Question Number 183031 by universe last updated on 18/Dec/22

Answered by aleks041103 last updated on 23/Dec/22
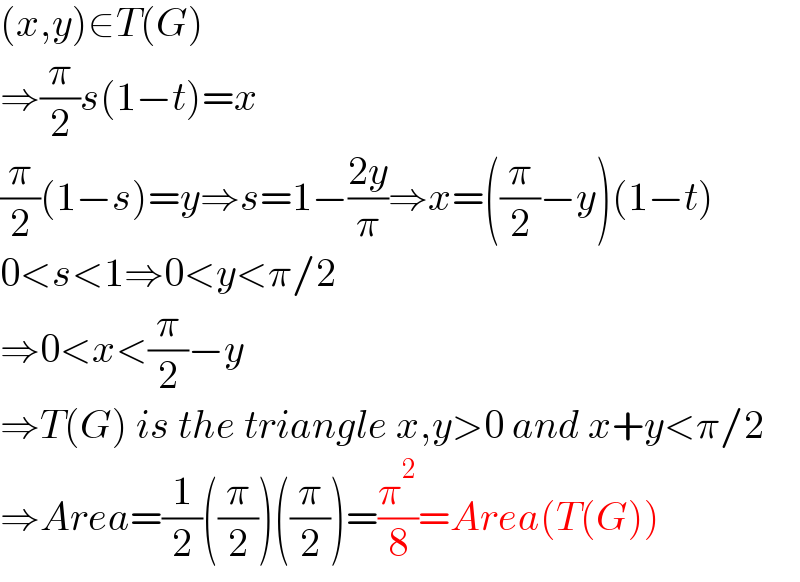
$$\left({x},{y}\right)\in{T}\left({G}\right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}{s}\left(\mathrm{1}−{t}\right)={x} \\ $$$$\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\left(\mathrm{1}−{s}\right)={y}\Rightarrow{s}=\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{2}{y}}{\pi}\Rightarrow{x}=\left(\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}−{y}\right)\left(\mathrm{1}−{t}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{0}<{s}<\mathrm{1}\Rightarrow\mathrm{0}<{y}<\pi/\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{0}<{x}<\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}−{y} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{T}\left({G}\right)\:{is}\:{the}\:{triangle}\:{x},{y}>\mathrm{0}\:{and}\:{x}+{y}<\pi/\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{Area}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left(\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\right)\left(\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\right)=\frac{\pi^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{8}}={Area}\left({T}\left({G}\right)\right) \\ $$
