Question Number 30627 by Tinkutara last updated on 23/Feb/18
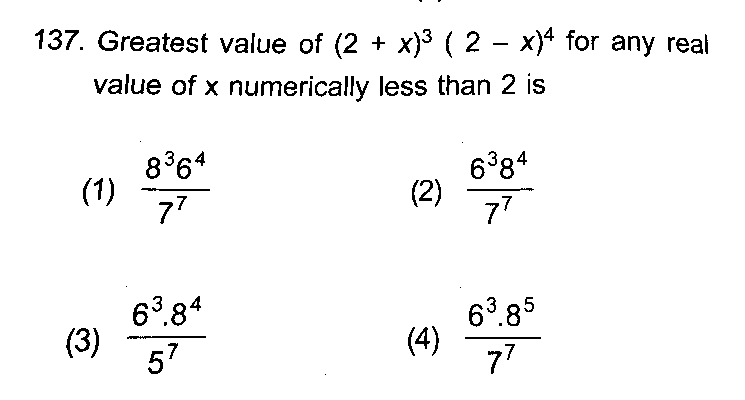
Answered by ajfour last updated on 23/Feb/18
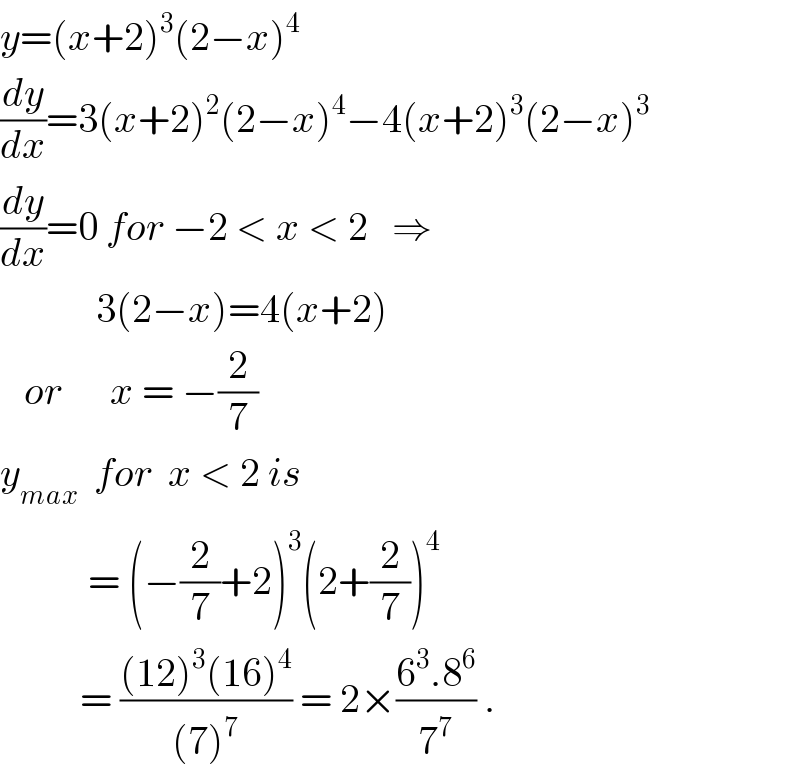
$${y}=\left({x}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{3}} \left(\mathrm{2}−{x}\right)^{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$$\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}=\mathrm{3}\left({x}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{2}−{x}\right)^{\mathrm{4}} −\mathrm{4}\left({x}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{3}} \left(\mathrm{2}−{x}\right)^{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$$$\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}=\mathrm{0}\:{for}\:−\mathrm{2}\:<\:{x}\:<\:\mathrm{2}\:\:\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{3}\left(\mathrm{2}−{x}\right)=\mathrm{4}\left({x}+\mathrm{2}\right) \\ $$$$\:\:\:{or}\:\:\:\:\:\:{x}\:=\:−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{7}} \\ $$$${y}_{{max}} \:\:{for}\:\:{x}\:<\:\mathrm{2}\:{is} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:=\:\left(−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{7}}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{3}} \left(\mathrm{2}+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{7}}\right)^{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:=\:\frac{\left(\mathrm{12}\right)^{\mathrm{3}} \left(\mathrm{16}\right)^{\mathrm{4}} }{\left(\mathrm{7}\right)^{\mathrm{7}} }\:=\:\mathrm{2}×\frac{\mathrm{6}^{\mathrm{3}} .\mathrm{8}^{\mathrm{6}} }{\mathrm{7}^{\mathrm{7}} }\:. \\ $$
Commented by Tinkutara last updated on 23/Feb/18
Ohh sorry that was the same answer
Commented by rahul 19 last updated on 23/Feb/18

$$\mathrm{To}\:\mathrm{Ajfour}\:\mathrm{sir}\::\:\:\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{cannot}\:\:\mathrm{apply} \\ $$$$\mathrm{Am}−\mathrm{Gm}\:\mathrm{method}\:\mathrm{as}\:\mathrm{here}\:{x}\:{can}\:{be}\:−{ve}\:{also}. \\ $$
Commented by ajfour last updated on 23/Feb/18
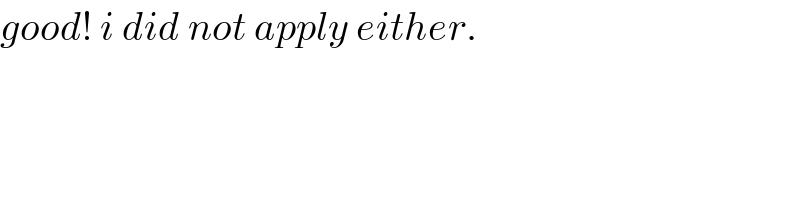
$${good}!\:{i}\:{did}\:{not}\:{apply}\:{either}. \\ $$
Commented by Tinkutara last updated on 24/Feb/18
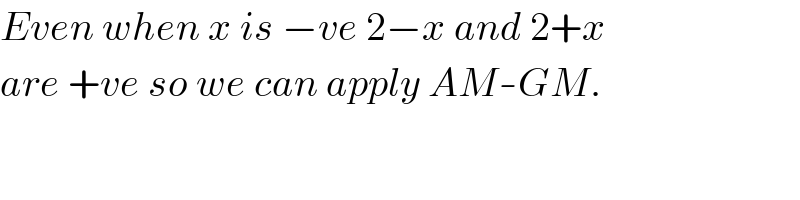
$${Even}\:{when}\:{x}\:{is}\:−{ve}\:\mathrm{2}−{x}\:{and}\:\mathrm{2}+{x} \\ $$$${are}\:+{ve}\:{so}\:{we}\:{can}\:{apply}\:{AM}-{GM}. \\ $$
