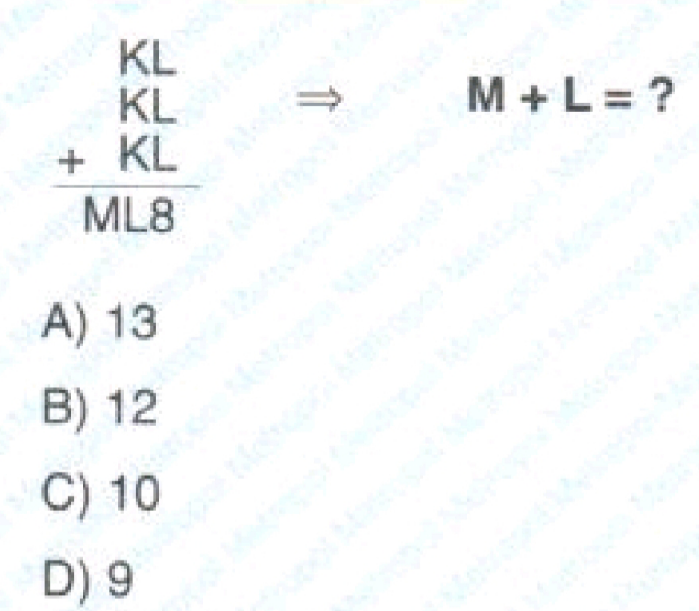
Question Number 182779 by Noorzai last updated on 14/Dec/22
Commented by Rasheed.Sindhi last updated on 14/Dec/22

$$\mathrm{M}+\mathrm{L}=\mathrm{7} \\ $$
Answered by TheSupreme last updated on 14/Dec/22
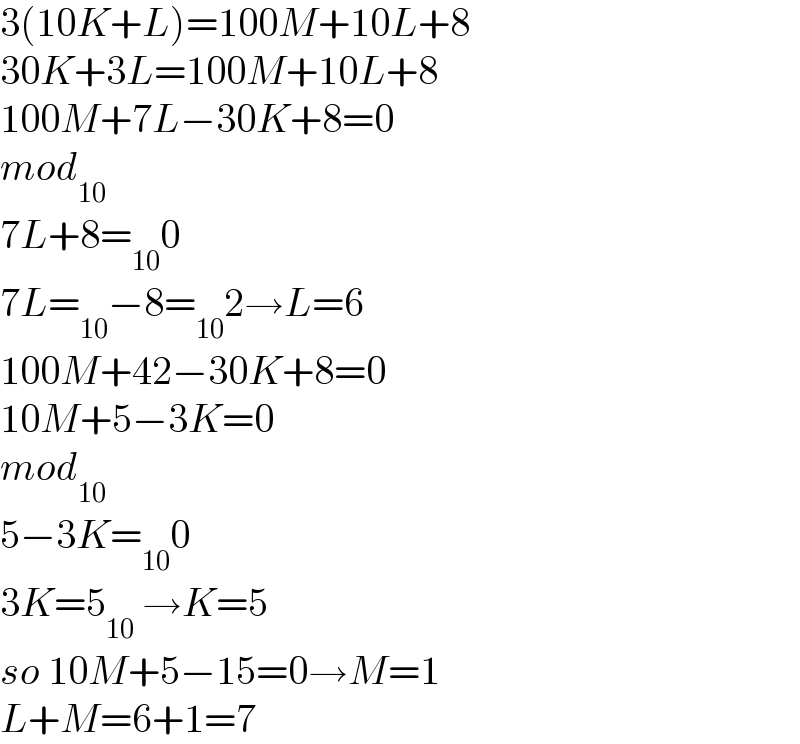
$$\mathrm{3}\left(\mathrm{10}{K}+{L}\right)=\mathrm{100}{M}+\mathrm{10}{L}+\mathrm{8} \\ $$$$\mathrm{30}{K}+\mathrm{3}{L}=\mathrm{100}{M}+\mathrm{10}{L}+\mathrm{8} \\ $$$$\mathrm{100}{M}+\mathrm{7}{L}−\mathrm{30}{K}+\mathrm{8}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${mod}_{\mathrm{10}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{7}{L}+\mathrm{8}=_{\mathrm{10}} \mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\mathrm{7}{L}=_{\mathrm{10}} −\mathrm{8}=_{\mathrm{10}} \mathrm{2}\rightarrow{L}=\mathrm{6} \\ $$$$\mathrm{100}{M}+\mathrm{42}−\mathrm{30}{K}+\mathrm{8}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\mathrm{10}{M}+\mathrm{5}−\mathrm{3}{K}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${mod}_{\mathrm{10}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{5}−\mathrm{3}{K}=_{\mathrm{10}} \mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\mathrm{3}{K}=\mathrm{5}_{\mathrm{10}} \:\rightarrow{K}=\mathrm{5} \\ $$$${so}\:\mathrm{10}{M}+\mathrm{5}−\mathrm{15}=\mathrm{0}\rightarrow{M}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${L}+{M}=\mathrm{6}+\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{7}\: \\ $$
Commented by Noorzai last updated on 14/Dec/22

$${Thanks} \\ $$
Answered by Rasheed.Sindhi last updated on 14/Dec/22
![0≤L≤9 Sum of units ⇒0≤3∙L≤27 3∙L=8^(×) ,18^( ✓) [3∙L≠8, ∵L is whole not 8/3] L=18/3=6 Sum of tens 3∙K+1=ML^(−) =M6^(−) 3∙K=M6^(−) −1=M5^(−) 3∙K=15^( ✓) ,25^(×) [3∙K≠25,∵K is whole not 25/3] K=15/3=5 M6^(−) =3∙K+1=3(5)+1=16 M=1 M+L=1+6=7](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q182784.png)
