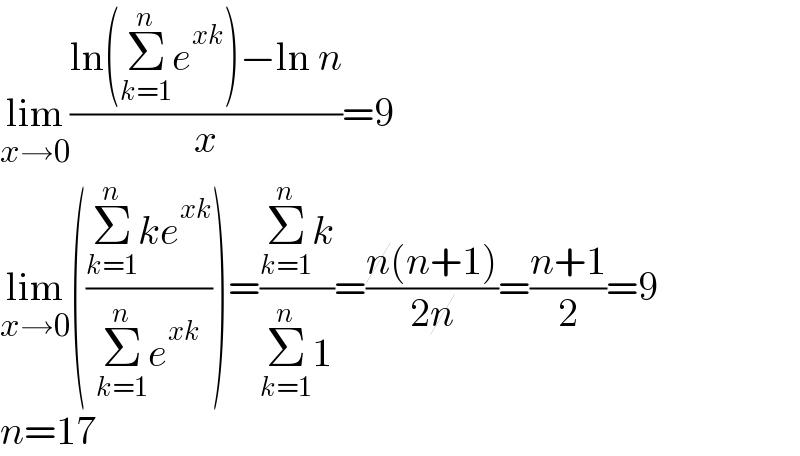
$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\mathrm{ln}\left(\underset{{k}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{{n}} {\sum}}{e}^{{xk}} \right)−\mathrm{ln}\:{n}}{{x}}=\mathrm{9} \\ $$$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\left(\frac{\underset{{k}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{{n}} {\sum}}{ke}^{{xk}} }{\underset{{k}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{{n}} {\sum}}{e}^{{xk}} }\right)=\frac{\underset{{k}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{{n}} {\sum}}{k}}{\underset{{k}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{{n}} {\sum}}\mathrm{1}}=\frac{\cancel{{n}}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)}{\mathrm{2}\cancel{{n}}}=\frac{{n}+\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}=\mathrm{9} \\ $$$${n}=\mathrm{17} \\ $$
Answered by qaz last updated on 09/Dec/22
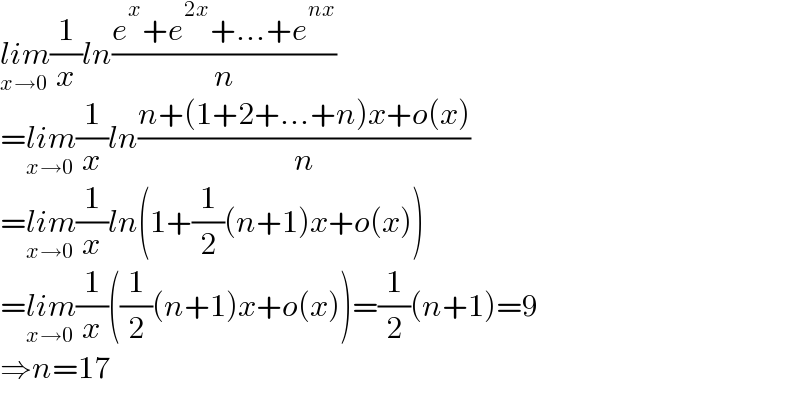
$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {{lim}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}{ln}\frac{{e}^{{x}} +{e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} +…+{e}^{{nx}} }{{n}} \\ $$$$=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {{lim}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}{ln}\frac{{n}+\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{2}+…+{n}\right){x}+{o}\left({x}\right)}{{n}} \\ $$$$=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {{lim}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right){x}+{o}\left({x}\right)\right) \\ $$$$=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {{lim}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right){x}+{o}\left({x}\right)\right)=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)=\mathrm{9} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{n}=\mathrm{17} \\ $$
Commented by mathlove last updated on 09/Dec/22

$${what}\:\:{o}\left({x}\right)??? \\ $$
Commented by mathlove last updated on 12/Dec/22

$$???? \\ $$
