Question Number 30257 by mondodotto@gmail.com last updated on 19/Feb/18
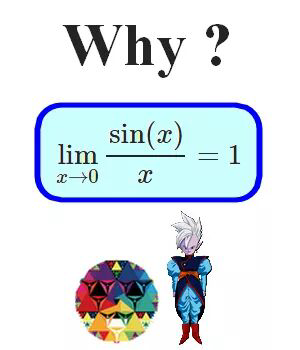
Commented by rahul 19 last updated on 19/Feb/18

$$\mathrm{Sandwhich}\:\mathrm{theorem}\:! \\ $$
Commented by abdo imad last updated on 21/Feb/18
$${this}\:{question}\:{is}\:{like}\:{why}\:{you}\:{eat}\:{bread}… \\ $$
Commented by rahul 19 last updated on 21/Feb/18

$$\left.\mathrm{To}\:\mathrm{survive}\::\right) \\ $$
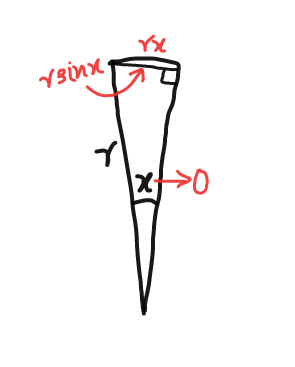
Commented by ajfour last updated on 21/Feb/18
Commented by abdo imad last updated on 21/Feb/18

$${exactly}… \\ $$
Answered by $@ty@m last updated on 19/Feb/18
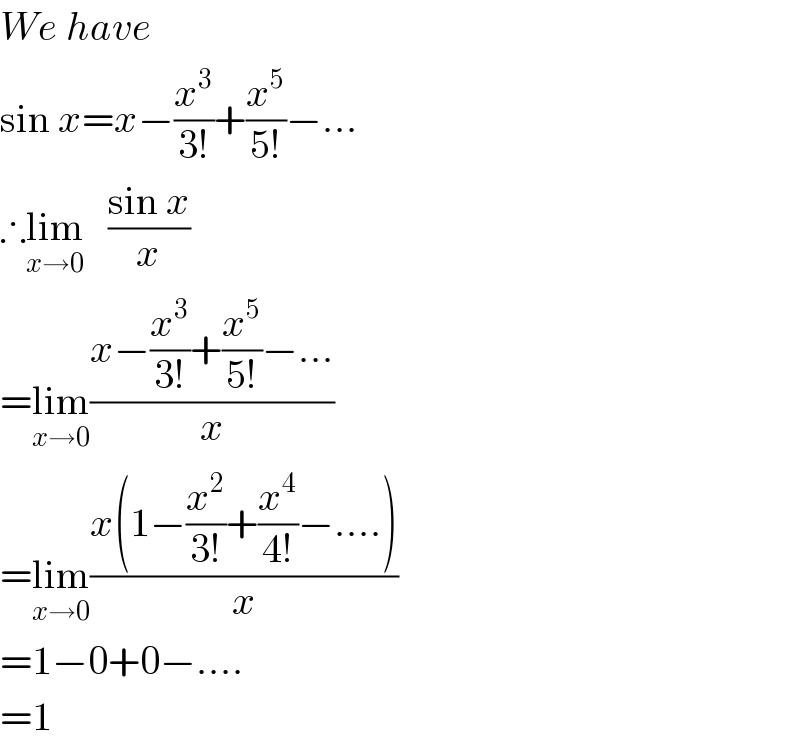
$${We}\:{have} \\ $$$$\mathrm{sin}\:{x}={x}−\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{3}!}+\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{5}} }{\mathrm{5}!}−… \\ $$$$\therefore\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\:\:\frac{\mathrm{sin}\:{x}}{{x}} \\ $$$$=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{{x}−\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{3}!}+\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{5}} }{\mathrm{5}!}−…}{{x}} \\ $$$$=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{{x}\left(\mathrm{1}−\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{3}!}+\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{4}} }{\mathrm{4}!}−….\right)}{{x}} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{0}+\mathrm{0}−…. \\ $$$$=\mathrm{1} \\ $$