$$\mathrm{0}\leqslant\mathrm{L}\leqslant\mathrm{9} \\ $$$$\:\:{Sum}\:{of}\:{units} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{0}\leqslant\mathrm{3}\centerdot\mathrm{L}\leqslant\mathrm{27} \\ $$$$\mathrm{3}\centerdot\mathrm{L}=\overset{×} {\mathrm{8}},\overset{\:\:\checkmark} {\mathrm{18}}\:\:\left[\mathrm{3}\centerdot\mathrm{L}\neq\mathrm{8},\:\because\mathrm{L}\:{is}\:{whole}\:{not}\:\mathrm{8}/\mathrm{3}\right] \\ $$$$\mathrm{L}=\mathrm{18}/\mathrm{3}=\mathrm{6} \\ $$$${Sum}\:{of}\:{tens} \\ $$$$\mathrm{3}\centerdot\mathrm{K}+\mathrm{1}=\overline {\mathrm{ML}}=\overline {\mathrm{M6}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{3}\centerdot\mathrm{K}=\overline {\mathrm{M6}}−\mathrm{1}=\overline {\mathrm{M5}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{3}\centerdot\mathrm{K}=\overset{\:\checkmark} {\mathrm{15}},\overset{×} {\mathrm{25}}\:\:\:\:\left[\mathrm{3}\centerdot\mathrm{K}\neq\mathrm{25},\because\mathrm{K}\:{is}\:{whole}\:{not}\:\mathrm{25}/\mathrm{3}\right] \\ $$$$\mathrm{K}=\mathrm{15}/\mathrm{3}=\mathrm{5} \\ $$$$\overline {\mathrm{M6}}=\mathrm{3}\centerdot\mathrm{K}+\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{3}\left(\mathrm{5}\right)+\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{16} \\ $$$$\mathrm{M}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\mathrm{M}+\mathrm{L}=\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{6}=\mathrm{7} \\ $$
Answered by manolex last updated on 14/Dec/22
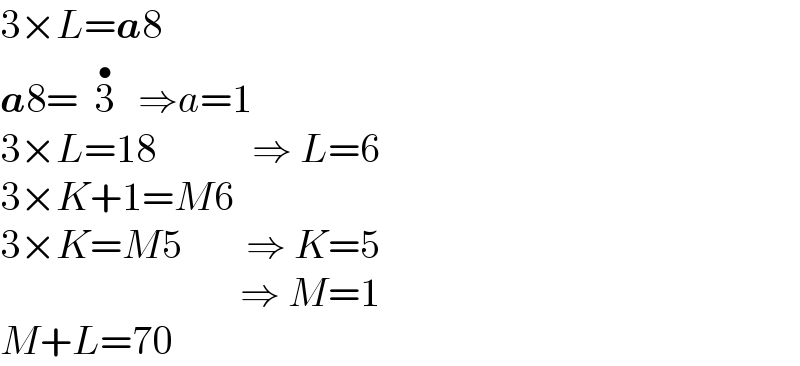
$$\mathrm{3}×{L}=\boldsymbol{{a}}\mathrm{8} \\ $$$$\boldsymbol{{a}}\mathrm{8}=\:\:\overset{\:\bullet} {\mathrm{3}}\:\:\:\Rightarrow{a}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\mathrm{3}×{L}=\mathrm{18}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\Rightarrow\:{L}=\mathrm{6} \\ $$$$\mathrm{3}×{K}+\mathrm{1}={M}\mathrm{6} \\ $$$$\mathrm{3}×{K}={M}\mathrm{5}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\Rightarrow\:{K}=\mathrm{5} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\Rightarrow\:{M}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${M}+{L}=\mathrm{70} \\ $$
