Question Number 183865 by Michaelfaraday last updated on 31/Dec/22
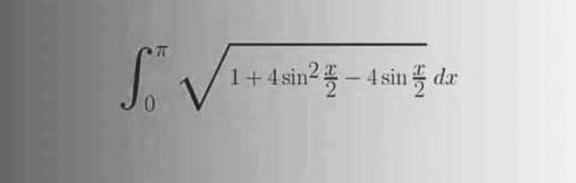
Answered by MJS_new last updated on 31/Dec/22
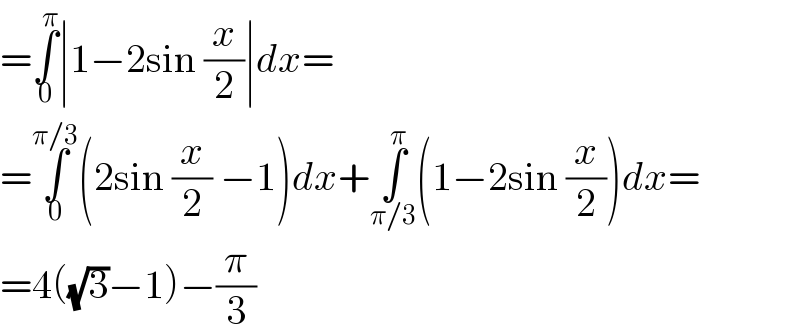
$$=\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\pi} {\int}}\mid\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{2sin}\:\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\mid{dx}= \\ $$$$=\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\pi/\mathrm{3}} {\int}}\left(\mathrm{2sin}\:\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\:−\mathrm{1}\right){dx}+\underset{\pi/\mathrm{3}} {\overset{\pi} {\int}}\left(\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{2sin}\:\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\right){dx}= \\ $$$$=\mathrm{4}\left(\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}−\mathrm{1}\right)−\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$
Commented by Michaelfaraday last updated on 31/Dec/22

$${thanks}\:{sir} \\ $$