Answered by Rasheed.Sindhi last updated on 15/Dec/22
![AnOther Way ML8^(−) is 3-digit number⇒M≠0 M is a carry of 3 2-digit numbers so max value of M is 2 ∴ M=1 or 2 0≤L≤9 ⇒0≤3∙L≤27 3∙L=8^(×) ,18^( ✓) [3∙L≠8, ∵L is whole not 8/3] L=18/3=6 ∴ ML8^(−) =168 or 268 ∵ 3 ∣ ML8^(−) [∵ ML8^(−) =3∙KL^(−) ] Hence finally ML8^(−) =168 So M+L=1+6=7](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q182837.png)
$$\underline{\boldsymbol{\mathrm{A}}\mathrm{n}\boldsymbol{\mathrm{O}}\mathrm{ther}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{W}}\mathrm{ay}} \\ $$$$\overline {\mathrm{ML8}}\:{is}\:\mathrm{3}-{digit}\:{number}\Rightarrow\mathrm{M}\neq\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\mathrm{M}\:{is}\:{a}\:{carry}\:{of}\:\mathrm{3}\:\:\:\mathrm{2}-{digit}\:{numbers} \\ $$$${so}\:{max}\:{value}\:{of}\:\mathrm{M}\:{is}\:\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\therefore\:\mathrm{M}=\mathrm{1}\:{or}\:\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\mathrm{0}\leqslant\mathrm{L}\leqslant\mathrm{9} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{0}\leqslant\mathrm{3}\centerdot\mathrm{L}\leqslant\mathrm{27} \\ $$$$\mathrm{3}\centerdot\mathrm{L}=\overset{×} {\mathrm{8}},\overset{\:\:\checkmark} {\mathrm{18}}\:\:\left[\mathrm{3}\centerdot\mathrm{L}\neq\mathrm{8},\:\because\mathrm{L}\:{is}\:{whole}\:{not}\:\mathrm{8}/\mathrm{3}\right] \\ $$$$\mathrm{L}=\mathrm{18}/\mathrm{3}=\mathrm{6} \\ $$$$\therefore\:\overline {\mathrm{ML8}}=\mathrm{168}\:{or}\:\mathrm{268} \\ $$$$\because\:\mathrm{3}\:\mid\:\overline {\mathrm{ML8}}\:\:\:\left[\because\:\overline {\mathrm{ML8}}=\mathrm{3}\centerdot\overline {\mathrm{KL}}\right] \\ $$$${Hence}\:{finally}\:\overline {\mathrm{ML8}}\:=\mathrm{168} \\ $$$${So}\:\mathrm{M}+\mathrm{L}=\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{6}=\mathrm{7} \\ $$
